Abstract
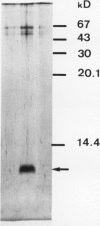
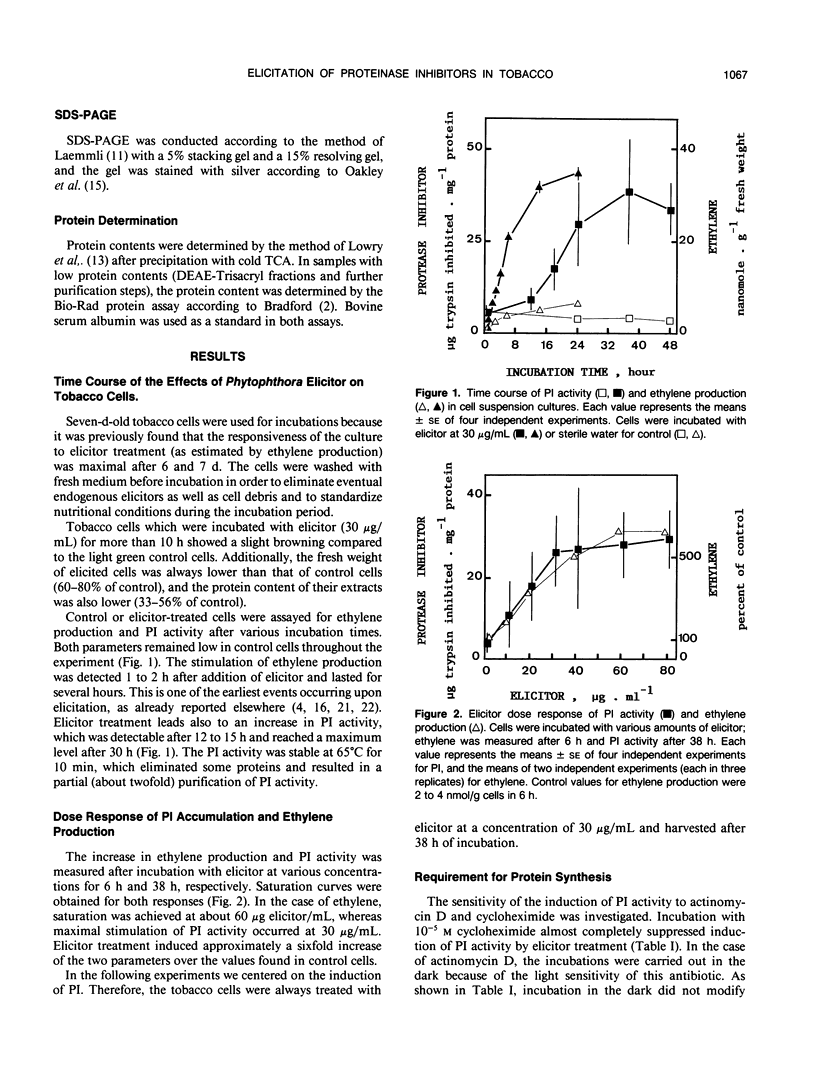
An elicitor preparation obtained from Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae, a pathogen of tobacco, induced an accumulation of proteinase inhibitors and a stimulation of ethylene synthesis in a tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cell suspension culture. About 30 micrograms per milliliter of elicitor were necessary for maximal induction of proteinase inhibitor accumulation, and the response was detectable after 12 hours of incubation with elicitor. Accumulation of proteinase inhibitors required de novo protein synthesis, since cycloheximide completely inhibited its elicitation, and actinomycin D inhibited it partially. One of the inhibitors was purified by a procedure that included heating, (NH4)2SO4 precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography, and affinity chromatography. The purified inhibitor was shown to be a single band on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with a molecular weight of about 10,500. It inhibited trypsin but not chymotrypsin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop P. D., Pearce G., Bryant J. E., Ryan C. A. Isolation and characterization of the proteinase inhibitor-inducing factor from tomato leaves. Identity and activity of poly- and oligogalacturonide fragments. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13172–13177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg I., Jonsson L., Bergenstråhle A., Söderhäll K. Purification of a trypsin inhibitor secreted by embryogenic carrot cells. Plant Physiol. 1987 May;84(1):197–200. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. R., Ryan C. A. Wound-Induced Proteinase Inhibitor in Plant Leaves: A Possible Defense Mechanism against Insects. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):776–777. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo T. M., Pearce G., Ryan C. A. Isolation and characterization of proteinase inhibitor I from etiolated tobacco leaves. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Brown W. E., Graham J. S., Pearce G., Fox E. A., Dreher T. W., Ahern K. G., Pearson G. D., Ryan C. A. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic studies of a wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor I gene in Lycopersicon species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7277–7281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradies I., Konze J. R., Elstner E. F. Ethylene: indicator but not inducer of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1106–1109. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toppan A., Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions : IV. Fungal Glycopeptides Which Elicit the Synthesis of Ethylene in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1133–1138. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toppan A., Roby D., Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions : III. In Vivo Effect of Ethylene on Hydroxyproline-Rich Glycoprotein Accumulation in the Cell Wall of Diseased Plants. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):82–86. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M., Jin D., West C. A., Hadwiger L., Ryan C. A. Comparison of proteinase inhibitor-inducing activities and phytoalexin elicitor activities of a pure fungal endopolygalacturonase, pectic fragments, and chitosans. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):833–836. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M., Ryan C. A. Proteinase inhibitor I accumulation in tomato suspension cultures : induction by plant and fungal cell wall fragments and an extracellular polysaccharide secreted into the medium. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):68–71. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M., Ryan C. A. Wound-induced Accumulation of Trypsin Inhibitor Activities in Plant Leaves: Survey of Several Plant Genera. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):437–439. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. P., Kuo T., Ryan C. A. Growth-dependent accumulation and utilization of proteinase inhibitor I in tobacco callus tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Mar 3;63(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]