Abstract
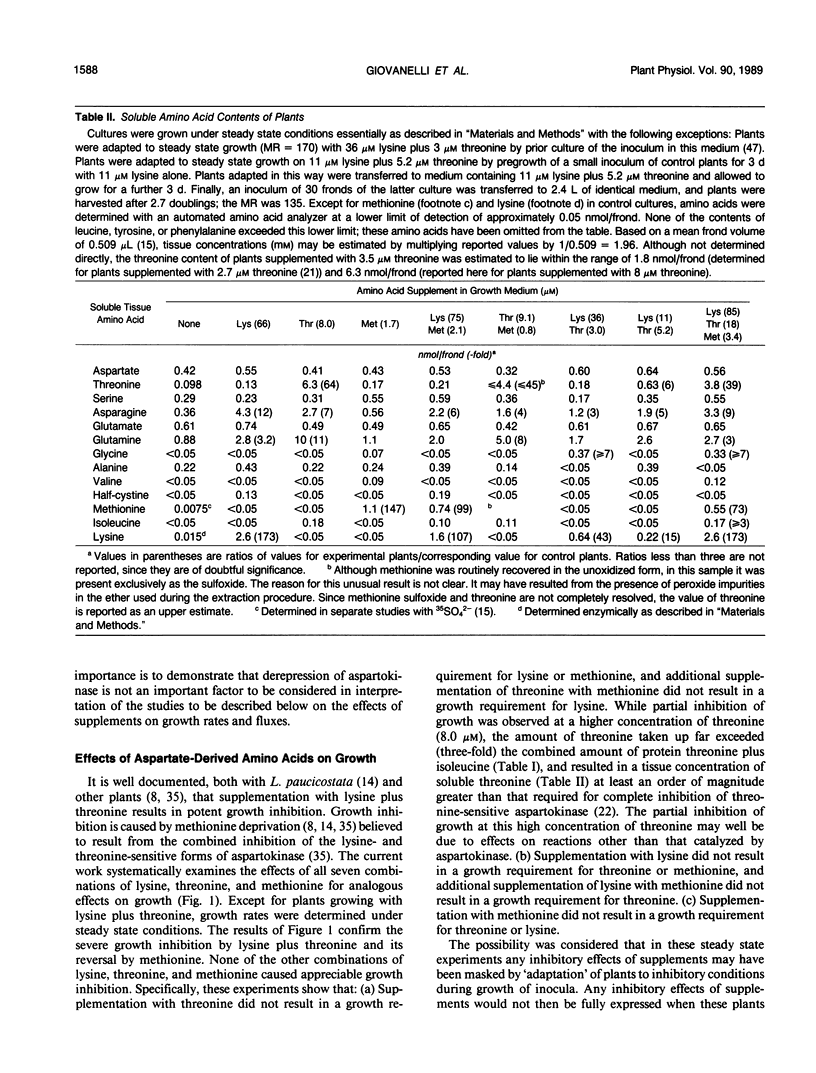
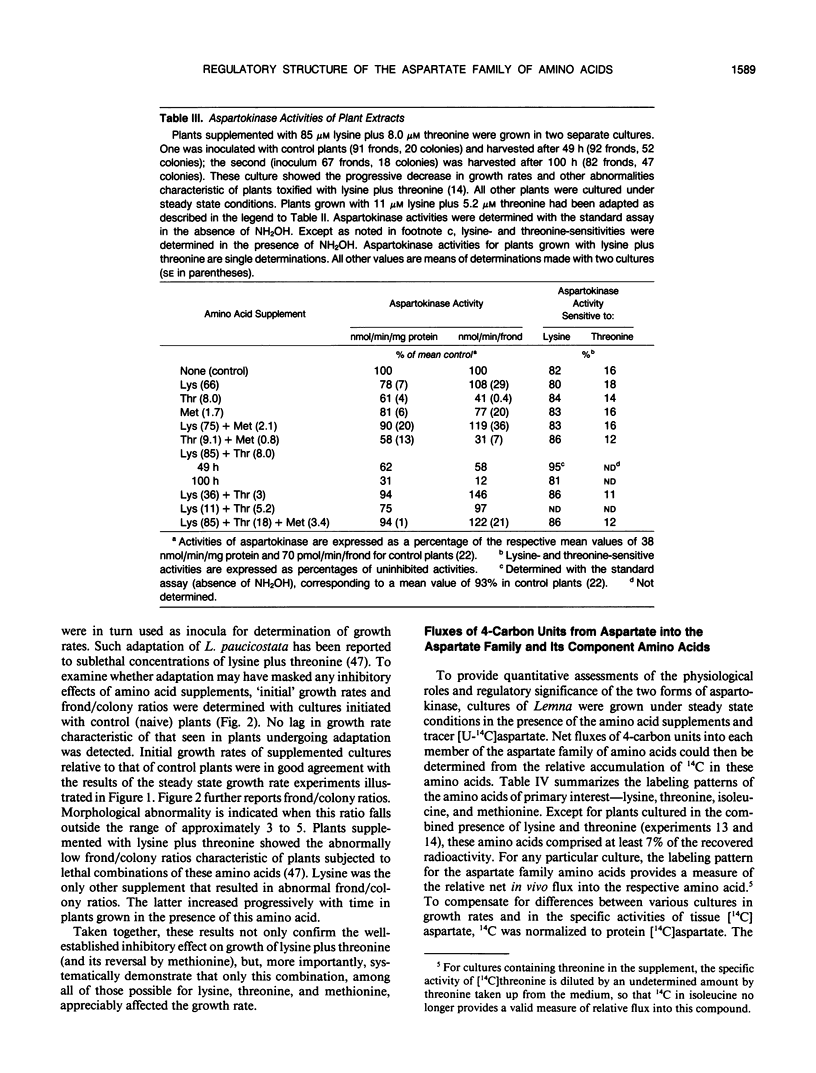
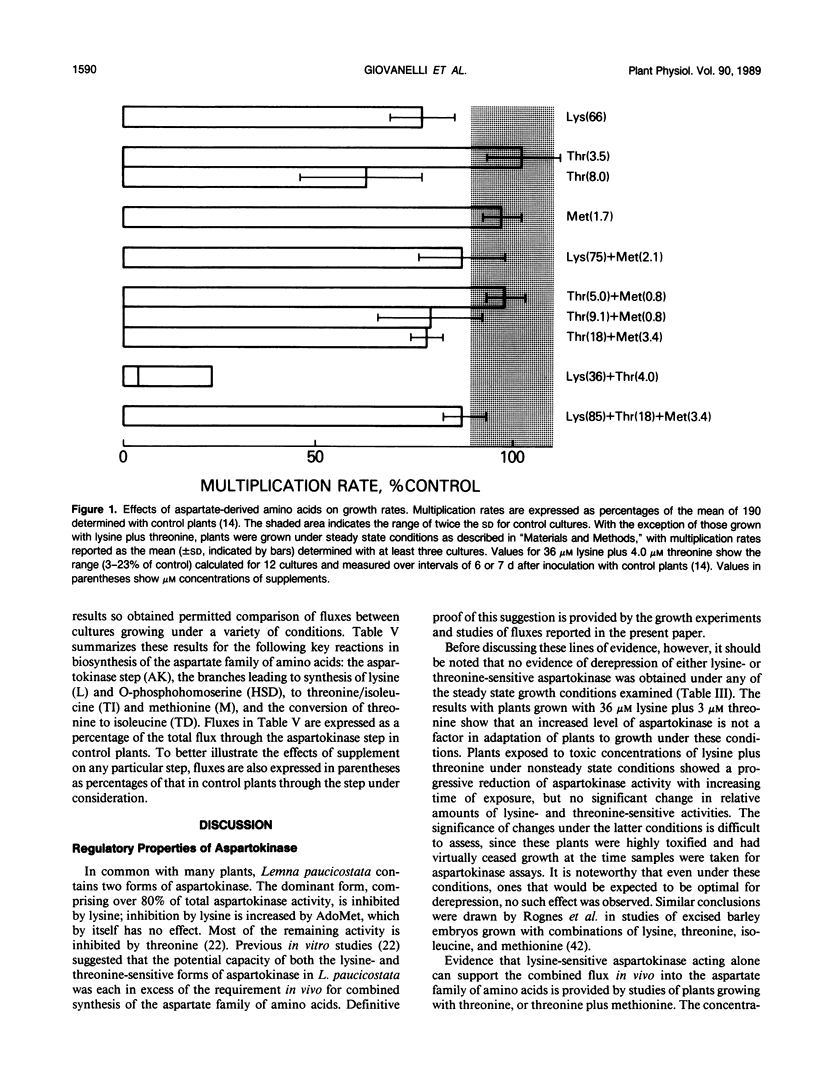
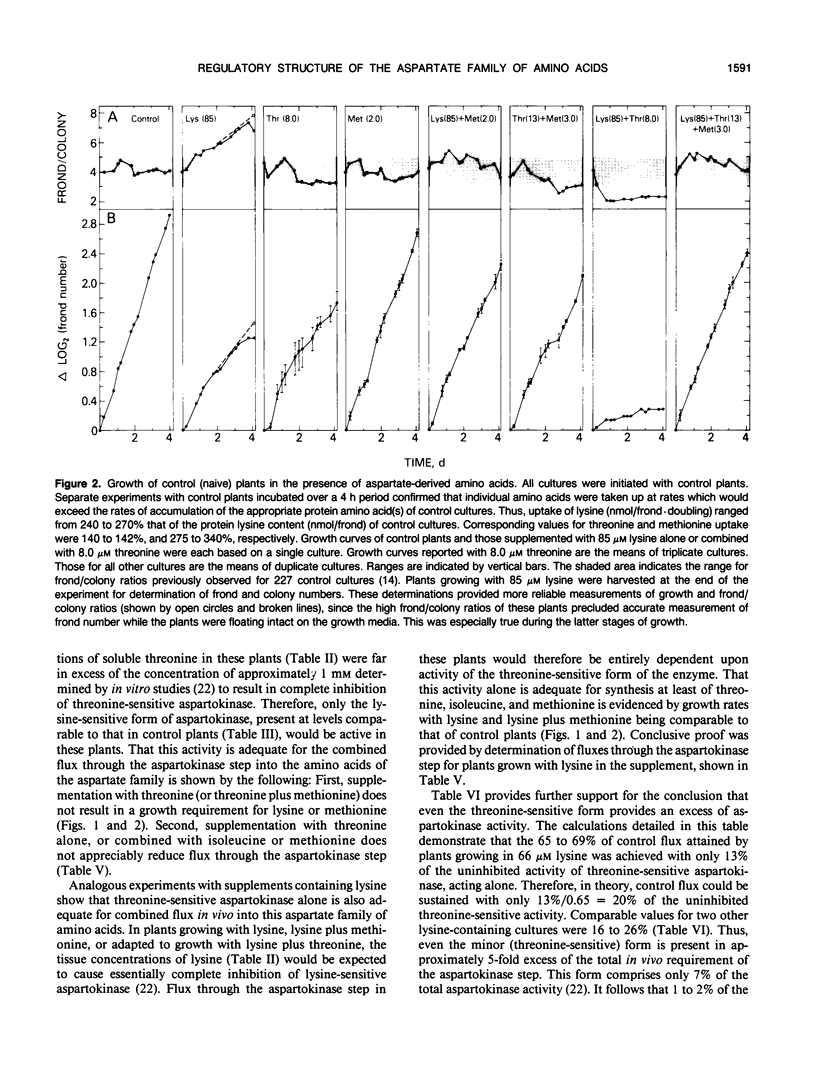
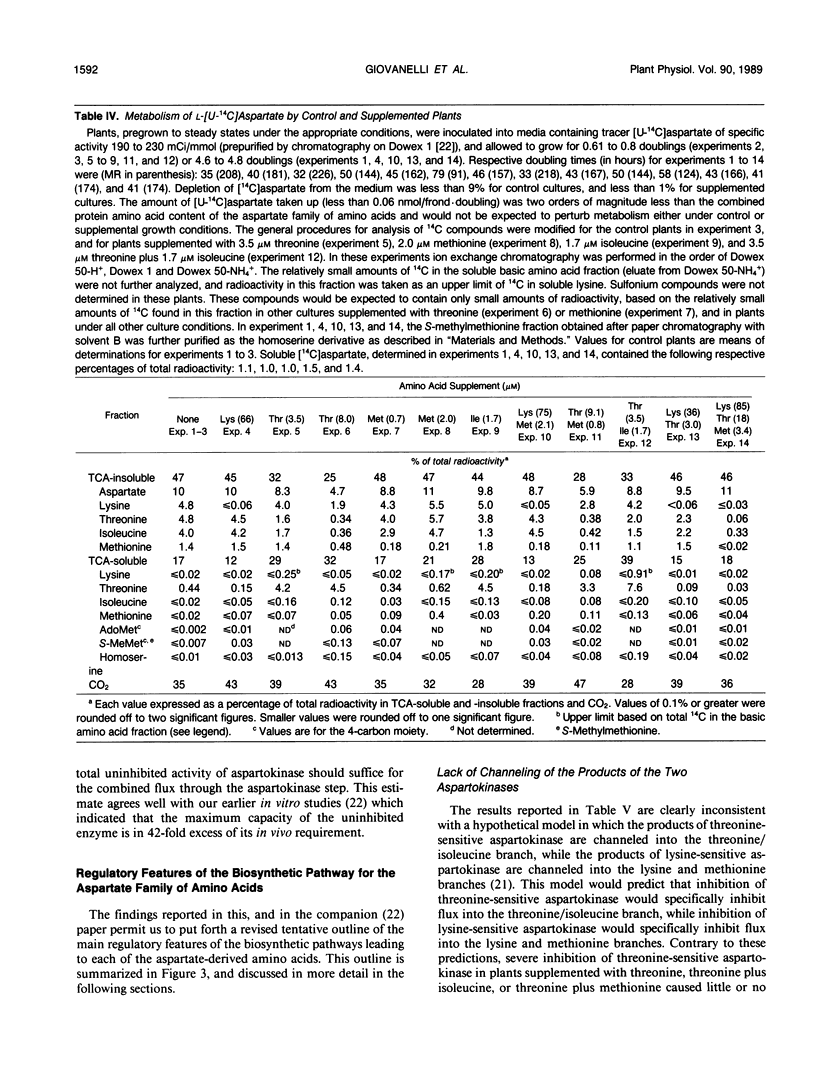
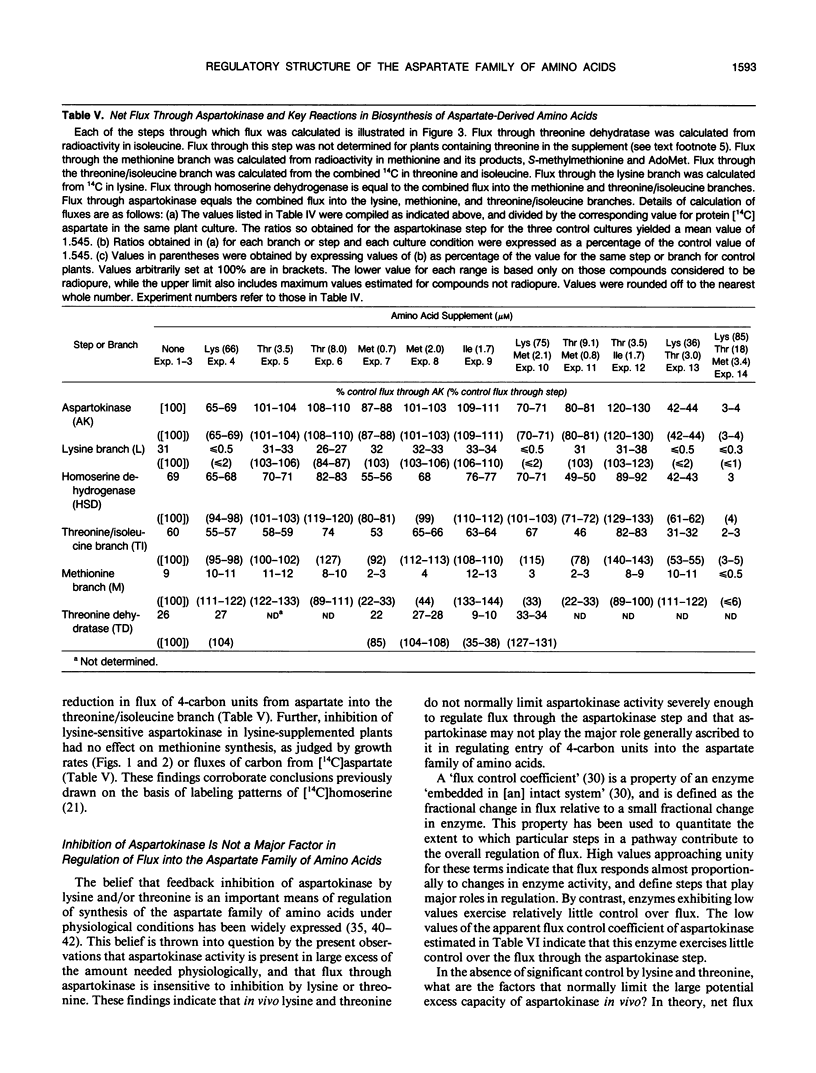
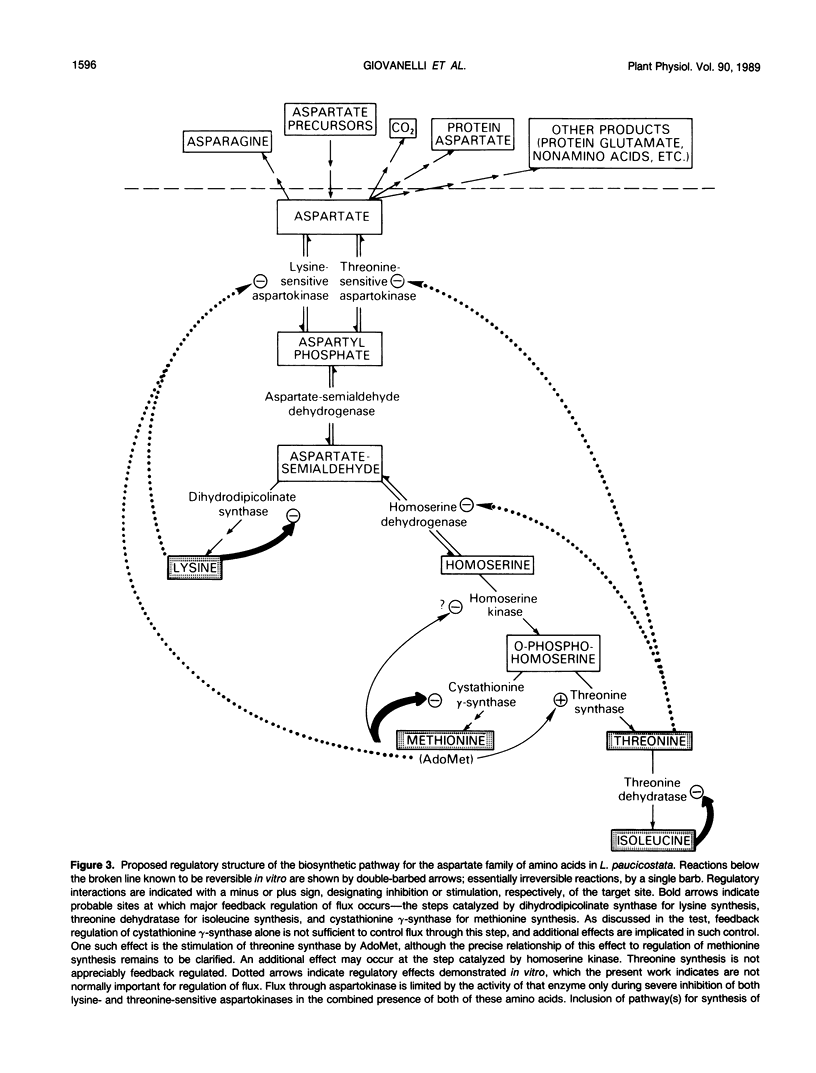
Comprehensive studies were made with Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746 of the effects of combinations of lysine, methionine, and threonine on growth rates, soluble amino acid contents, aspartokinase activities, and fluxes of 4-carbon moieties from aspartate through the aspartokinase step into the amino acids of the aspartate family. These studies show that flux in vitro through the aspartokinase step is insensitive to inhibition by lysine or threonine, and confirm previous in vitro data in establishing that aspartokinase in vivo is present in two orders of magnitude excess of its requirements. No evidence of channeling of the products of the lysine- and threonine-sensitive aspartokinases was obtained, either form of the enzyme alone being more than adequate for the combined in vivo flux through the aspartokinase step. The marked insensitivity of flux through the aspartokinase step to inhibition by lysine or threonine strongly suggests that inhibition of aspartokinase by these amino acids is not normally a major factor in regulation of entry of 4-carbon units into the aspartate family of amino acids. Direct measurement of fluxes of 4-carbon units demonstrated that: (a) Lysine strongly feedback regulates its own synthesis, probably at the step catalyzed by dihydrodipicolinate synthase. (b) Threonine alone does not regulate its own synthesis in vivo, thereby confirming previous studies of the metabolism of [14C]threonine and [14C]homoserine in Lemna. This finding excludes not only aspartokinases as an important regulatory determinant of threonine synthesis, but also two other enzymes (homoserine dehydrogenase and threonine synthase) suggested to fulfill this role. Complete inhibition of threonine synthesis was observed only in the combined presence of accumulated threonine and lysine. The physiological significance of this single example of apparent regulation of flux at the aspartokinase step, albeit under unusually stringent conditions of aspartokinase inhibition, remains to be determined. (c) Isoleucine strongly inhibits its own synthesis, probably at threonine dehydratase, without causing compensatory reduction in threonine synthesis. A fundamentally changed scheme for regulation of synthesis of the aspartate family of amino acids is presented that has important implications for improvement of the nutritional contents of these amino acids in plants.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK S., WRIGHT N. G. Aspartic beta-semialdehyde dehydrogenase and aspartic beta-semialdehyde. J Biol Chem. 1955 Mar;213(1):39–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK S., WRIGHT N. G. beta-Aspartokinase and beta-aspartyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1955 Mar;213(1):27–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright S. W., Miflin B. J., Rognes S. E. Threonine accumulation in the seeds of a barley mutant with an altered aspartate kinase. Biochem Genet. 1982 Apr;20(3-4):229–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00484421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree B., Newsholme E. A. A quantitative approach to metabolic control. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1985;25:21–76. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152825-6.50006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H. Homocysteine biosynthesis in green plants. O-Phosphorylhomoserine as the physiological substrate for cystathionine gamma-synthase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1139–1155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Giovanelli J. Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746: DEVELOPMENT OF STANDARDIZED GROWTH CONDITIONS SUITABLE FOR BIOCHEMICAL EXPERIMENTATION. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):906–912. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Methionine biosynthesis in lemna: inhibitor studies. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1070–1076. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Responses of Sulfur-Containing Compounds in Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746 to Changes in Availability of Sulfur Sources. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):474–479. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Uptake of Amino Acids and Other Organic Compounds by Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):770–778. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies H. M., Miflin B. J. Regulatory isoenzymes of aspartate kinase and the control of lysine and threonine biosynthesis in carrot cell suspension culture. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):536–541. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Aspartokinase of Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1577–1583. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. In Vivo Regulation of Threonine and Isoleucine Biosynthesis in Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):369–377. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. In vivo regulation of de novo methionine biosynthesis in a higher plant (lemna). Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):450–455. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H., Thompson G. A. Effects of Orthophosphate and Adenosine 5'-Phosphate on Threonine Synthase and Cystathionine gamma-Synthate of Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):577–583. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Veluthambi K., Thompson G. A., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Threonine Synthase of Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):285–292. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacser H., Burns J. A. The control of flux. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1973;27:65–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpaisal R., Hashimoto T., Yamada Y. Purification and characterization of dihydrodipicolinate synthase from wheat suspension cultures. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):145–151. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnicol P. K. Determination of specific radioactivity of plant amino acids using dansylation. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90275-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison J. T., Thompson J. F. Threonine synthetase from higher plants: stimulation by S-adenosylmethionine and inhibition by cysteine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90842-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Methionine methyl group metabolism in lemna. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):103–114. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A., Crabtree B. Theoretical principles in the approaches to control of metabolic pathways and their application to glycolysis in muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1979 Sep;11(9):839–856. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(79)90480-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler N. Use of the dansyl reaction in biochemical analysis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:259–337. doi: 10.1002/9780470110362.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Adaptation of Lemna paucicostata to Sublethal Methionine Deprivation. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):241–247. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Giovanelli J. Methionine Biosynthesis in Lemna: STUDIES ON THE REGULATION OF CYSTATHIONINE gamma-SYNTHASE, O-PHOSPHOHOMOSERINE SULFHYDRYLASE, AND O-ACETYLSERINE SULFHYDRYLASE. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1077–1083. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Methionine Synthesis in Lemna: Inhibition of Cystathionine gamma-Synthase by Propargylglycine. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1347–1352. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace J. C., Galili G., Kawata E. E., Cuellar R. E., Shotwell M. A., Larkins B. A. Aggregation of lysine-containing zeins into protein bodies in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):662–664. doi: 10.1126/science.2834822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



