Abstract
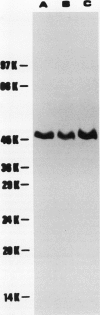
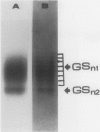
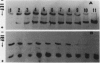
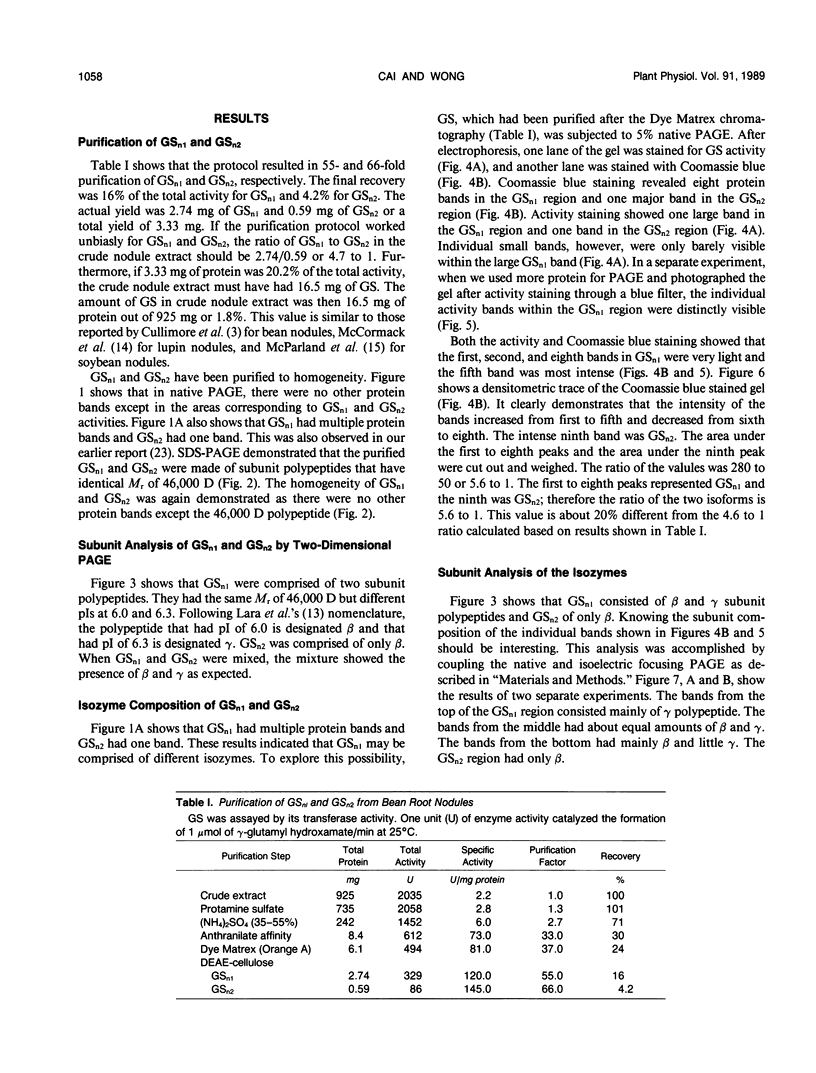
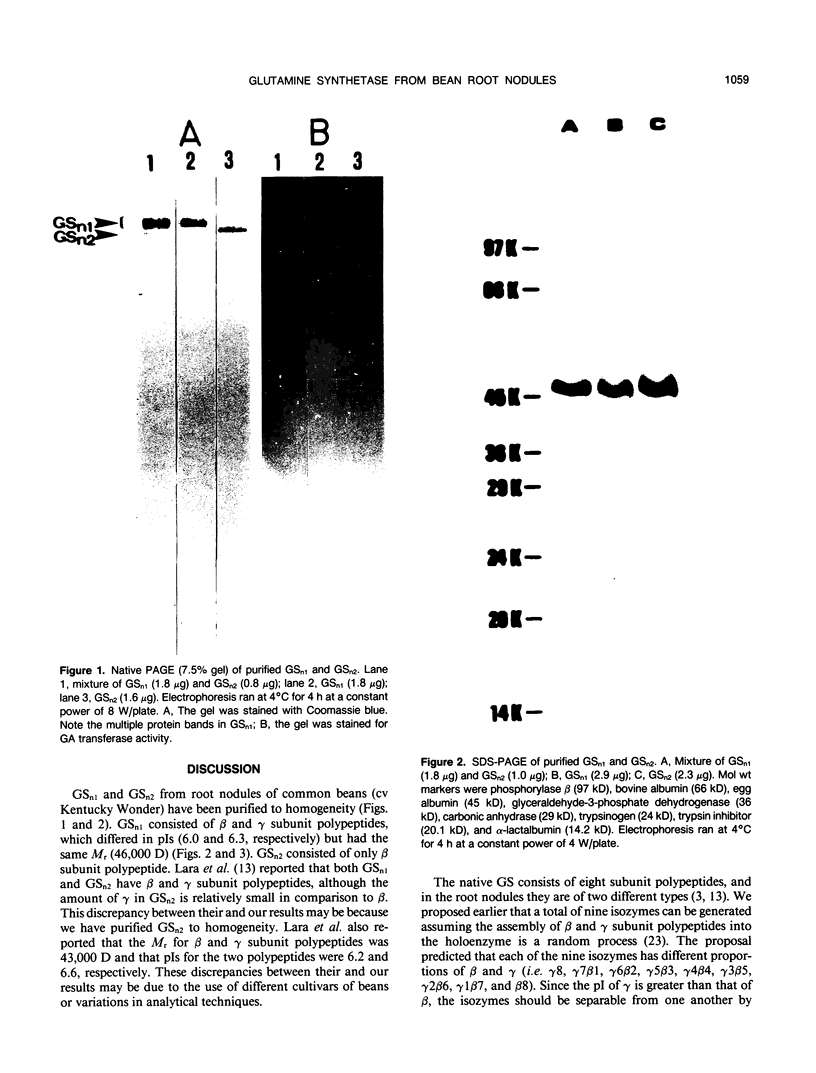
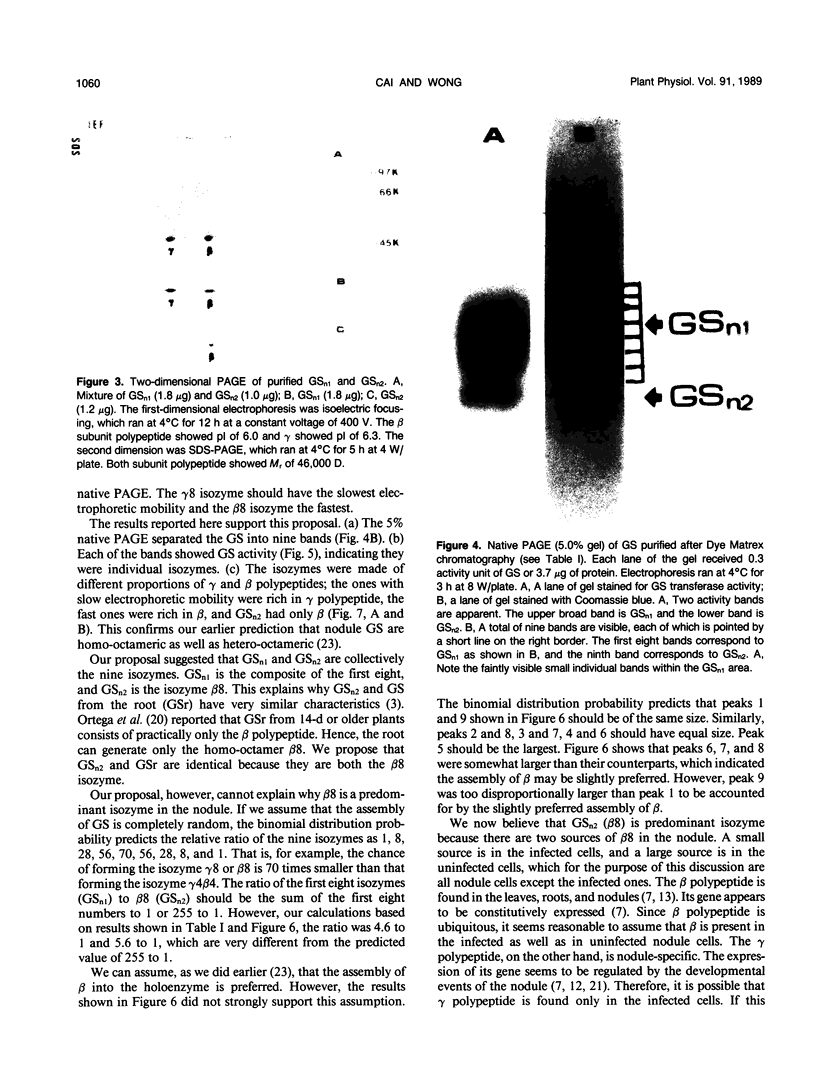
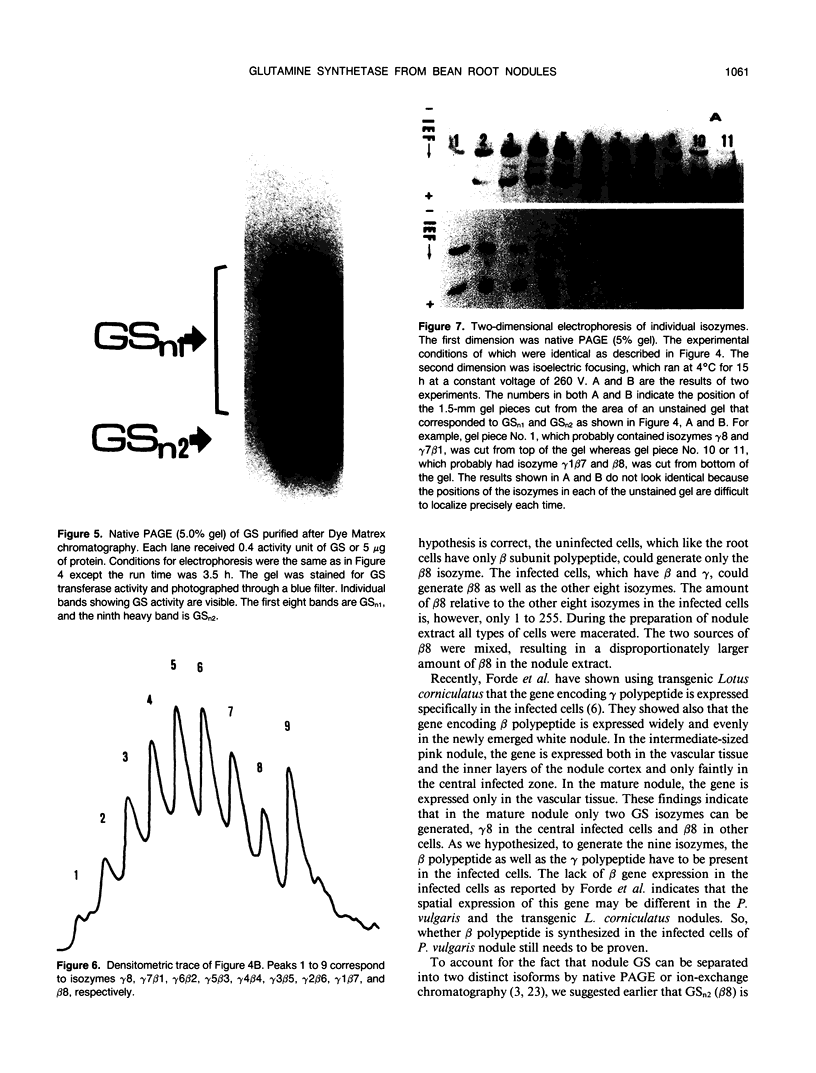
Glutamine synthetase from bean nodules can be separated into two isoforms, GSn1 and GSn2. A purification protocol has been developed. It included protamine sulfate precipitation, ammonium sulfate fractionation, anthranilate-affinity chromatography, Dye-Matrex (Orange A) chromatography, and diethylaminoethyl-cellulose ion-exchange chromatography. GSn1 and GSn2 have been purified to homogeneity. Subunit structure analysis using two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed that GSn1 was composed of two different types of subunit polypeptides. They differed in isoelectric points (6.0 and 6.3) but had the same molecular weights (46,000 Daltons). GSn2 was composed of only one type of subunit polypeptide. It had an isoelectric point of 6.0 and a molecular weight of 46,000 Daltons. It was apparently identical to one of the polypeptides found in GSn1. Glutamine synthetase holoenzyme consisted of eight subunits. In the nodule there are two different types of glutamine synthetase subunit polypeptides. Random combinations of the polypeptides should generate nine different isozymes. Our electrophoretic analysis revealed that GSn2 was but one of the isozymes, and GSn1 was a composite of the other eight. Hence, nodule glutamine synthetase isozymes were homo-octameric as well as hetero-octameric.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forde B. G., Day H. M., Turton J. F., Shen W. J., Cullimore J. V., Oliver J. E. Two glutamine synthetase genes from Phaseolus vulgaris L. display contrasting developmental and spatial patterns of expression in transgenic Lotus corniculatus plants. Plant Cell. 1989 Apr;1(4):391–401. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.4.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt C., Oliver J. E., Forde B. G., Saarelainen R., Miflin B. J. Primary structure and differential expression of glutamine synthetase genes in nodules, roots and leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1429–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04379.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groat R. G., Schrader L. E. Isolation and Immunochemical Characterization of Plant Glutamine Synthetase in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Nodules. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1759–1761. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I. R. Primary products of symbiotic nitrogen fixation. I. Short-term exposures of serradella nodules to 15N2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. D., Sakano K., Wildman S. G. Multiple peptide composition of the large and small subunits of Nicotiana tabacum fraction I protein ascertained by fingerprinting and electrofocusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 13;365(1):138–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lara M., Porta H., Padilla J., Folch J., Sánchez F. Heterogeneity of Glutamine Synthetase Polypeptides in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):1019–1023. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manhart J. R., Wong P. P. Nitrate reductase activities of rhizobia and the correlation between nitrate reduction and nitrogen fixation. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1169–1174. doi: 10.1139/m79-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mc Cormack D. K., Farnden K. J., Boland M. J. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from the plant cytosol fraction of lupin nodules. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Oct 15;218(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90380-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McParland R. H., Guevara J. G., Becker R. R., Evans H. J. The purification and properties of the glutamine synthetase from the cytosol of Soya-bean root nodules. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):597–606. doi: 10.1042/bj1530597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortega J. L., Campos F., Sánchez F., Lara M. Expression of Two Different Glutamine Synthetase Polypeptides during Root Development in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Apr;80(4):1051–1054. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R. Neurospora crassa glutamine synthetase. Purification by affinity chromatography and characterization of subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4787–4791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert F. M., Wong P. P. Isozymes of Glutamine Synthetase in Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Phaseolus lunatus L. Root Nodules. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):142–148. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]