Abstract
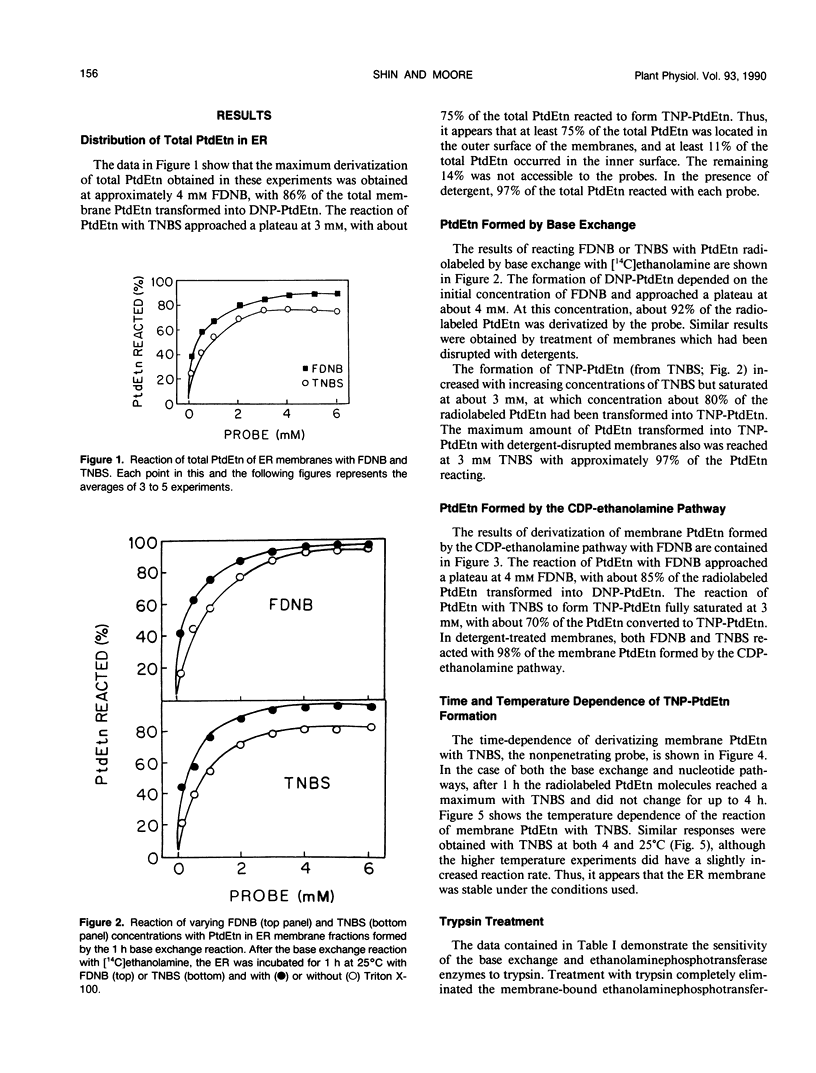
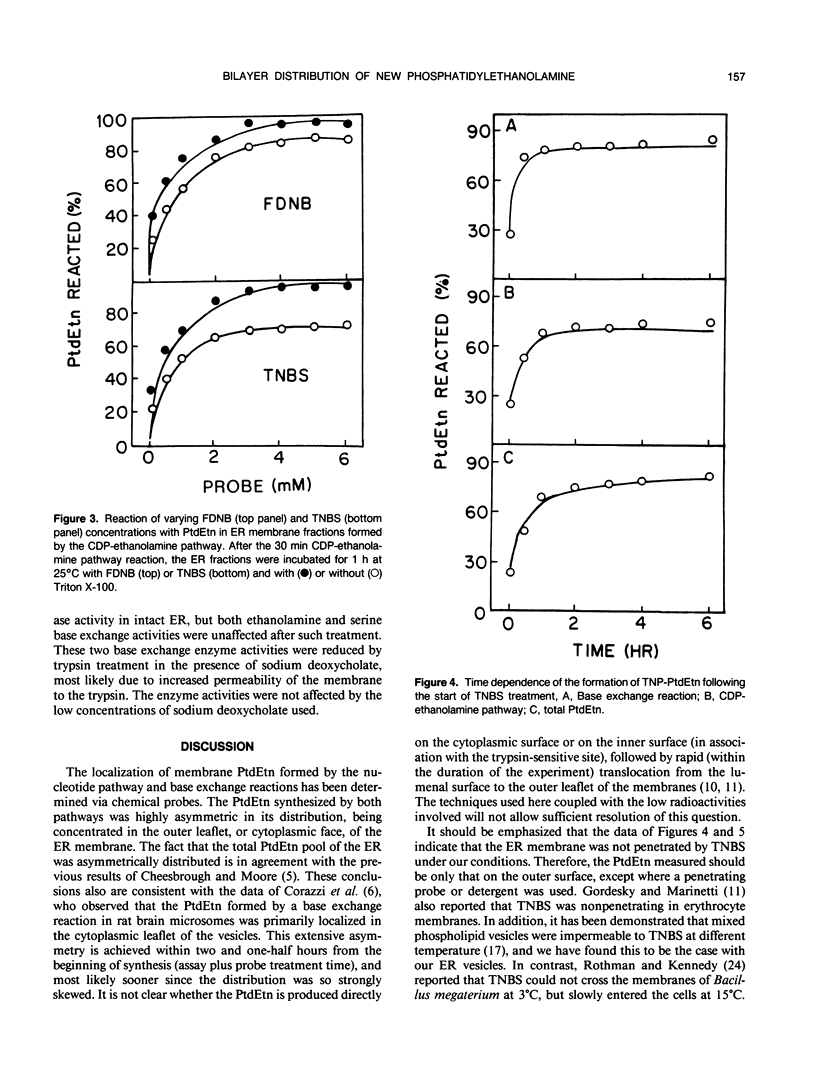
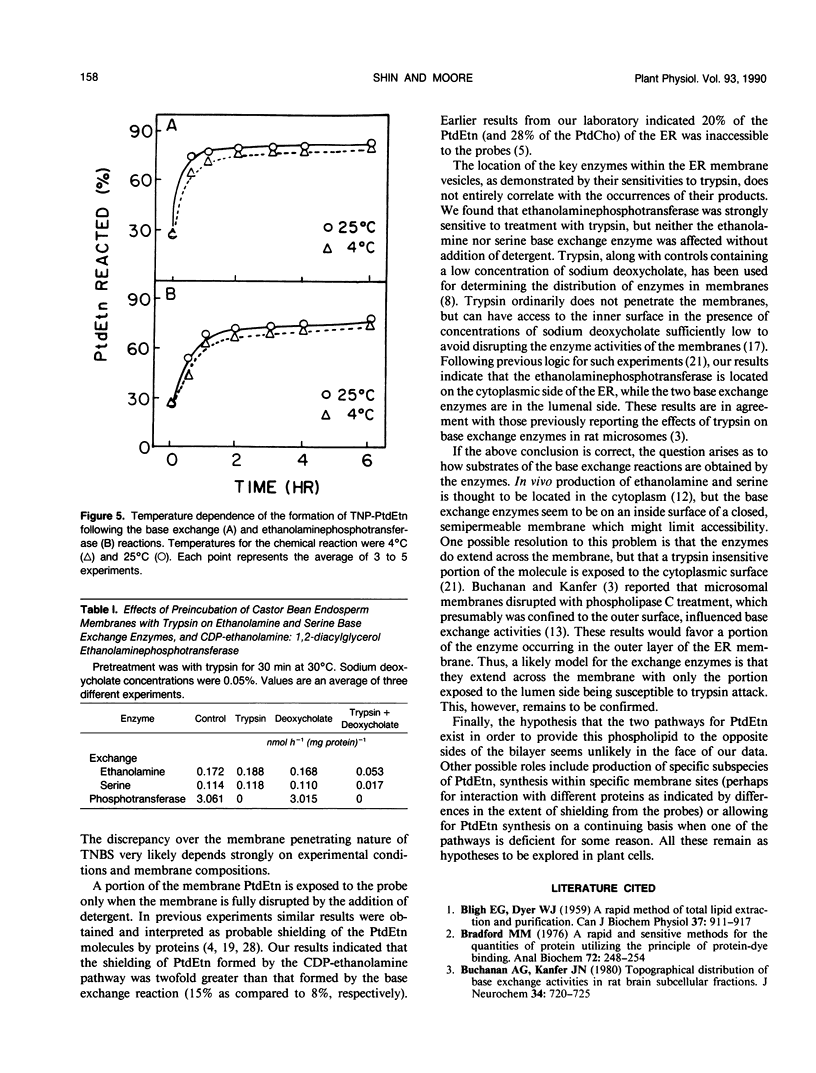
The bilayer distribution of phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) in the endoplasmic reticulum of castor bean (Ricinus communis L. var Hale) endosperm following synthesis by both the CDP-ethanolamine: 1,2-diacylglycerol ethanolaminephosphotransferase and ethanolamine base exchange reactions have been studied. Two chemical probes, 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (FDNB) and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS), which covalently bind to the free amino groups, were utilized. The endoplasmic reticulum membranes were impermeable to TNBS at 4 and 25°C, but were permeable to FDNB at both temperatures. FDNB treatment of the PtdEtn from the base exchange reacted with 92% of the PtdEtn, while 80% of the lipid reacted with TNBS. Thus, at least 80% of the PtdEtn synthesized by the base exchange reaction was localized in the outer leaflet of the membrane, with about 12% occurring on the inner leaflet and about 8% being inaccessible. For PtdEtn formed by the CDP-ethanolamine pathway, 85% reacted with FDNB and 70% with TNBS, indicating that at least 70% was produced to the cytoplasmic face of the ER and 15% to the lumen side. The remainder was inaccessible to the probes. The sensitivity to trypsin of the two reactions also was tested. The ethanolamine base exchange enzyme, as well as that for l-serine exchange, retained activity following exposure to trypsin, but the activity of ethanolaminephosphotransferase disappeared after such treatment. This indicates that both base exchange enzymes are exposed to the lumenal side of the ER, while CDP-ethanolamine: 1,2-diacylglycerol ethanolaminephosphotransferase is exposed on the outer or cytoplasmic side. These results are discussed with respect to the final phospholipid distributions and the presumed sources of the water-soluble substrates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan A. G., Kanfer J. N. Topographical distribution of base exchange activities in rat brain subcellular fractions. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):720–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheesbrough T. M., Moore T. S. Transverse Distribution of Phospholipids in Organelle Membranes from Ricinus communis L. var. Hale Endosperm: MITOCHONDRIA AND GLYOXYSOMES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jun;65(6):1076–1080. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.6.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazzi L., Binaglia L., Roberti R., Freysz L., Arienti G., Porcellati G. Compartmentation of membrane phosphatidylethanolamine formed by base-exchange reaction in rat brain microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 21;730(1):104–110. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90322-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawidowicz E. A. Dynamics of membrane lipid metabolism and turnover. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:43–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePierre J. W., Ernster L. Enzyme topology of intracellular membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:201–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etemadi A. H. Membrane asymmetry. A survey and critical appraisal of the methodology. II. Methods for assessing the unequal distribution of lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 31;604(3):423–475. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90579-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Scott N. A. Betaine Synthesis from Radioactive Precursors in Attached, Water-stressed Barley Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):342–348. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Miller N., Kemp P., Laser H. The activation of phospholipase C from Clostridium Welchii by quinine: an absolute requirement for calcium ions. Chem Phys Lipids. 1975 Sep;15(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(75)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., McConnell H. M. Inside-outside transitions of phospholipids in vesicle membranes. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1111–1120. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Debey P., Sabatini D. D. Selective release of content from microsomal vesicles without membrane disassembly. I. Permeability changes induced by low detergent concentrations. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):436–462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman B. J. Determination of molecular asymmetry in the phosphatidylethanolamine surface distribution in mixed phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2844–2848. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. M., Kagawa T., Moore T. S., Beevers H. Endoplasmic reticulum as the site of lecithin formation in castor bean endosperm. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):659–667. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti G. V., Love R. Differential reaction of cell membrane phospholipids and proteins with chemical probes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1976 Jul;16(4):239–254. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(76)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. S. Phosphatidylserine synthesis in castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1975 Aug;56(2):177–180. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O. S., Dallner G. Enzyme and phospholipid asymmetry in liver microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):568–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O. S., Dallner G. Transverse asymmetry of phospholipids in subcellular membranes of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 21;464(2):453–458. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Kennedy E. P. Asymmetrical distribution of phospholipids in the membrane of Bacillus megaterium. J Mol Biol. 1977 Mar 5;110(3):603–618. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Lenard J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):743–753. doi: 10.1126/science.402030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S., Moore T. S. Phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis by castor bean endosperm : a base exchange reaction. Plant Physiol. 1990 May;93(1):148–153. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparace S. A., Wagner L. K., Moore T. S. Phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis in castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):922–925. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale M. G. Localization of the amino phospholipids in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes revealed by trinitrobenzenesulfonate and fluorodinitrobenzene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 15;471(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., Kastelijn D., van Deenen L. L. The asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the human red cell membrane. A combined study using phospholipases and freeze-etch electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):178–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


