Abstract
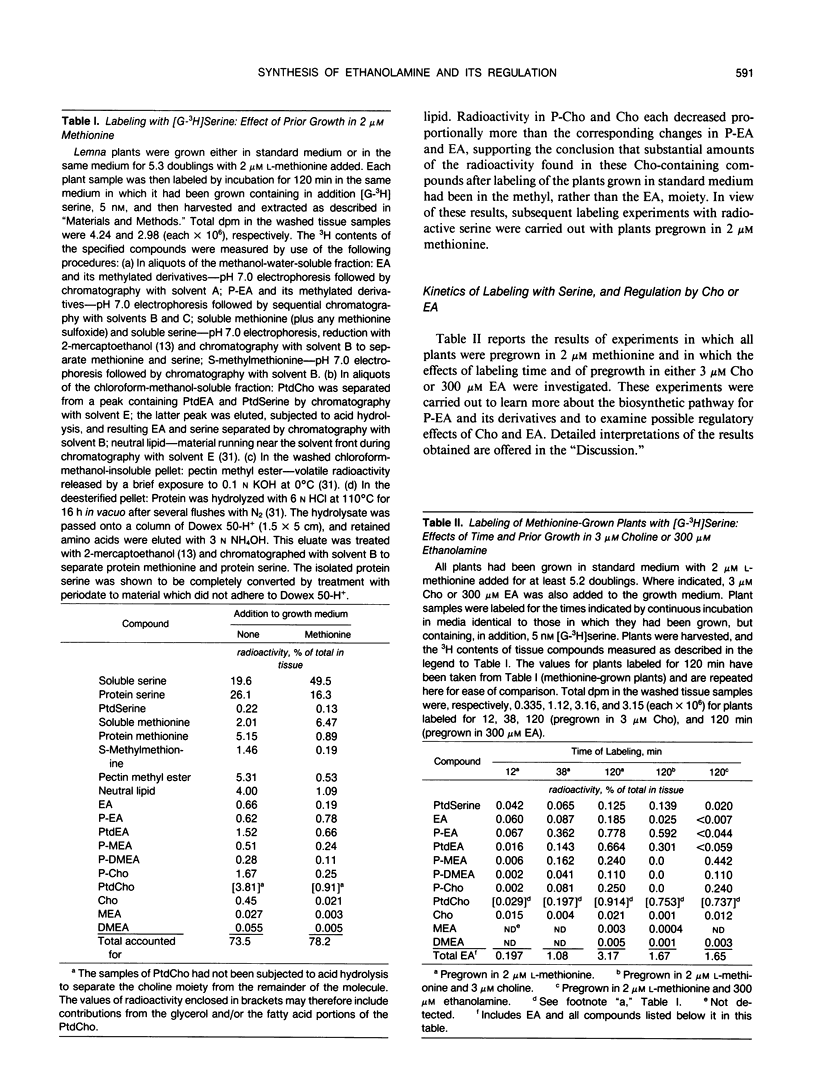
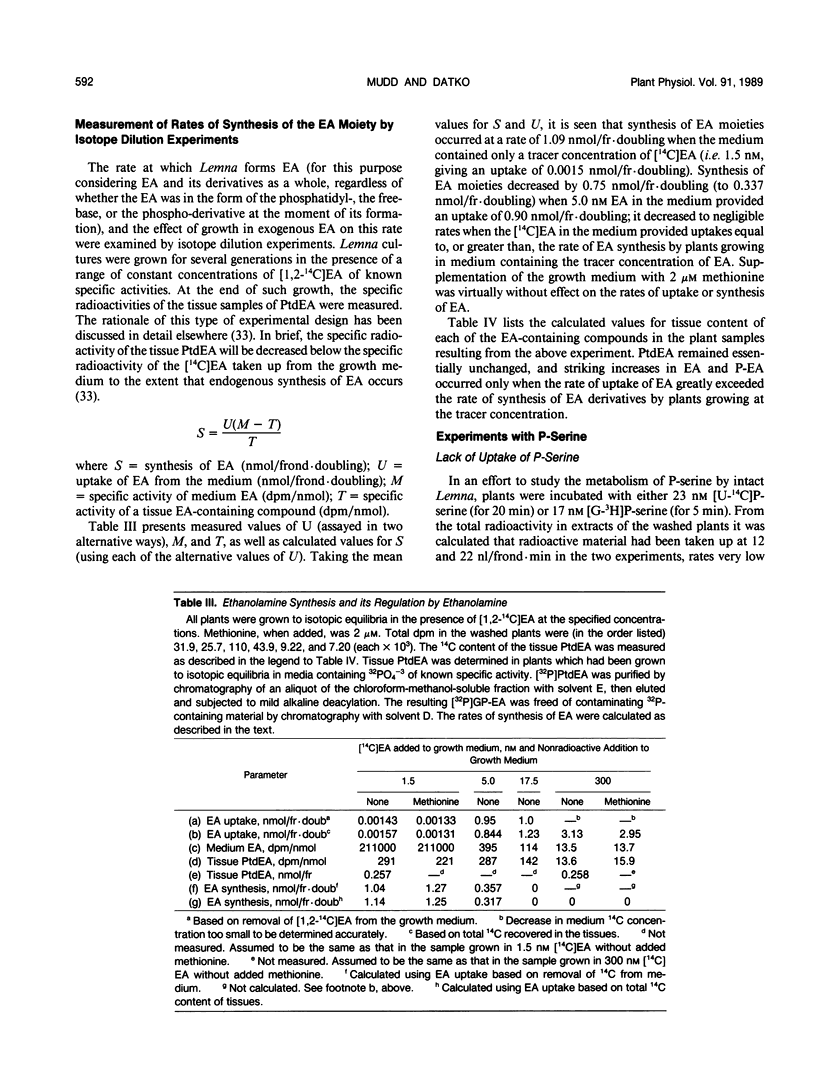
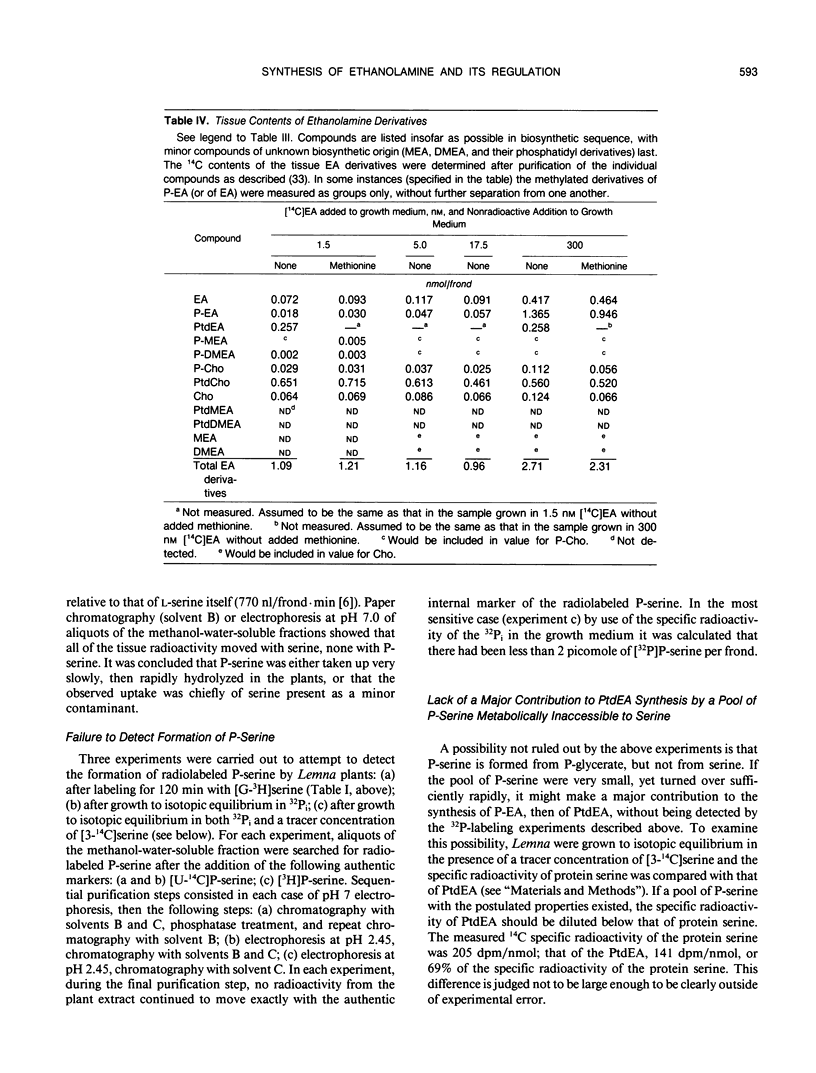
The metabolism of ethanolamine and its derivatives in Lemna paucicostata has been investigated, with emphasis on the path-way for synthesis of phosphoethanolamine, a precursor of phosphatidylcholine in higher plants. In experiments involving labeling of intact plants with radioactive serine, ambiguities of interpretation due to entry of radioactivity into methyl groups of methylated ethanolamine derivatives were mitigated by pregrowth of plants with methionine. Difficulties due to labeling of diacylglyceryl moieties of phospholipids were avoided by acid hydrolysis of crucial samples and determination of radioactivity in isolated serine or ethanolamine moieties. The results obtained from such experiments are most readily reconciled with the biosynthetic sequence: serine → ethanolamine → phosphoethanolamine → phosphatidylethanolamine. A possible alternative is: serine → phosphatidylserine → phosphatidylethanolamine → ethanolamine → phosphoethanolamine. Cell-free extracts of L. paucicostata were shown to produce CO2 from the carbon originating as C-1 of serine at a rate sufficient to satisfy the demand for ethanolamine moieties. A number of experiments produced no support for a hypothetical role for phosphoserine in phosphoethanolamine formation. Uptake of exogenous ethanolamine commensurately down-regulates the synthesis of ethanolamine moieties (considered as a whole, and regardless of their state of derivatization at the time of their formation). In agreement with previous observations, uptake of exogenous choline down-regulates the methylation of phosphoethanolamine, without being accompanied by secondary accumulation of a marked excess of ethanolamine derivatives.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barańska J. Biosynthesis and transport of phosphatidylserine in the cell. Adv Lipid Res. 1982;19:163–184. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024919-0.50011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerve K. S. The phospholipid substrates in the Ca2+ -stimulated incorporation of nitrogen bases into microsomal phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 21;306(3):396–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Enzymes of phosphatidylcholine synthesis in lemna, soybean, and carrot. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1338–1348. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Giovanelli J. Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746: DEVELOPMENT OF STANDARDIZED GROWTH CONDITIONS SUITABLE FOR BIOCHEMICAL EXPERIMENTATION. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):906–912. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Phosphatidylcholine synthesis: differing patterns in soybean and carrot. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):854–861. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datko A. H., Mudd S. H. Uptake of Amino Acids and Other Organic Compounds by Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):770–778. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes C. W., Kay J., Harwood J. L. Incorporation of choline and ethanolamine into phospholipids in germinating soya bean. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 15;158(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1580575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Datko A. H., Mudd S. H., Thompson G. A. In vivo metabolism of 5'-methylthioadenosine in lemna. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):319–326. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. In vivo regulation of de novo methionine biosynthesis in a higher plant (lemna). Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):450–455. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Veluthambi K., Thompson G. A., Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Threonine Synthase of Lemna paucicostata Hegelm. 6746. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):285–292. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goracci G., Horrocks L. A., Porcellati G. Reversibility of ethanolamine and choline phosphotransferases (EC 2.7.8.1 and EC 2.7.8.2) in rat brain microsomes with labelled alkylacylglycerols. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Scott N. A. Betaine Synthesis from Radioactive Precursors in Attached, Water-stressed Barley Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):342–348. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. P., WEISS S. B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano H., Ono K. Utilization of endogenous phospholipids by the backreaction of CDP-choline (-ethanolamine): 1,2-diglyceride choline (ethanolamine)-phosphotransferase in rat liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 24;306(2):203–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney A. J., Moore T. S. Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis in Castor Bean Endosperm : I. Metabolism of l-Serine. Plant Physiol. 1987 May;84(1):78–81. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. O., Kates M. Biosynthesis of nitrogenous phospholipids in spinach leaves. Can J Biochem. 1974 Jun;52(6):469–482. doi: 10.1139/o74-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. O., Kates M. Biosynthesis of phosphatidyl ethanolamine and phosphatidyl choline in spinach leaves. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 15;31(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. S. Phosphatidylserine synthesis in castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1975 Aug;56(2):177–180. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Methionine methyl group metabolism in lemna. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):103–114. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Phosphoethanolamine bases as intermediates in phosphatidylcholine synthesis by lemna. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):126–135. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S. H., Datko A. H. Synthesis of methylated ethanolamine moieties: regulation by choline in lemna. Plant Physiol. 1989 May;90(1):296–305. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy A. K., Carson M. A., Moore J. F., Waechter C. J. Control of phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in yeast: diacylglycerol ethanolaminephosphotransferase and diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase are separate enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Apr;230(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcellati G., Gaiti A., Woelk H., De Medio G. E., Brunetti M., Francescangeli E., Trovarelli G. Membrane-bound base-exchange reactions in animal tissues. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;101:287–299. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9071-2_28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. V., Moore K., Towers G. H. Degradation of aromatic amino acids by fungi. II. Purification and properties of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Ustilago hordei. Can J Biochem. 1967 Dec;45(12):1863–1872. doi: 10.1139/o67-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandor S. L., Richardson K. E. Incorporation of ethanolamine-1,2-14C into plant microsomal phospholipids. Can J Biochem. 1968 Oct;46(10):1309–1315. doi: 10.1139/o68-196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



