Abstract
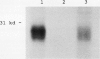
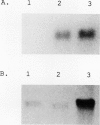
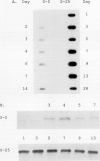
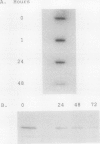
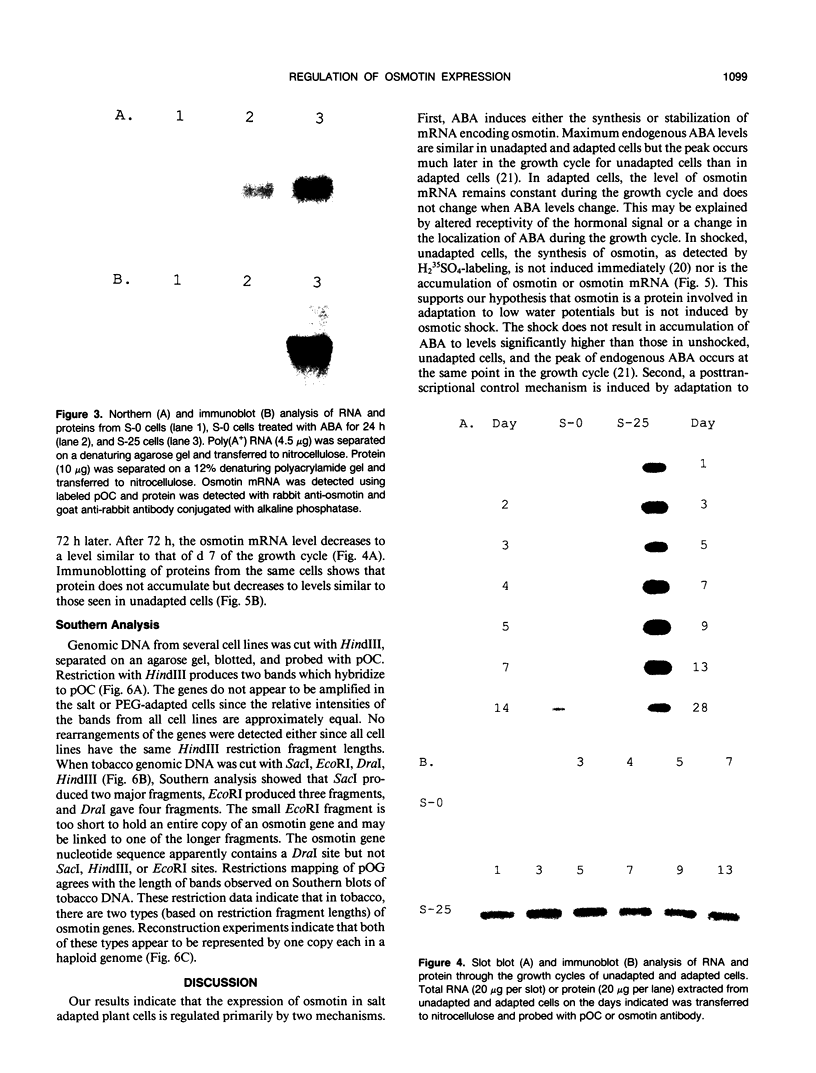
In response to adaptation to NaCl, cultured tobacco cells (Nicotiana tabacum L. cv Wisconsin 38) synthesize a major 26 kilodalton protein which has been named osmotin due to its induction by low water potentials. To help characterize the expression of osmotin in adapted cells, a cDNA clone for osmotin has been isolated. Abscisic acid induces messenger RNA encoding osmotin. Levels of this mRNA in adapted cells are approximately 15-fold higher than in unadapted cells. Message for osmotin is present at constant levels through the growth cycle of adapted cells, while in unadapted cells, the level decreases during exponential phase of growth and increases again when the cells approach stationary phase. While abscisic acid induces the message for osmotin, a low water potential environment appears to be required for accumulation of the protein. An osmotic shock to unadapted cells does not increase the amount of message or protein present most likely because this treatment does not induce immediately the accumulation of abscisic acid. The increased expression of osmotin in adapted cells is not correlated with an increase in osmotin gene copy number. Osmotin is homologous to a 24 kilodalton NaCl-induced protein in tomato, as well as thaumatin, maize α-amylase/trypsin inhibitor and a tobacco mosaic virus-induced pathogenesis-related protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binzel M. L., Hasegawa P. M., Handa A. K., Bressan R. A. Adaptation of Tobacco Cells to NaCl. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):118–125. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binzel M. L., Hasegawa P. M., Rhodes D., Handa S., Handa A. K., Bressan R. A. Solute Accumulation in Tobacco Cells Adapted to NaCl. Plant Physiol. 1987 Aug;84(4):1408–1415. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binzel M. L., Hess F. D., Bressan R. A., Hasegawa P. M. Intracellular compartmentation of ions in salt adapted tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):607–614. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen B. J., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Bol J. F. A tobacco mosaic virus-induced tobacco protein is homologous to the sweet-tasting protein thaumatin. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):531–532. doi: 10.1038/321531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edens L., Heslinga L., Klok R., Ledeboer A. M., Maat J., Toonen M. Y., Visser C., Verrips C. T. Cloning of cDNA encoding the sweet-tasting plant protein thaumatin and its expression in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larosa P. C., Handa A. K., Hasegawa P. M., Bressan R. A. Abscisic Acid accelerates adaptation of cultured tobacco cells to salt. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):138–142. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Bracker C. A., Hasegawa P. M., Handa A. K., Buckel S., Hermodson M. A., Pfankoch E., Regnier F. E., Bressan R. A. Characterization of osmotin : a thaumatin-like protein associated with osmotic adaptation in plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1987 Oct;85(2):529–536. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Handa A. K., Hasegawa P. M., Bressan R. A. Proteins Associated with Adaptation of Cultured Tobacco Cells to NaCl. Plant Physiol. 1985 Sep;79(1):126–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Larosa P. C., Handa A. K., Hasegawa P. M., Bressan R. A. Hormonal regulation of protein synthesis associated with salt tolerance in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):739–743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Hatada M., van der Wel H., Krabbendam H., Peerdeman A. F., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of thaumatin I, an intensely sweet protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1406–1409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]