Abstract
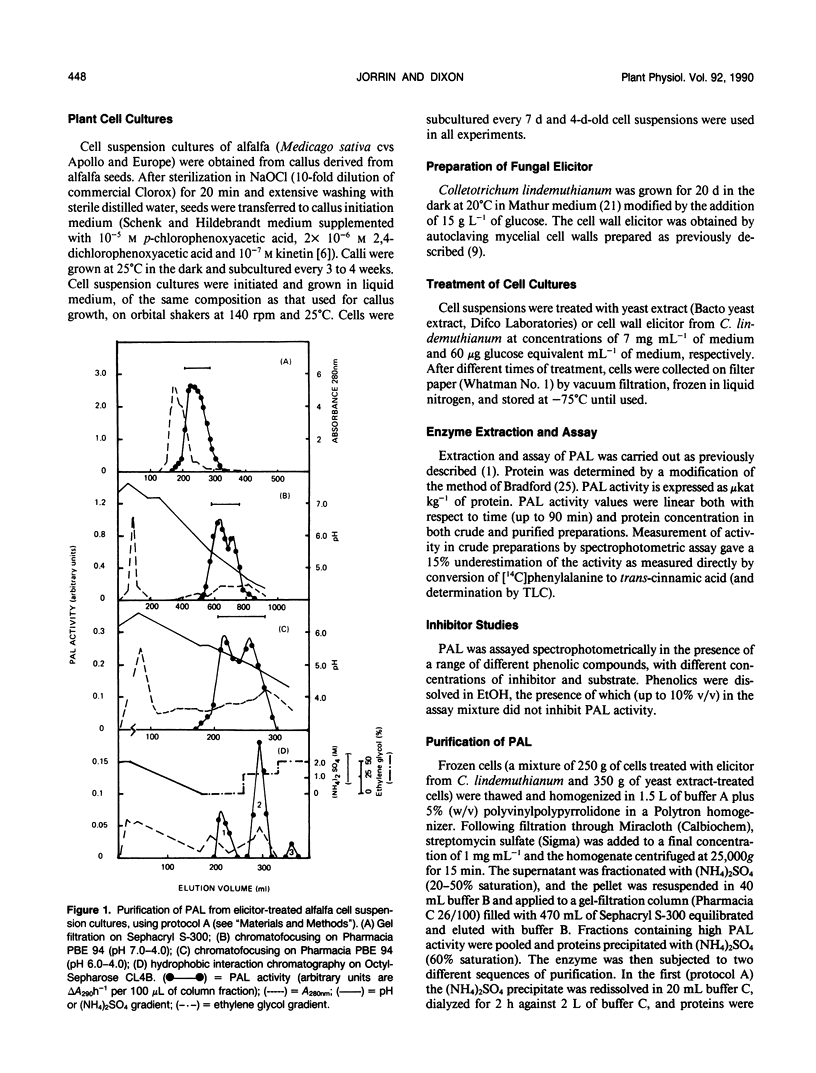
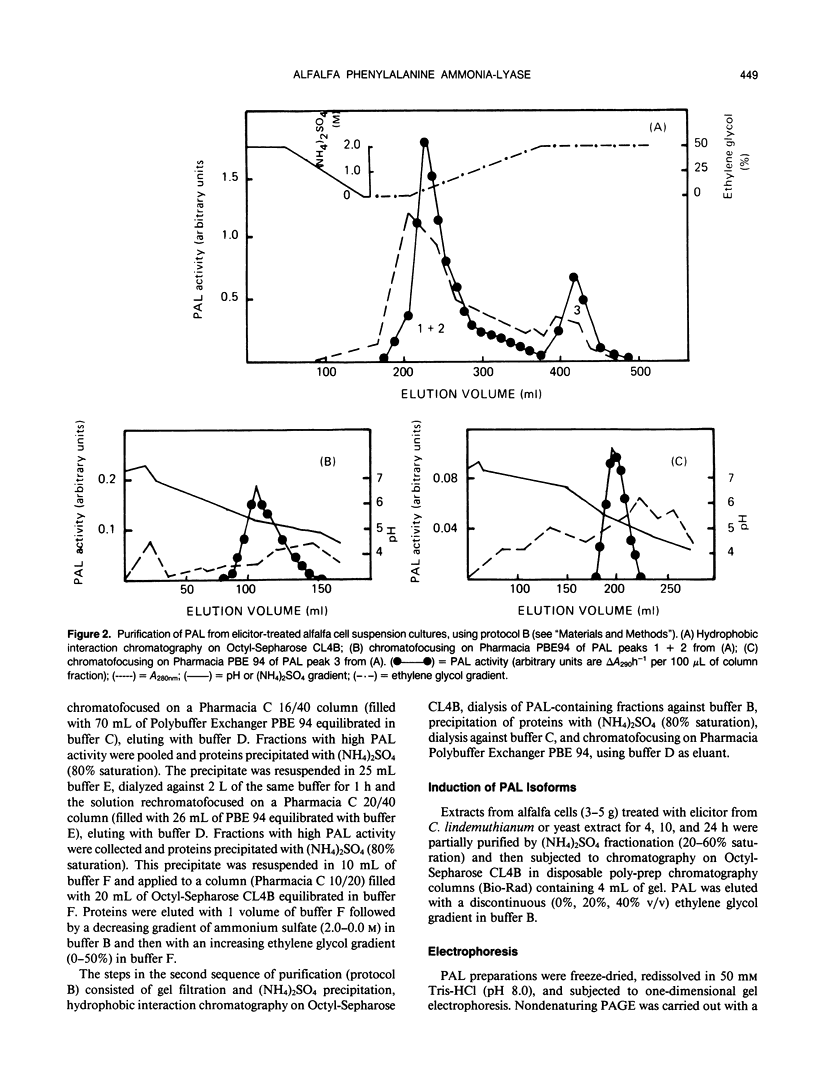
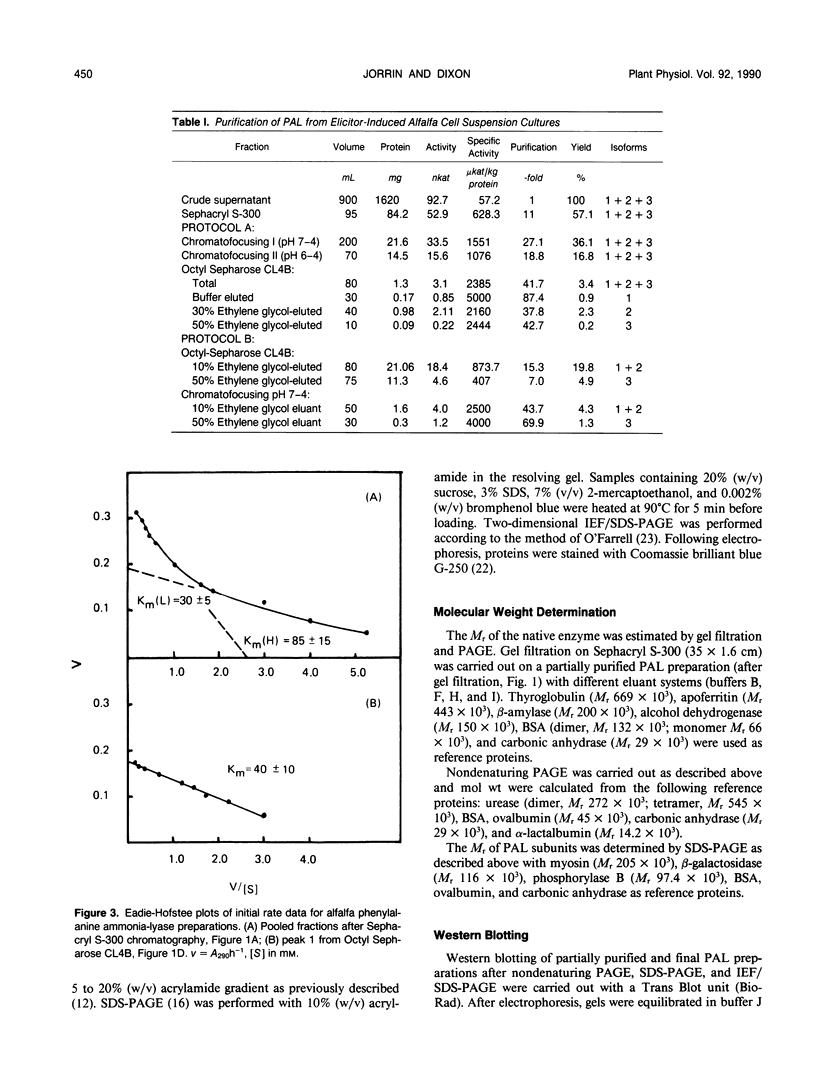
l-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase has been purified from elicitor-treated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cell suspension cultures using two protocols based on different sequences of chromatofocusing and hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Three distinct forms of the intact enzyme were separated on the basis of affinity for Octyl-Sepharose, with isoelectric points in the range pH 5.1 to 5.4. The native enzyme was a tetramer of Mr 311,000; the intact subunit Mr was about 79,000, although polypeptides of Mr 71,000, 67,000 and 56,000, probably arising from degradation of the intact subunit, were observed in all preparations. Two-dimensional gel analysis revealed the presence of several subunit isoforms of differing isoelectric points. The purified isoforms of the native enzyme had different Km values for l-phenylalanine in the range 40 to 110 micromolar, although mixtures of the forms in crude preparations exhibited apparent negative rate cooperativity. The enzyme activity was induced approximately 16-fold within 6 hours of exposure of alfalfa cells to a fungal elicitor or yeast extract. Analysis by hydrophobic interaction chromatography revealed different proportions of the different active enzyme isoforms, depending upon either time after elicitation or the elicitor used. The elicitor-induced increase in enzyme activity was associated with increased translatable phenylalanine ammonia-lyase mRNA activity in the polysomal fraction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolwell G. P., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Schuch W., Lamb C. J., Dixon R. A. L-Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Phaseolus vulgaris. Characterisation and differential induction of multiple forms from elicitor-treated cell suspension cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):411–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08941.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalkin K., Edwards R., Edington B., Dixon R. A. Stress Responses in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): I. Induction of Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis and Hydrolytic Enzymes in Elicitor-Treated Cell Suspension Cultures. Plant Physiol. 1990 Feb;92(2):440–446. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Dey P. M., Lamb C. J. Phytoalexins: enzymology and molecular biology. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;55:1–136. doi: 10.1002/9780470123010.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Stimulation of de novo synthesis of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in relation to phytoalexin accumulation in Colletotrichum lindemuthianum elicitor-treated cell suspension cultures of french bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 3;586(3):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K., Cramer C. L., Bolwell G. P., Dixon R. A., Schuch W., Lamb C. J. Rapid transient induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase mRNA in elicitor-treated bean cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6731–6735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P. C., Mehta F. S., Pindborg J. J., Aghi M. B., Bhonsle R. B., Daftary D. K., Murti P. R., Shah H. T., Sinor P. N. Intervention study for primary prevention of oral cancer among 36 000 Indian tobacco users. Lancet. 1986 May 31;1(8492):1235–1239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton M. A., Dixon R. A., Hahlbrock K., Lamb C. J. Elicitor induction of mRNA activity. Rapid effects of elicitor on phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase mRNA activities in bean cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):131–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton M. A., Lamb C. J. Transcriptional activation of plant defense genes by fungal elicitor, wounding, and infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):335–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang X. W., Dron M., Cramer C. L., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Differential regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase genes during plant development and by environmental cues. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14486–14492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhoff V., Arold N., Taube D., Ehrhardt W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jun;9(6):255–262. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read S. M., Northcote D. H. Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue G dye-binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J., Betz B., Hahlbrock K. Light-induced enzyme synthesis in cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Demonstration in a heterologous cell-free system of rapid changes in the rate of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):527–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]