Abstract
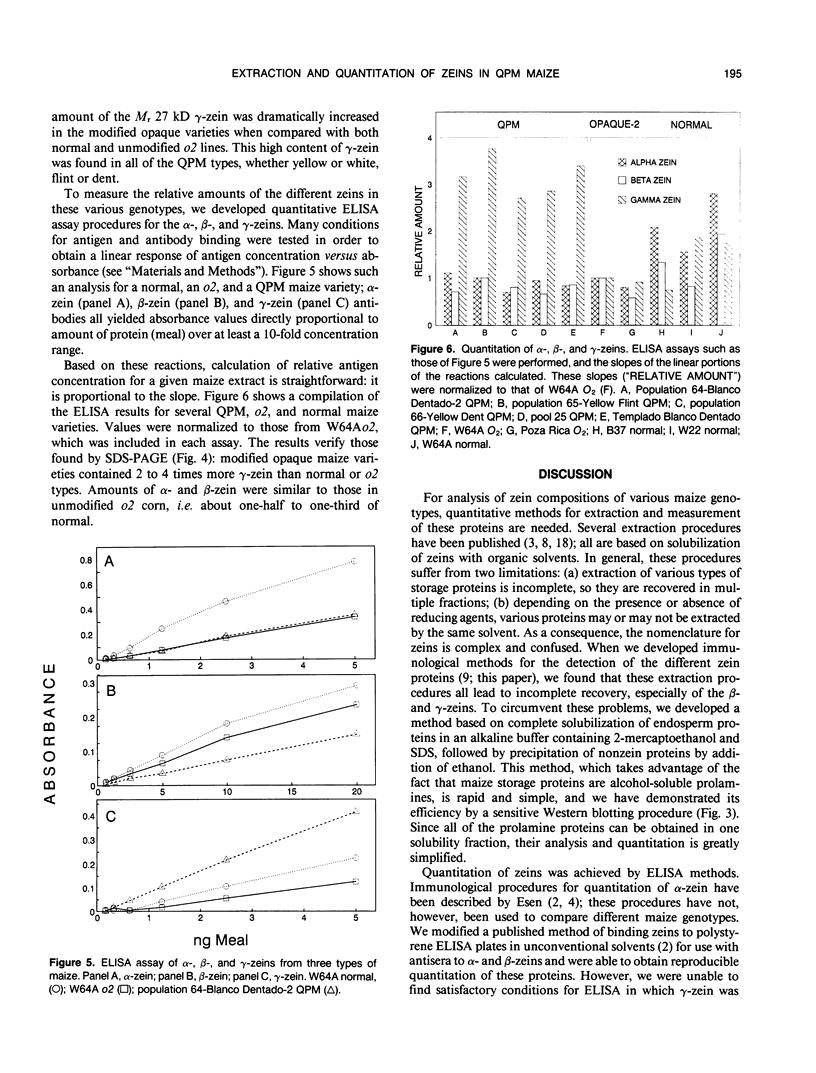
We have developed methods for quantitative extraction and analysis of zeins from maize (Zea mays L.) flour. Extraction involved solubilization of total endosperm proteins in an alkaline buffer containing SDS and 2-mercaptoethanol with subsequent precipitation of nonzein proteins by the addition of ethanol to 70%. Analysis of these proteins by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie blue staining and by Western blotting and ELISA assay with zein antibodies revealed that this extraction method is more quantitative than the traditional Landry-Moureaux procedure, especially for the β- and γ-zeins. This method was used to extract and analyze the zein content of several `Quality Protein Maize' (QPM) varieties developed by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center. QPM varieties contain `modifier genes' that confer a vitreous phenotype on opaque-2 genotypes, while maintaining the elevated levels of lysine and tryptophan characteristic of this mutant. This analysis revealed that the QPM types contain 2 to 4 times the amount of the γ-zein than unmodified opaque-2 or normal maize varieties. Possible relationships between the high expression of the γ-zein and the modified opaque phenotype are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conroy J. M., Esen A. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for zein and other proteins using unconventional solvents for antigen adsorption. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):182–187. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90368-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esen A., Conroy J. M., Wang S. Z. A simple and rapid dot-immunobinding assay for zein and other prolamins. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;132(2):462–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esen A. Separation of alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) from maize into three fractions by differential solubility. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):623–627. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Dimond R. L. Visualization of antigenic proteins on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodrzycki R., Boston R. S., Larkins B. A. The opaque-2 mutation of maize differentially reduces zein gene transcription. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):105–114. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Moureaux T. Hétérogénéité des glutélines du grain de mais: extraction sélective et composition en acides amines des trois fractions isolées. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1970;52(10):1021–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTZ E. T., BATES L. S., NELSON O. E. MUTANT GENE THAT CHANGES PROTEIN COMPOSITION AND INCREASES LYSINE CONTENT OF MAIZE ENDOSPERM. Science. 1964 Jul 17;145(3629):279–280. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3629.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat S., Cortadas J., Puigdomènech P., Palau J. Nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences of the maize endosperm protein glutelin-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1493–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Larkins B. A., Glover D. V. Interaction of the opaque-2 gene with starch-forming mutant genes on the synthesis of zein in maize endosperm. Biochem Genet. 1978 Oct;16(9-10):883–896. doi: 10.1007/BF00483740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Z., Esen A. Primary structure of a proline-rich zein and its cDNA. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):70–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]