Abstract
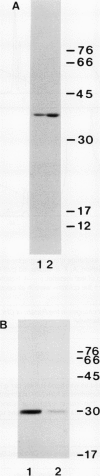
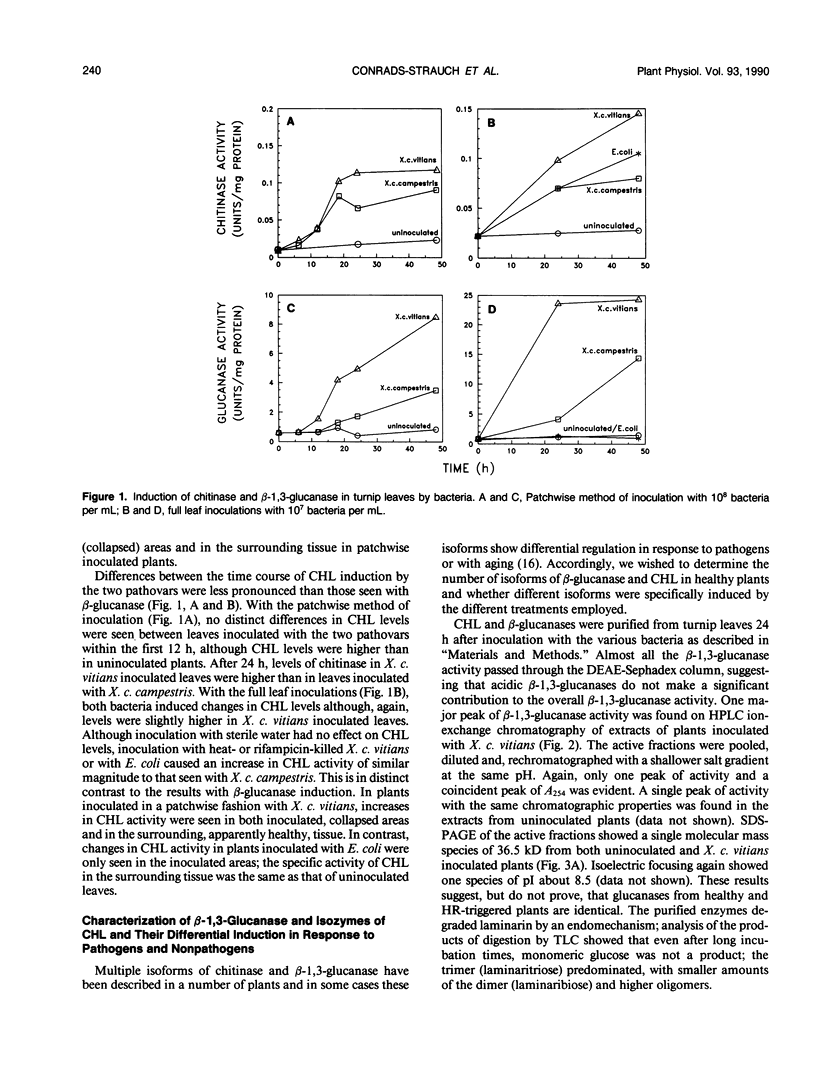
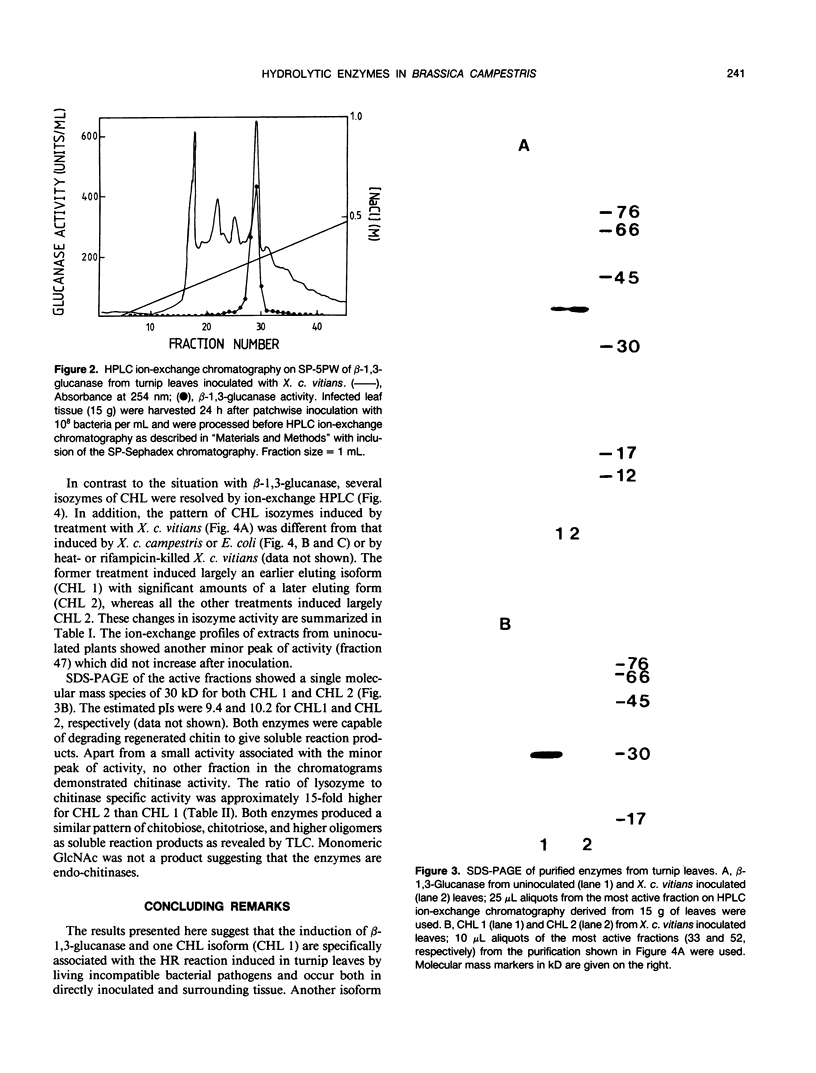
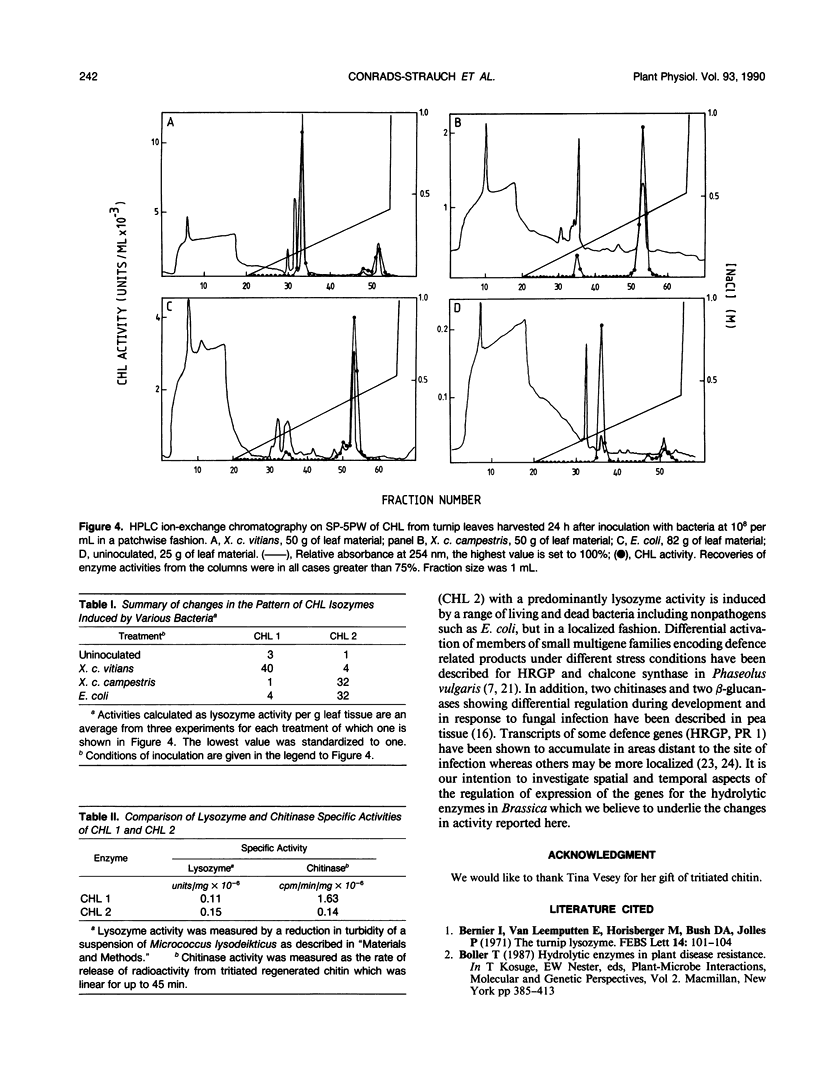
Inoculation of mature leaves of turnip (Brassica campestris) with the incompatible Xanthomonas campestris pv vitians resulted in the induction of β-1,3-glucanase and chitinase/lysozyme (CHL) activity. No increase in the basal activity of β-1,3-glucanase was observed after inoculation of leaves with heat- or rifampicin-killed X. c. vitians, Escherichia coli, or sterile water. Inoculation with the compatible X. campestris pv campestris resulted in a slower induction of glucanase than that seen with X. c. vitians. In contrast, all bacteria caused an induction of CHL activity. One major β-1,3-glucanase (molecular mass 36.5 kilodaltons, isoelectric point [pl] ~8.5) was purified from both inoculated and untreated leaves by ion-exchange chromatography. The enzyme degraded laminarin by an endo-glycolytic mechanism. Two major CHL isozymes (CHL 1 and CHL 2, molecular mass 30 kilodaltons and pl 9.4 and 10.2, respectively) were purified from X. c. vitians inoculated leaves by affinity chromatography on a chitin column followed by ion-exchange chromatography. Both enzymes degraded chitin by an endo-glycolytic mechanism although the ratio of lysozyme to chitinase specific activities for CHL 1 and CHL2 were different. The induction of CHL 1 was associated with the hypersensitive reaction caused by X. c. vitians whereas all other treatments induced largely CHL 2.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernier I., Van Leemputten E., Horisberger M., Bush D. A., Jollès P. The turnip lysozyme. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr;14(2):100–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bounias M. N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride as a new reagent for nanomole quantification of sugars on thin-layer plates by a mathematical calibration process. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin D. R., Sauer N., Lamb C. J. Differential regulation of a hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein gene family in wounded and infected plants. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4337–4344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. A., Bell J. N., Boller T., Lamb C. J. Chitinase cDNA cloning and mRNA induction by fungal elicitor, wounding, and infection. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):182–186. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joosten M. H., De Wit P. J. Identification of Several Pathogenesis-Related Proteins in Tomato Leaves Inoculated with Cladosporium fulvum (syn. Fulvia fulva) as 1,3-beta-Glucanases and Chitinases. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):945–951. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kombrink E., Schröder M., Hahlbrock K. Several "pathogenesis-related" proteins in potato are 1,3-beta-glucanases and chitinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):782–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Hadwiger L. A., Boller T. Antifungal Hydrolases in Pea Tissue : I. Purification and Characterization of Two Chitinases and Two beta-1,3-Glucanases Differentially Regulated during Development and in Response to Fungal Infection. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jun;87(2):325–333. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Mauch-Mani B., Boller T. Antifungal Hydrolases in Pea Tissue : II. Inhibition of Fungal Growth by Combinations of Chitinase and beta-1,3-Glucanase. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):936–942. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molano J., Durán A., Cabib E. A rapid and sensitive assay for chitinase using tritiated chitin. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson E. F., Dannelly H. K., Malloy P. J., Reeves H. C. Rapid isoelectric focusing in a vertical polyacrylamide minigel system. Anal Biochem. 1987 Dec;167(2):290–294. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder T. B., Hedrick S. A., Bell J. N., Liang X. W., Clouse S. D., Lamb C. J. Organization and differential activation of a gene family encoding the plant defense enzyme chalcone synthase in Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):219–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00325687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somssich I. E., Schmelzer E., Kawalleck P., Hahlbrock K. Gene structure and in situ transcript localization of pathogenesis-related protein 1 in parsley. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):93–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00333403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]