Abstract
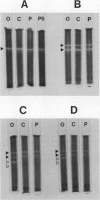
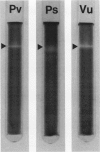
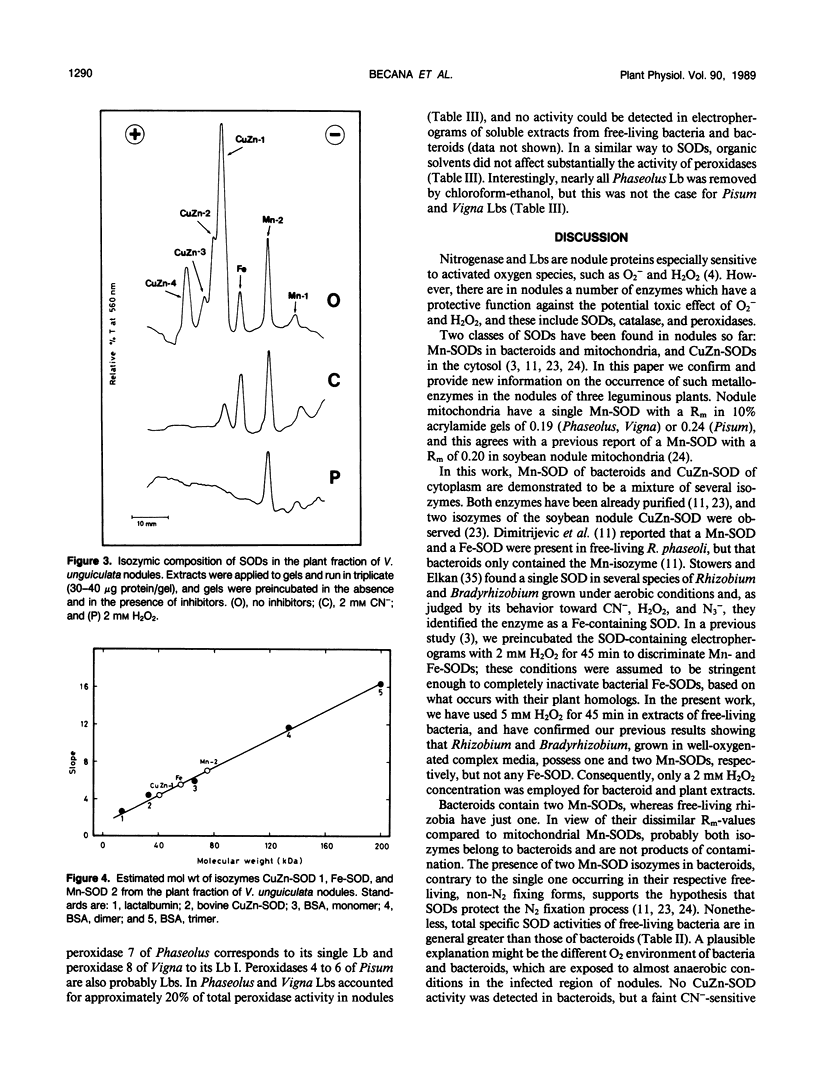
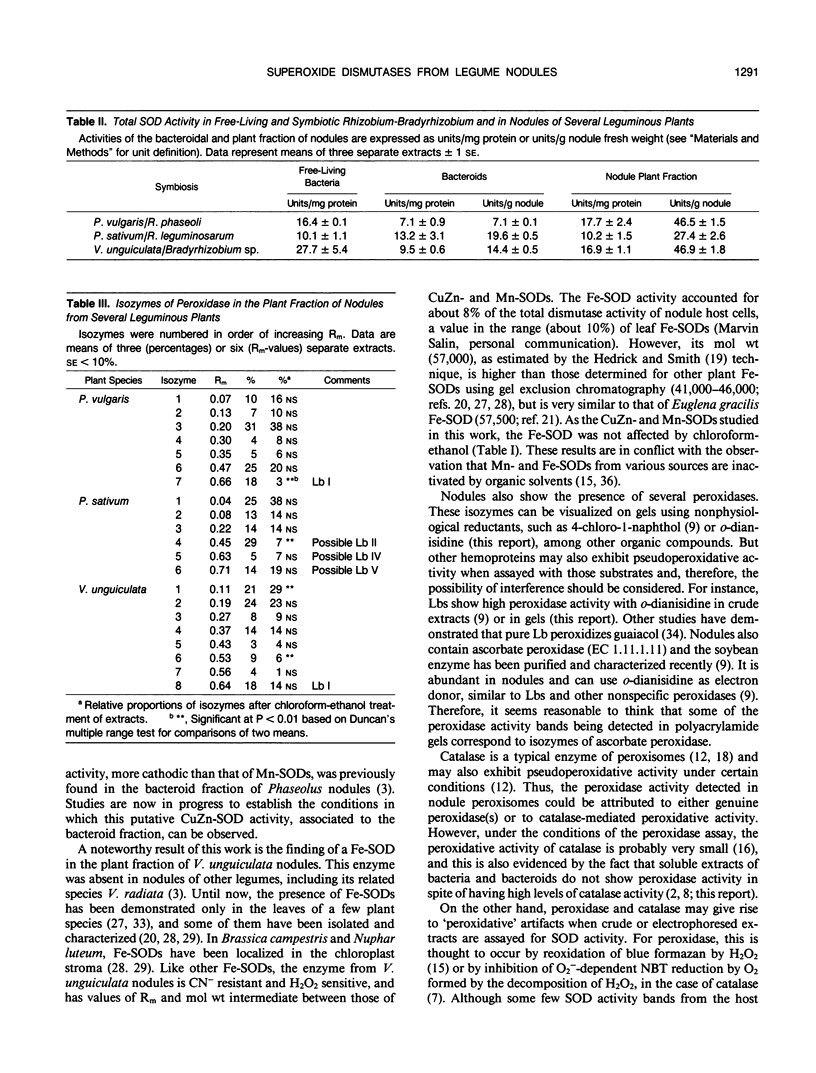
The activity and isozymic composition of superoxide dismutase (SOD; EC 1.15.1.1) were determined in nodules of Phaseolus vulgaris L., Pisum sativum L., and Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. formed by Rhizobium phaseoll 3622, R. Ieguminosarum 3855, and Bradyrhizobium sp. BR7301, respectively. A Mn-SOD was present in Rhizobium and two in Bradyrhizobium and bacteroids. Nodule mitochondria from all three legume species had a single Mn-SOD with similar relative mobility, whereas the cytosol contained several CuZn-SODs: two in Phaseolus and Pisum, and four in Vigna. In the cytoplasm of V. unguiculata nodules, a Fe-containing SOD was also present, with an electrophoretic mobility between those of CuZn- and Mn-SODs, and an estimated molecular weight of 57,000. Total SOD activity of the soluble fraction of host cells, expressed on a nodule fresh weight basis, exceeded markedly that of bacteroids. Likewise, specific SOD activities of free-living bacteria were superior or equal to those of their symbiotic forms. Soluble extracts of bacteria and bacteroids did not show peroxidase activity (EC 1.11.1.7), but the nodule cell cytoplasm contained diverse peroxidase isozymes which were readily distinguishable from leghemoglobin components by electrophoresis. Data indicated that peroxidases and leghemoglobins did not significantly interfere with SOD localization on gels. Treatment with chloroform-ethanol scarcely affected the isozymic pattern of SODs and peroxidases, and had limited success in the removal of leghemoglobin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–126. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges S. M., Salin M. L. Distribution of iron-containing superoxide dismutase in vascular plants. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):275–278. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare D. A., Duong M. N., Darr D., Archibald F., Fridovich I. Effects of molecular oxygen on detection of superoxide radical with nitroblue tetrazolium and on activity stains for catalase. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):532–537. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton D. A., Hanus F. J., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Purification, properties, and distribution of ascorbate peroxidase in legume root nodules. Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):789–794. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton D. A., Russell S. A., Hanus F. J., Pascoe G. A., Evans H. J. Enzymatic reactions of ascorbate and glutathione that prevent peroxide damage in soybean root nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3811–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Biological effects of the superoxide radical. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 May 15;247(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90526-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannopolitis C. N., Ries S. K. Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1977 Feb;59(2):309–314. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B. Oxidation of formate by peroxisomes and mitochondria from spinach leaves. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;138(1):77–85. doi: 10.1042/bj1380077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks J. F., Tolbert N. E., Schubert K. R. Localization of enzymes of ureide biosynthesis in peroxisomes and microsomes of nodules. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):65–69. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatowski J., Safianowska A., Kaniuga Z. Isolation and characterization of an iron-containing superoxide dismutase from tomato leaves, Lycopersicon esculentum. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):459–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengfelder E., Elstner E. F. Cyanide insensitive iron superoxide dismutase in Euglena gracilis. Comparison of the reliabilities of different test systems for superoxide dismutases. Z Naturforsch C. 1979 May-Jun;34C(5-6):374–380. doi: 10.1515/znc-1979-5-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reibach P. H., Mask P. L., Streeter J. G. A rapid one-step method for the isolation of bacteroids from root nodules of soybean plants, utilizing self-generating Percoll gradients. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):491–495. doi: 10.1139/m81-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., Bridges S. M. Isolation and characterization of an iron-containing superoxide dismutase from a eucaryote, Brassica campestris. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 May;201(2):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90524-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnarrenberger C., Oeser A., Tolbert N. E. Development of Microbodies in Sunflower Cotyledons and Castor Bean Endosperm during Germination. Plant Physiol. 1971 Nov;48(5):566–574. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.5.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sievers G., Rönnberg M. Study of the pseudoperoxidatic activity of soybean leghemoglobin and sperm whale myoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 26;533(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. Organelle specificity. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3582–3592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]