Figure 1. INKBRITE identifies p16INK4A+ cells with senescent characteristics in vivo.
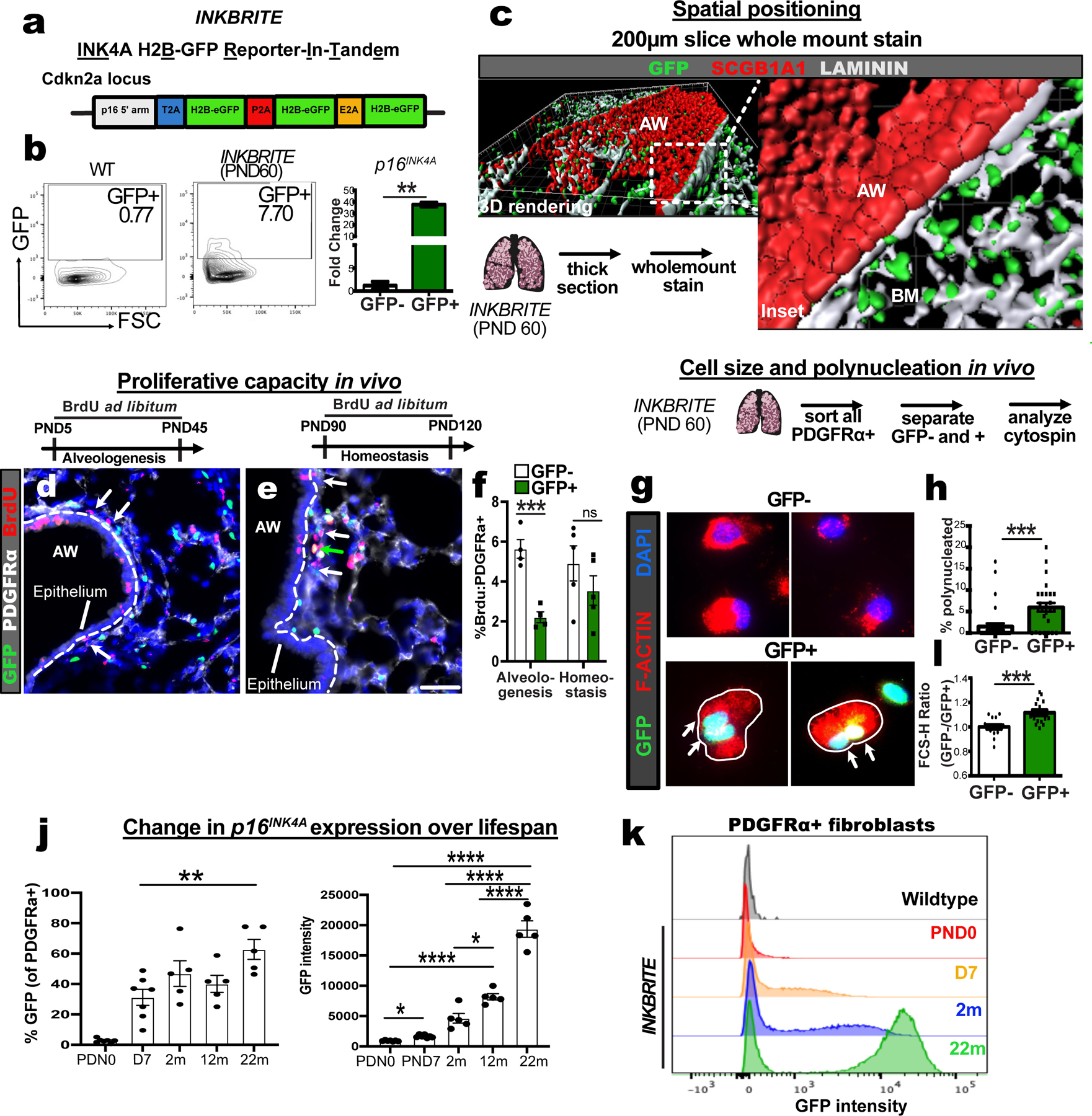
(A) Target construct design for INKBRITE. (B) FACS analysis of GFP+ cells from INKBRITE lungs and qPCR of sorted GFP+ and GFP−neg cells (n=2). (C) Wholemount image of the airway from thick-sectioned INKBRITE lung rendered on Imaris. (D to F) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and quantification of BrdU incorporation into PDGFRα+ and GFP– (white arrows) or PDGFRα+ and GFP+ (green arrows) cells during alveologenesis or homeostasis (n=4 alveologenesis, n=5 homeostasis). (G and H) IHC and quantification of freshly sorted of GFP+ and GFP– fibroblasts for polynucleation (2 experiments, n=29–31 images per cell type). (I) FACS data with quantification of % GFP+ cells and mean GFP+ intensity of PDGFRα+ fibroblasts over the lifespan of INKBRITE animals (n; PND0=7, PND7=7, 2m=5, 22m=5). (J) Histogram display the of GFP intensity in PND0, PND7, 2m, and 22m PDGFRα+ lung fibroblasts (n= 5 per timepoint, 2 experiments). AW=airway, BM=basement membrane, PND=Postnatal day. Scale bars 100υm. Each point in graph represents one animal or one distinct image for in vitro studies with mean ± s.e.m. All p values determined by one-tailed t-test and two-way ANOVA when applicable. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001.
