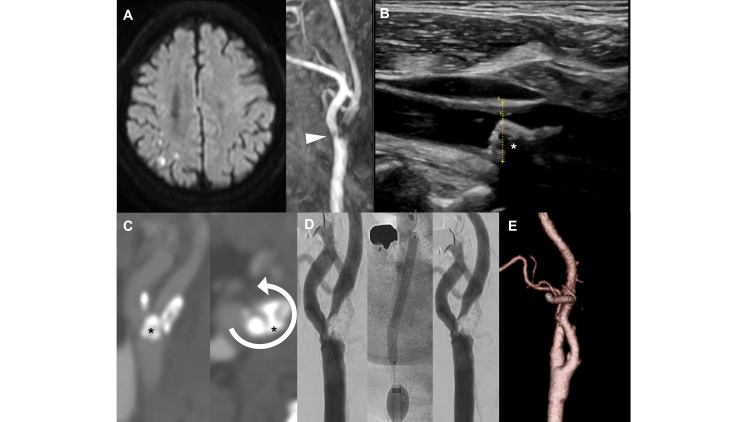
Figure 1. Neuroimaging and intraoperative findings.
(A) Cranial MR diffusion-weighted imaging performed one day after the presentation of transient dysarthria and hemiparalysis shows scattered high-intensity areas. The MR angiography shows a defect of flow signal in the ICA just distal to the bifurcation (arrowhead). (B) The ultrasound image shows a low echoic plaque protruding into the lumen of the ICA with an acoustic shadow (asterisk). (C) The CT angiography shows right carotid artery stenosis with an irregular luminal surface and a nodular calcification protruding into the vessel lumen (asterisk), and its circumference degree was 3/4 (arrow). (D) In the procedure of CAS, the stenotic lesion was immediately re-stenosed despite repeated balloon dilations. (E) The angiography one week after CEA shows a complete resolution of stenosis.
ICA: internal carotid artery; MR: magnetic resonancy; CT: computed tomography; CAS: carotid artery stenting; CEA: carotid endarterectomy