Abstract
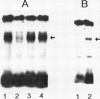
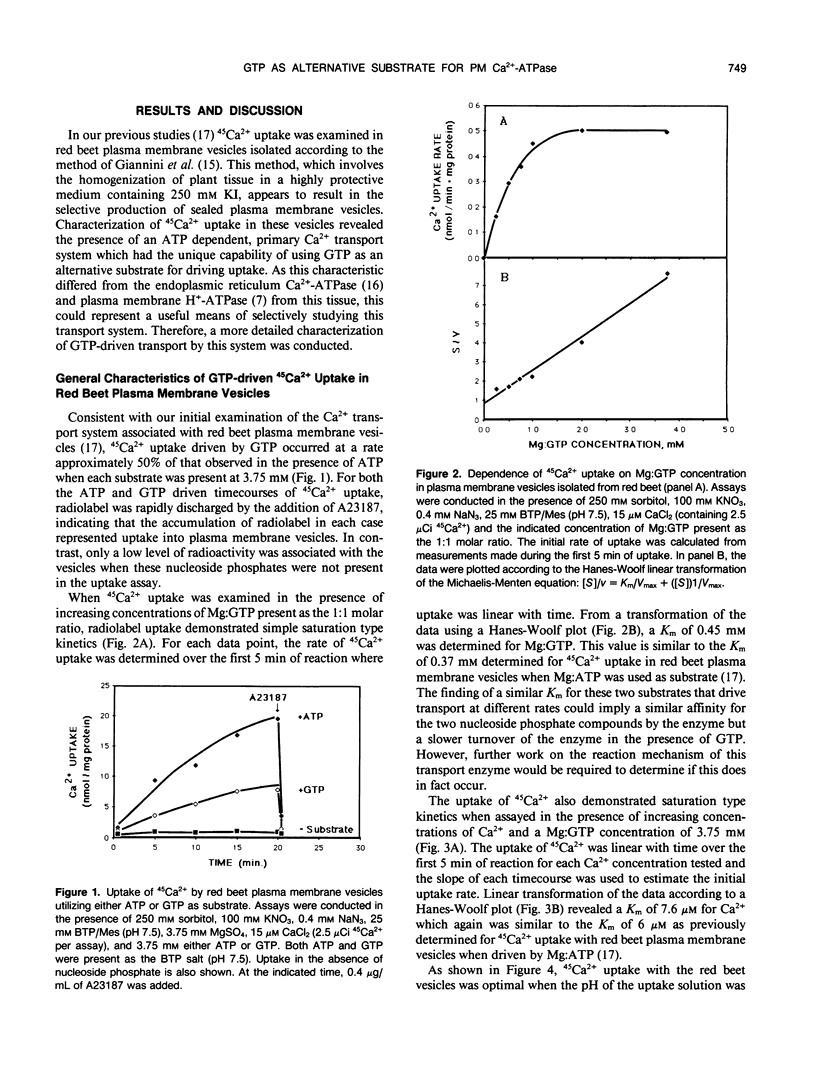
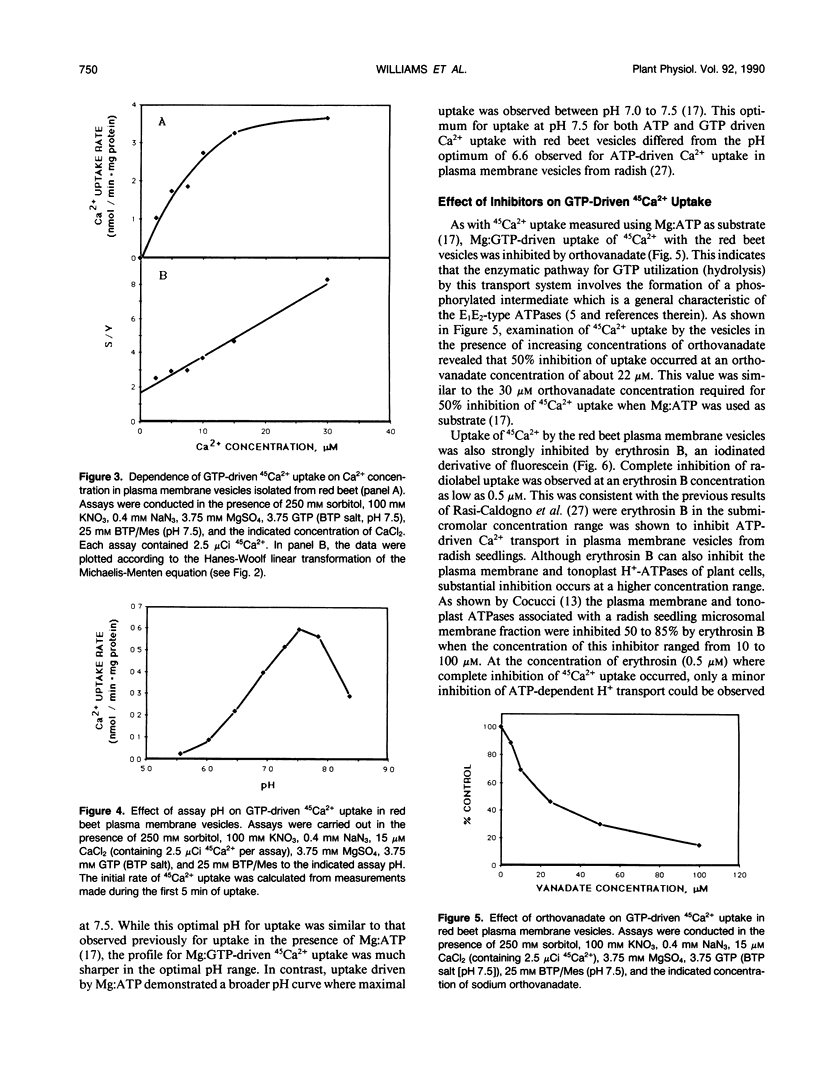
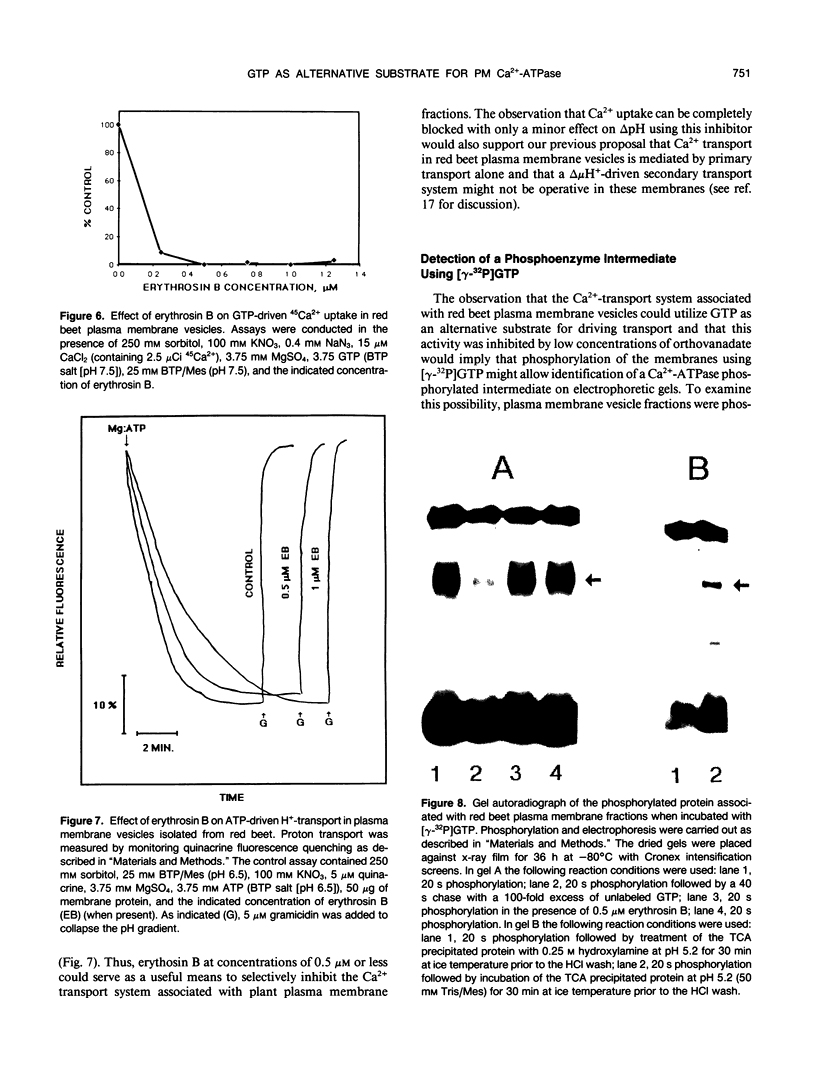
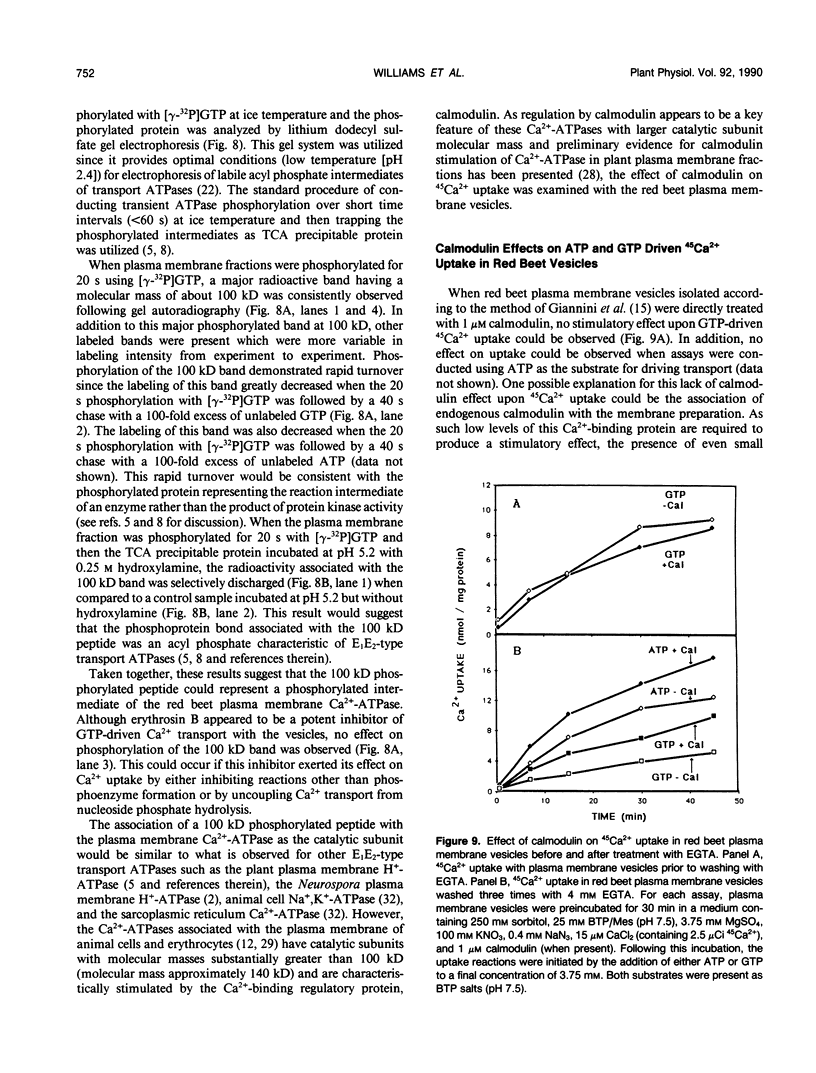
The GTP-driven component of Ca2+ uptake in red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) plasma membrane vesicles was further characterized to confirm its association with the plasma membrane Ca2+-translocating ATPase and assess its utility as a probe for this transport system. Uptake of 45Ca2+ in the presence of GTP demonstrated similar properties to those previously observed for red beet plasma membrane vesicles utilizing ATP with respect to pH optimum, sensitivity to orthovanadate, dependence on Mg:substrate concentration and dependence on Ca2+ concentration. Calcium uptake in the presence of GTP was also strongly inhibited by erythrosin B, a potent inhibitor of the plant plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase. Furthermore, after treatment with EGTA to remove endogenous calmodulin, the stimulation of 45Ca2+-uptake by exogenous calmodulin was nearly equivalent in the presence of either ATP or GTP. Taken together these results support the proposal that GTP-driven 45Ca2+ uptake represents the capacity of the plasma membrane Ca2+-translocating ATPase to utilize this nucleoside triphosphate as an alternative substrate. When plasma membrane vesicles were phosphorylated with [γ-32P]-GTP, a rapidly turning over, 100 kilodalton phosphorylated peptide was observed which contained an acyl-phosphate linkage. While it is proposed that this peptide could represent the catalytic subunit of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase, it is noted that this molecular weight is considerably lower than the 140 kilodalton size generally observed for plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPases present in animal cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumwald E., Poole R. J. Kinetics of Ca/H Antiport in Isolated Tonoplast Vesicles from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Mar;80(3):727–731. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Bowman E. J. H+-ATPases from mitochondria, plasma membranes, and vacuoles of fungal cells. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(2):83–97. doi: 10.1007/BF01871190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Leonard R. T. Phosphorylation of the adenosine triphosphatase in a deoxycholate-treated plasma membrane fraction from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1459–1464. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Poole R. J. Plasma membrane ATPase of red beet forms a phosphorylated intermediate. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):507–512. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckhout T. J. Characterization of Ca Transport in Purified Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Vesicles from Lepidium sativum L. Roots. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):962–967. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini J. L., Gildensoph L. H., Briskin D. P. Selective production of sealed plasma membrane vesicles from red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) storage tissue. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 1;254(2):621–630. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini J. L., Gildensoph L. H., Reynolds-Niesman I., Briskin D. P. Calcium Transport in Sealed Vesicles from Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Storage Tissue : I. Characterization of a Ca-Pumping ATPase Associated with the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Plant Physiol. 1987 Dec;85(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannini J. L., Ruiz-Cristin J., Briskin D. P. Calcium Transport in Sealed Vesicles from Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Storage Tissue : II. Characterization of Ca Uptake into Plasma Membrane Vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1987 Dec;85(4):1137–1142. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J., Marmé D. ATP-dependent Ca uptake into plant membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1232–1236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew R. R., Briskin D. P., Wyse R. E. Ca uptake by endoplasmic reticulum from zucchini hypocotyls : the use of chlorotetracycline as a probe for ca uptake. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):47–53. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtner R., Wolf H. U. Dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis at low pH values and low temperatures. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):759–761. doi: 10.1042/bj1810759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. J., Briskin D. P., Krátký Z., Johnstone R. M. Density gradient localization of plasma membrane and tonoplast from storage tissue of growing and dormant red beet : characterization of proton-transport and ATPase in tonoplast vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):549–556. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium messenger system in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1987;6(1):47–103. doi: 10.1080/07352688709382247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasi-Caldogno F., Pugliarello M. C., De Michelis M. I. The Ca-Transport ATPase of Plant Plasma Membrane Catalyzes a nH/Ca Exchange. Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):994–1000. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker K. S., Sze H. A Ca/H Antiport System Driven by the Proton Electrochemical Gradient of a Tonoplast H-ATPase from Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Dec;79(4):1111–1117. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]