Abstract
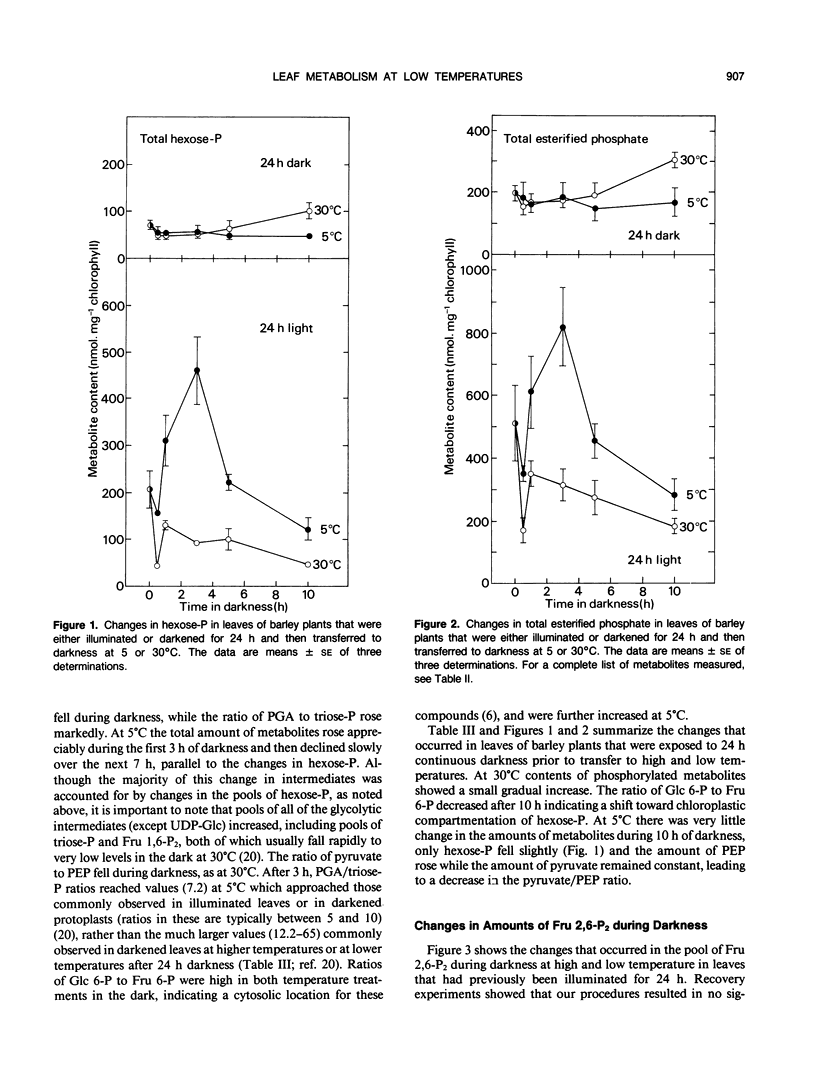
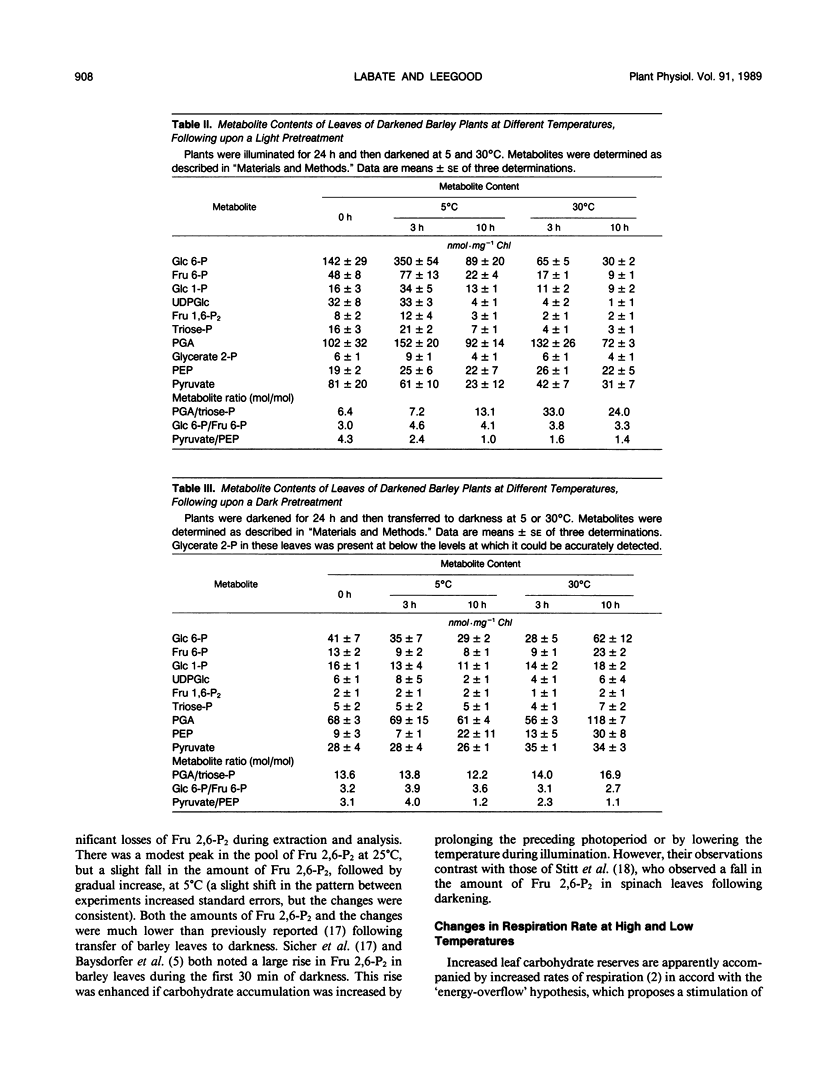
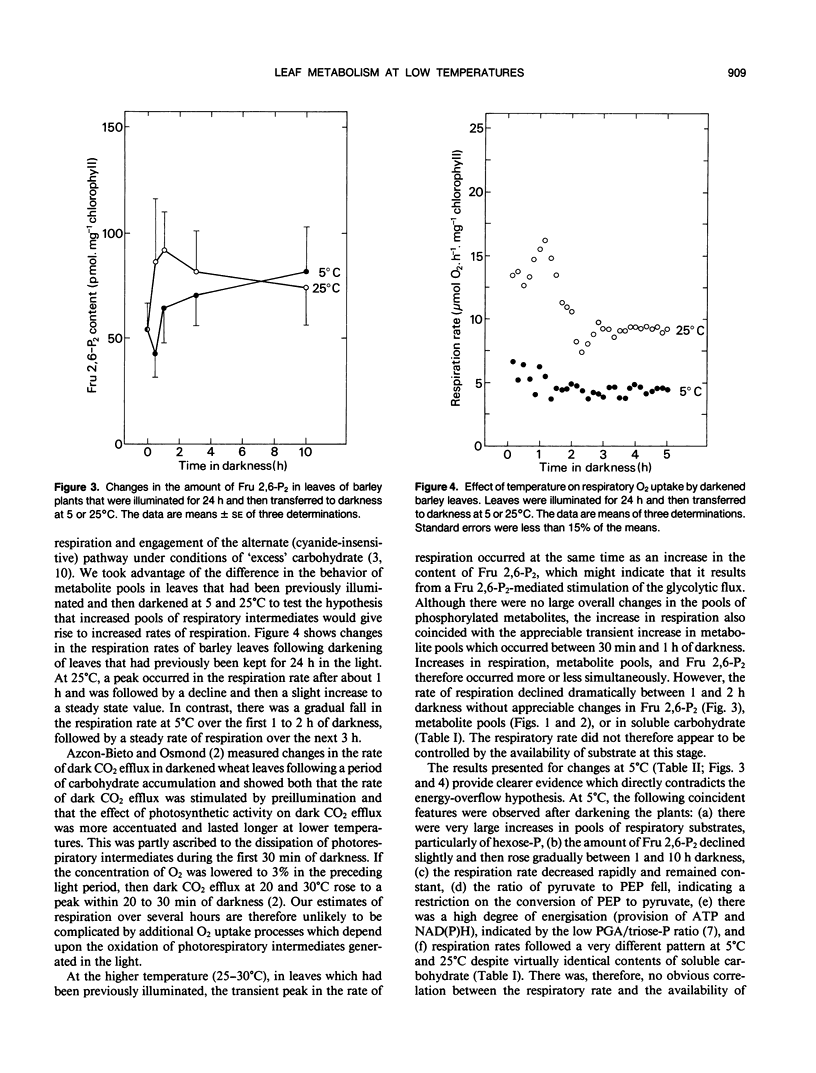
The aim of this work was to examine the effect of exposure of leaves to low temperatures (5°C) upon the contents of phosphorylated intermediates and respiration in darkened barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) plants which differed in their carbohydrate status. In leaves that had previously been illuminated for 24 hours, there was a large increase in amounts of phosphorylated metabolites at 5°C during the first 3 hours of darkness, compared with control plants kept at 30°C. Hexose phosphates accounted for about two-thirds of this increase, which reached a peak after about 3 hours. At higher temperatures, there was a peak in the amount of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and the rate of respiration which accompanied the transient increase in phosphorylated intermediates. At 5°C the increase in phosphorylated intermediates was not accompanied by appreciable changes in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, and there was a rapid decline in the rate of respiration. Leaves that had previously been darkened for 24 hours and that were low in carbohydrate failed to accumulate phosphorylated intermediates when exposed to low temperatures. The results are discussed with respect to the acclimation of carbohydrate metabolism to low temperatures. The results suggest that respiratory carbohydrate metabolism is strictly controlled even when the carbohydrate supply and glycolytic intermediates are abundant. The possibility that accumulation of hexose phosphates may be involved in acclimation of metabolism to low temperature is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azcón-Bieto J. Inhibition of photosynthesis by carbohydrates in wheat leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):681–686. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azcón-Bieto J., Lambers H., Day D. A. Effect of photosynthesis and carbohydrate status on respiratory rates and the involvement of the alternative pathway in leaf respiration. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):598–603. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azcón-Bieto J., Osmond C. B. Relationship between Photosynthesis and Respiration: The Effect of Carbohydrate Status on the Rate of CO(2) Production by Respiration in Darkened and Illuminated Wheat Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):574–581. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baysdorfer C., Sicher R. C., Kremer D. F. Relationship between Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate and Carbohydrate Metabolism in Darkened Barley Primary Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):766–769. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhardt R., Stitt M., Heldt H. W. Subcellular Metabolite Levels in Spinach Leaves : Regulation of Sucrose Synthesis during Diurnal Alterations in Photosynthetic Partitioning. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):399–407. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. G., Outlaw W. H., Lowry O. H. Enzymic assay of 10 to 10 moles of sucrose in plant tissues. Plant Physiol. 1977 Sep;60(3):379–383. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Kremer D. F., Harris W. G. Control of photosynthetic sucrose synthesis in barley primary leaves: role of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):15–18. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Gerhardt R., Kürzel B., Heldt H. W. A role for fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the regulation of sucrose synthesis in spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1139–1141. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Kürzel B., Heldt H. W. Control of Photosynthetic Sucrose Synthesis by Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate : II. Partitioning between Sucrose and Starch. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):554–560. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeden N. F., Buchanan B. B. Leaf Cytosolic Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase : A Potential Target Site in Low Temperature Stress. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):259–261. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



