Abstract
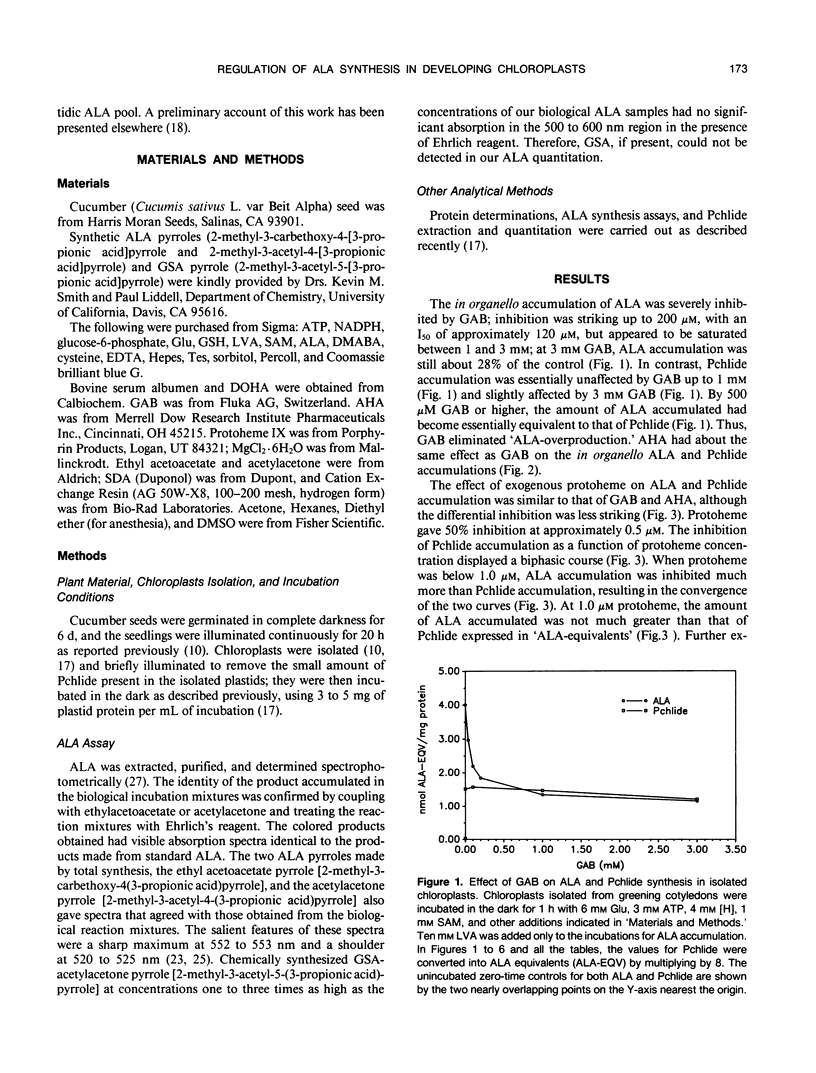
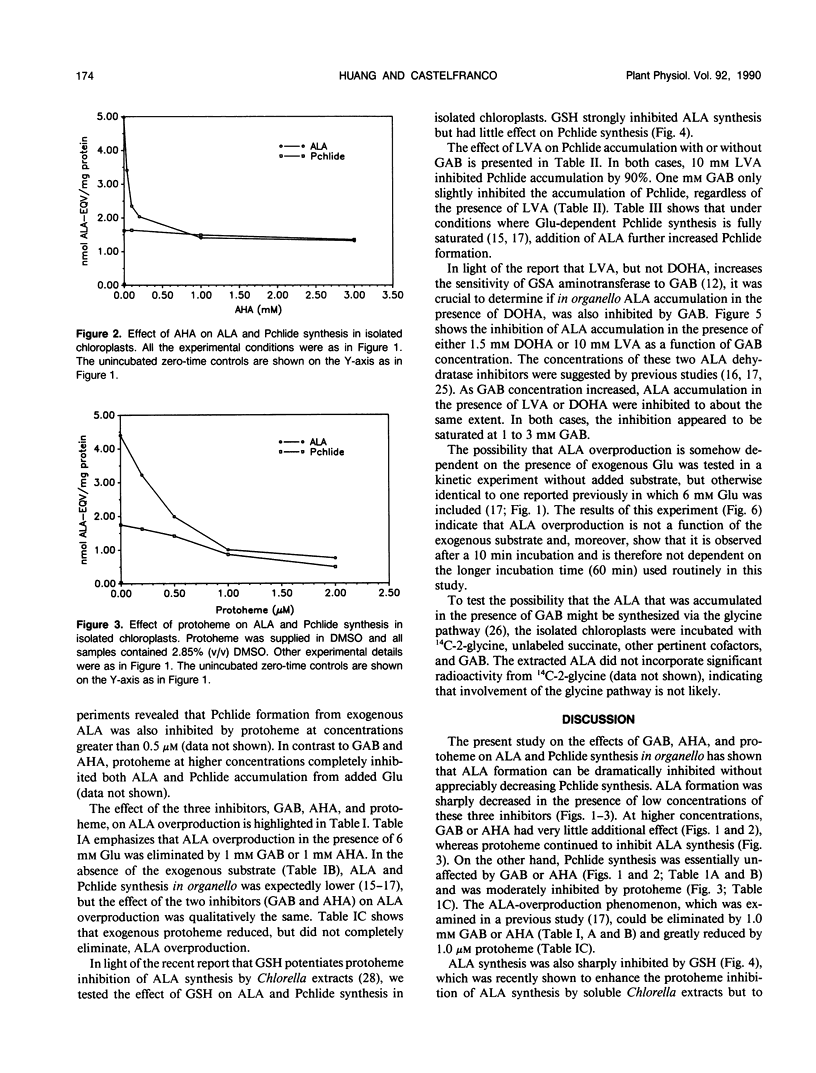
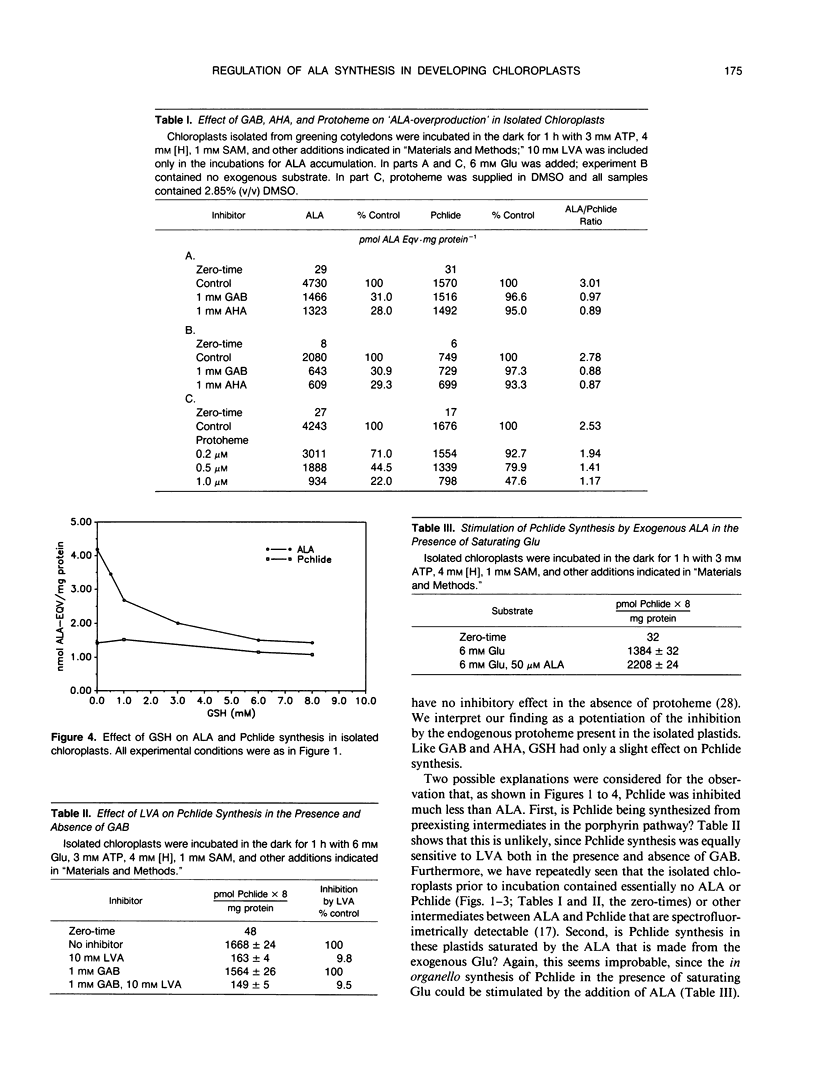
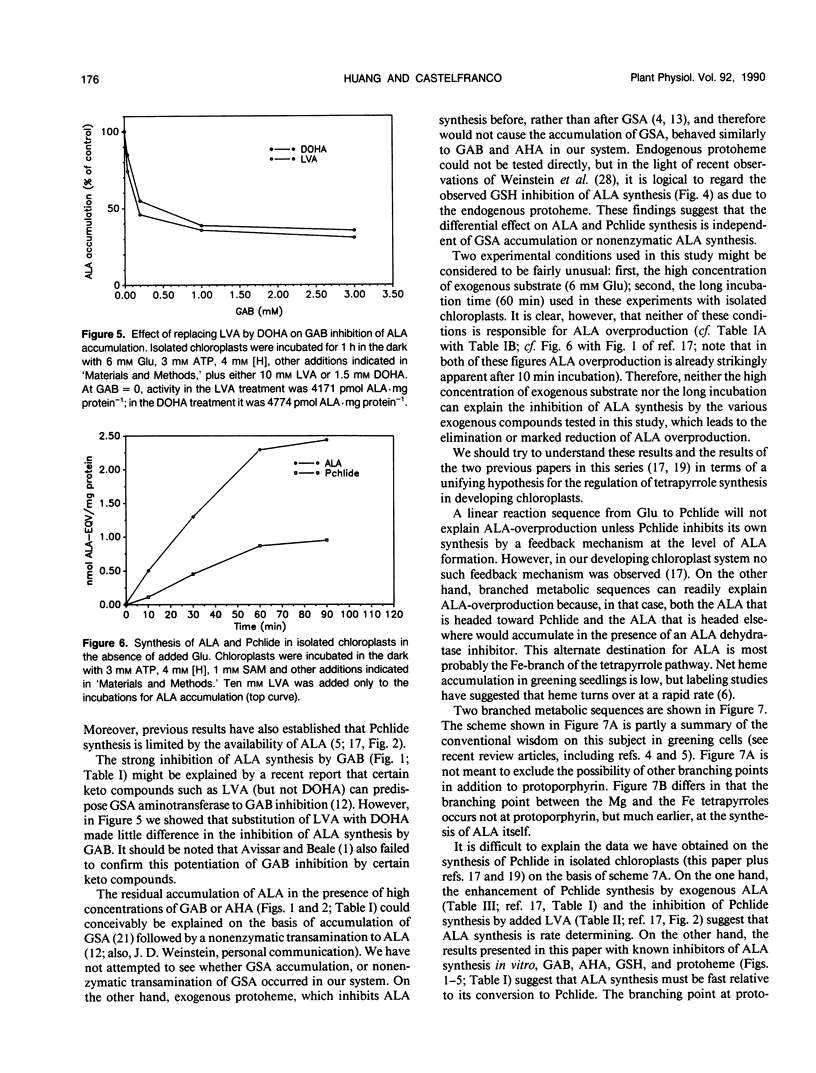
Gabaculine and 4-amino-5-hexynoic acid (AHA) up to 3.0 millimolar concentration strongly inhibited 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthesis in developing cucumber (Cucumis sativus L. var Beit Alpha) chloroplasts, while they hardly affected protochlorophyllide (Pchlide) synthesis. Exogenous protoheme up to 1.0 micromolar had a similar effect. Exogenous glutathione also exhibited a strong inhibitory effect on ALA synthesis in organello but hardly inhibited Pchlide synthesis. Pchlide synthesis in organello was highly sensitive to inhibition by levulinic acid, both in the presence and in the absence of gabaculine, indicating that the Pchlide was indeed formed from precursor(s) before the ALA dehydratase step. The synthesis of Pchlide in the presence of saturating concentrations of glutamate was stimulated by exogenous ALA, confirming that Pchlide synthesis was limited at the formation of ALA. The gabaculine inhibition of ALA accumulation occurred whether levulinic acid or 4,6-dioxohepatonic acid was used in the ALA assay system. ALA overproduction was also observed in the absence of added glutamate and was noticeable after 10-minute incubation. These observations suggest that although Pchlide synthesis in organello is limited by ALA formation, it does not utilize all the ALA that is made in the in organello assay system. Gabaculine, AHA, and probably also protoheme, inhibit preferentially the formation of that portion of ALA that is not destined for Pchlide. A model proposing a heterogenous ALA pool is described.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avissar Y. J., Beale S. I. Biosynthesis of Tetrapyrrole Pigment Precursors : Pyridoxal Requirement of the Aminotransferase Step in the Formation of delta-Aminolevulinate from Glutamate in Extracts of Chlorella vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):852–859. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale S. I., Castelfranco P. A. 14 C incorporation from exogenous compounds into -aminolevulinic acid by greening cucumber cotyledons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90966-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale S. I., Castelfranco P. A. The Biosynthesis of delta-Aminolevulinic Acid in Higher Plants: II. Formation of C-delta-Aminolevulinic Acid from Labeled Precursors in Greening Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1974 Feb;53(2):297–303. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelfranco P. A., Jones O. T. Protoheme turnover and chlorophyll synthesis in greening barley tissue. Plant Physiol. 1975 Mar;55(3):485–490. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.3.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elich T. D., Lagarias J. C. 4-amino-5-hexynoic Acid-a potent inhibitor of tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in plants. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):747–751. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elich T. D., Lagarias J. C. Phytochrome Chromophore Biosynthesis : Both 5-Aminolevulinic Acid and Biliverdin Overcome Inhibition by Gabaculine in Etiolated Avena sativa L. Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):304–310. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett W. F., Dunn M. F. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae Pathovars in Infected Leaves of Susceptible Hosts. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):5–9. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett W. F., Dunn M. F. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae Pathovars in Infected Leaves of Susceptible Hosts. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):5–9. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fufsler T. P., Castelfranco P. A., Wong Y. S. Formation of Mg-Containing Chlorophyll Precursors from Protoporphyrin IX, delta-Aminolevulinic Acid, and Glutamate in Isolated, Photosynthetically Competent, Developing Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):928–933. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. M., Pearson S. A., Smith A. J., Rogers L. J. Inhibition of chlorophyll synthesis in Hordeum vulgare by 3-amino 2,3-dihydrobenzoic acid (gabaculin). Biosci Rep. 1985 Sep;5(9):775–781. doi: 10.1007/BF01119876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Kahn A., Ash D. E., Gough S., Kannangara C. G. Biosynthesis of delta-aminolevulinate in greening barley leaves. IX. Structure of the substrate, mode of gabaculine inhibition, and the catalytic mechanism of glutamate 1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. Carlsberg Res Commun. 1988;53(1):11–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02908411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. D., Wang W. Y. Chlorophyll biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas starts with the formation of glutamyl-tRNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13451–13455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. D., Wang W. Y., Gough S. P., Kannangara C. G. delta-Aminolevulinic acid-synthesizing enzymes need an RNA moiety for activity. Science. 1984 Sep 28;225(4669):1482–1484. doi: 10.1126/science.6206568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Bonner B. A., Castelfranco P. A. Regulation of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid (ALA) Synthesis in Developing Chloroplasts : II. Regulation of ALA-Synthesizing Capacity by Phytochrome. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):1003–1008. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Castelfranco P. A. Regeneration of Magnesium-2,4-Divinylpheoporphyrin a(5) (Divinyl Protochlorophyllide) in Isolated Developing Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):285–288. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Castelfranco P. A. Regulation of 5-aminolevulinic Acid synthesis in developing chloroplasts : I. Effect of light/dark treatments in vivo and in organello. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jul;90(3):996–1002. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.3.996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannangara C. G., Gough S. P., Bruyant P., Hoober J. K., Kahn A., von Wettstein D. tRNA(Glu) as a cofactor in delta-aminolevulinate biosynthesis: steps that regulate chlorophyll synthesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Apr;13(4):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer S. M., Beale S. I., Weinstein J. D. Enzymatic conversion of glutamate to delta-aminolevulinic acid in soluble extracts of Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12541–12549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller E., Gassman M. L. The effects of levulinic Acid and 4,6-dioxoheptanoic Acid on the metabolism of etiolated and greening barley leaves. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):728–732. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J. D., Beale S. I. Enzymatic conversion of glutamate to delta-aminolevulinate in soluble extracts of the unicellular green alga, Chlorella vulgaris. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Mar;237(2):454–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90299-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


