Abstract
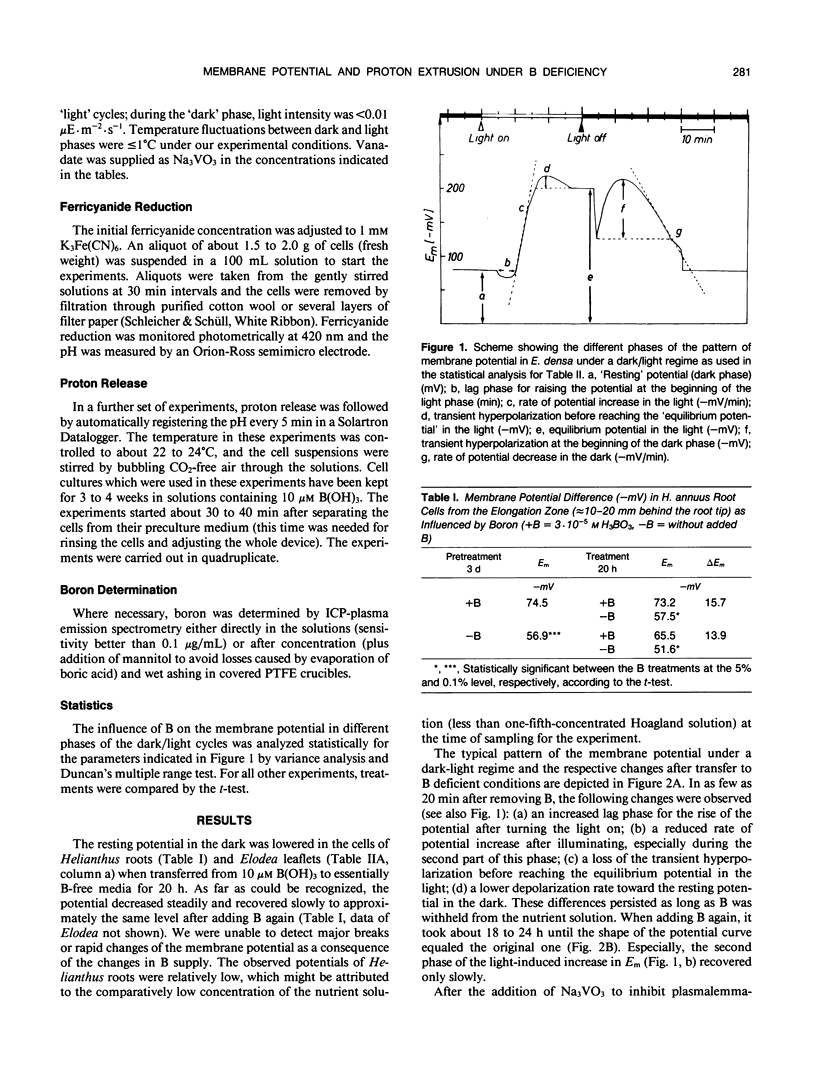
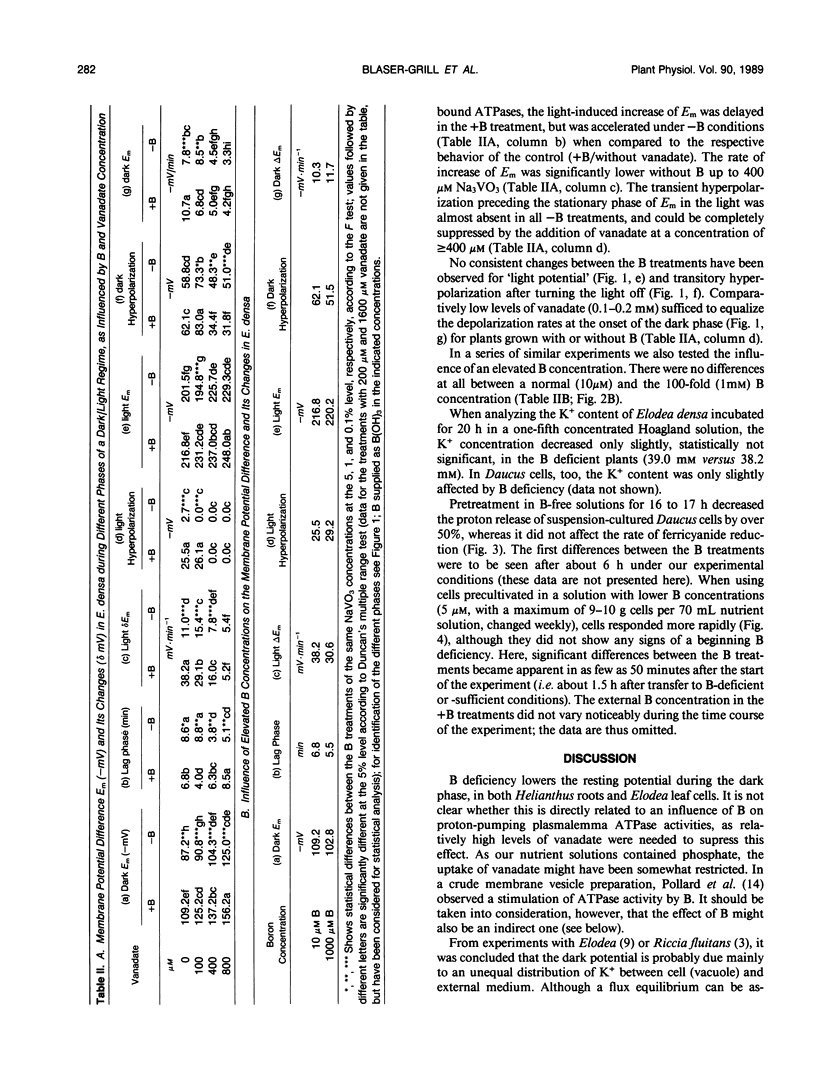
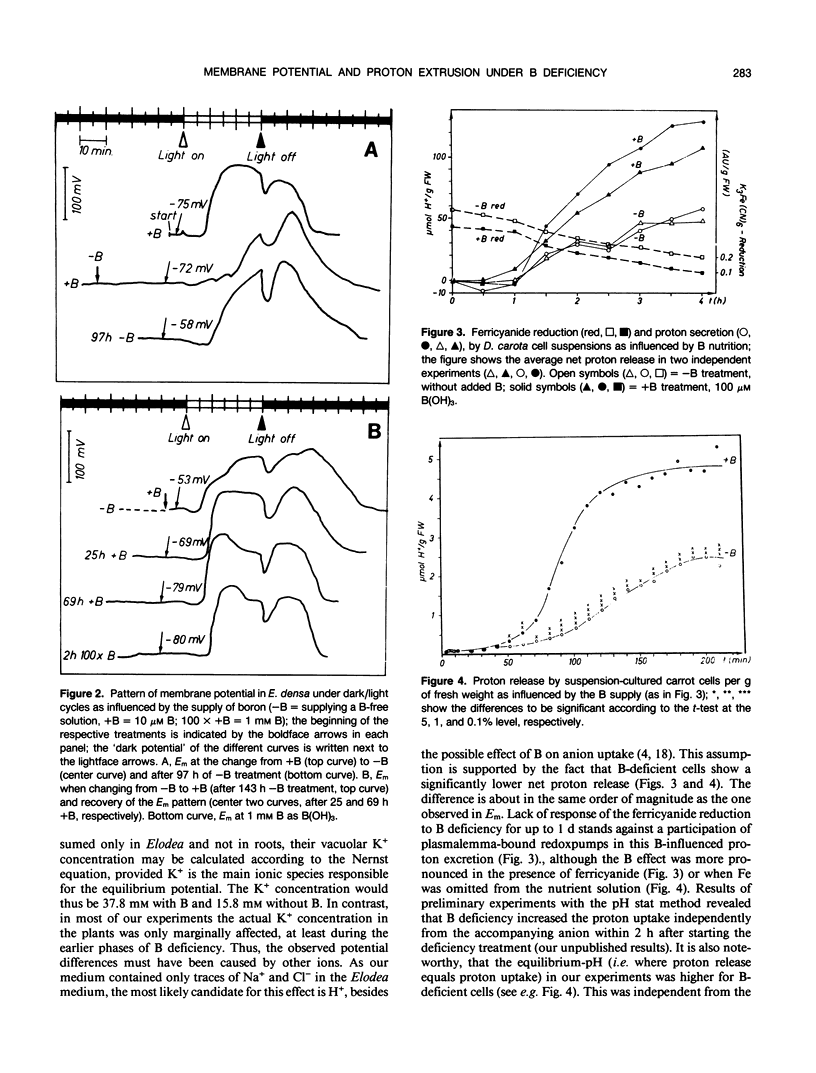
When following the membrane potential of Elodea densa leaf cells during a dark-light regime and analysing the different phases of the cycle, the pattern under boron deficiency resembled the one reported to occur after 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea application. The potential in the dark slowly decreased when transferring Elodea densa leaflets and Helianthus annuus roots to a B-free medium and increased in the same way after B was added again. Addition of vanadate to inhibit plasmalemma ATPases in part mimicked the effects of B deficiency. It is suggested that B directly or indirectly affects the formation of a proton gradient. The effect of B on proton secretion was observed in various experiments with Daucus carota cell cultures. The results are discussed with respect to the possible involvement of B in membrane function and transport processes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mitchell J. W., Dugger W. M., Jr, Gauch H. G. Increased Translocation of Plant-Growth-Modifying Substances Due to Application of Boron. Science. 1953 Sep 25;118(3065):354–355. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3065.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römheld V., Müller C., Marschner H. Localization and capacity of proton pumps in roots of intact sunflower plants. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):603–606. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. A., Dugger W. M. Effects of Boron Deficiency on Rubidium Uptake and Photosynthesis in the Diatom Cylindrotheca fusiformis. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):692–695. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanada T. Boron-induced Bioelectric Field Change in Mung Bean Hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1974 May;53(5):775–776. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.5.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang P. M., Dela Fuente R. K. Boron and calcium sites involved in indole-3-acetic Acid transport in sunflower hypocotyl segments. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):651–655. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


