Abstract
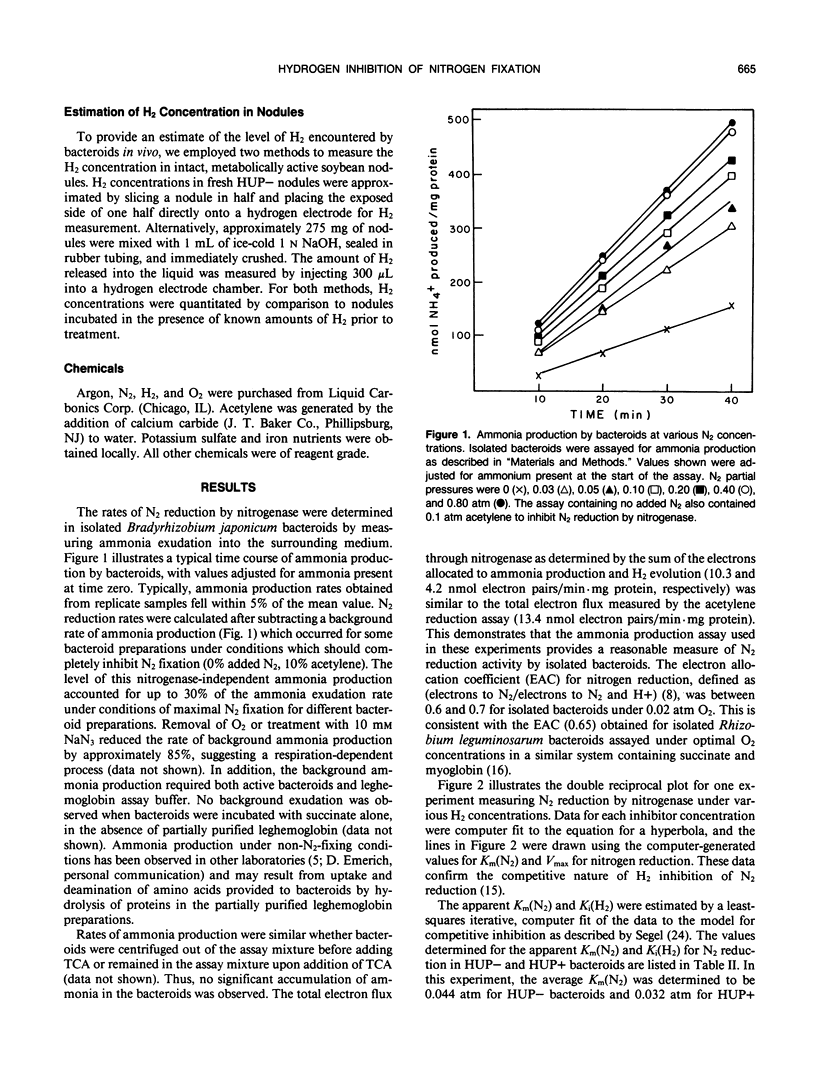
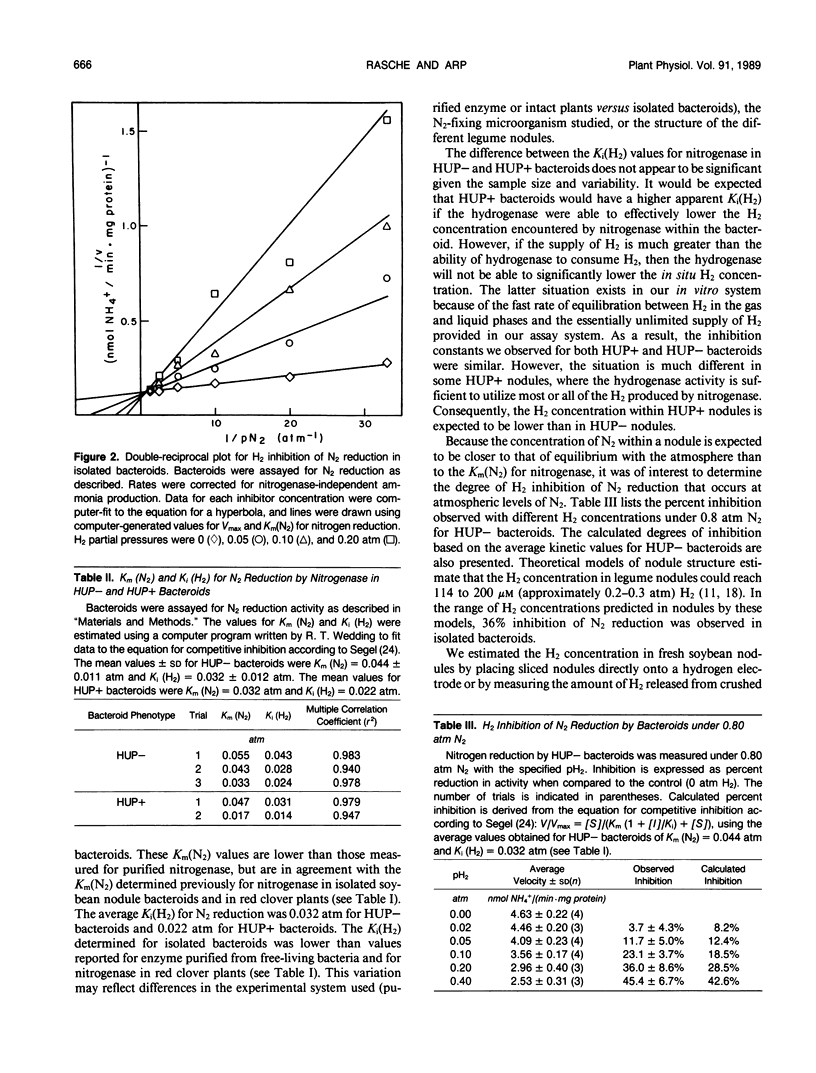
Dihydrogen, a by-product of biological nitrogen fixation, is a competitive inhibitor of N2 reduction by nitrogenase. To evaluate the significance of H2 inhibition in vivo, we have measured the apparent inhibition constant for H2 inhibition of N2 reduction in Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroids isolated from soybean nodules. The rate of N2 reduction was measured as ammonia production by bacteroids incubated in a buffer containing 200 micromolar leghemoglobin and 10 millimolar succinate under 0.02 atmosphere O2 and various concentrations of N2 and H2. The apparent inhibition constant for H2 under these conditions was determined to be approximately 0.03 atmosphere. This relatively low value strengthens the proposal that H2 inhibition of N2 reduction may be a significant factor in lowering the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in legume nodules.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht S. L., Maier R. J., Hanus F. J., Russell S. A., Emerich D. W., Evans H. J. Hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum Increases Nitrogen Fixation by Nodulated Soybeans. Science. 1979 Mar 23;203(4386):1255–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.203.4386.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleby C. A. The separation and properties of low-spin (haemochrome) and native, high-spin forms of leghaemoglobin from soybean nodule extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 21;189(2):267–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arp D. J., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of the particulate hydrogenase from the bacteroids of soybean root nodules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 11;570(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen F. J., Turner G. L. Systems utilizing oxygenated leghemoglobin and myoglobin as sources of free dissolved O2 at low concentrations for experiments with bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 1;96(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90569-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen J. F., Turner G. L. Nitrogen fixation by the bacteroid fraction of breis of soybean root nodules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 29;141(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Guevara J. G., Engelke J. A., Evans H. J. Relation between Glutamine Synthetase and Nitrogenase Activities in the Symbiotic Association between Rhizobium japonicum and Glycine max. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):542–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. O. Hydrogenase in legume root nodule bacteroids: occurrence and properties. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;85(3):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00408844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. O. Hydrogenase in pea root nodule bacterioids. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;62(3):272–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00413898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. J., Koch B., Klucas R. Preparation of nitrogenase from nodules and separation into components. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:470–476. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth J. H., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase-catalyzed NH3 formation by H2. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5111–5122. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaker H., Wassink H. Electron allocation to H+ and N2 by nitrogenase in Rhizobium leguminosarum bacteroids. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 2;142(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadfield K. L., Bulen W. A. Adenosine triphosphate requirement of nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):5103–5108. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. C., Chen C. H., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase-catalyzed reductions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):256–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepo J. E., Hickok R. E., Cantrell M. A., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Revertible hydrogen uptake-deficient mutants of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):614–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.614-620.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshin A., Burris R. H. Inhibitors of nitrogen fixation in extracts from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 15;111(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. B., Burris R. H. A nitrogen pressure of 50 atmospheres does not prevent evolution of hydrogen by nitrogenase. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1095–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.6585956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



