Abstract
Background
Quantitative interstitial abnormalities (QIA) are an automated computed tomography (CT) finding of early parenchymal lung disease, associated with worse lung function, reduced exercise capacity, increased respiratory symptoms, and death. The metabolomic perturbations associated with QIA are not well known. We sought to identify plasma metabolites associated with QIA in smokers. We also sought to identify shared and differentiating metabolomics features between QIA and emphysema, another smoking-related advanced radiographic abnormality.
Methods
In 928 former and current smokers in the Genetic Epidemiology of COPD cohort, we measured QIA and emphysema using an automated local density histogram method and generated metabolite profiles from plasma samples using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (Metabolon). We assessed the associations between metabolite levels and QIA using multivariable linear regression models adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, pack-years, and inhaled corticosteroid use, at a Benjamini–Hochberg False Discovery Rate p-value of ≤ 0.05. Using multinomial regression models adjusted for these covariates, we assessed the associations between metabolite levels and the following CT phenotypes: QIA-predominant, emphysema-predominant, combined-predominant, and neither- predominant. Pathway enrichment analyses were performed using MetaboAnalyst.
Results
We found 85 metabolites significantly associated with QIA, with overrepresentation of the nicotinate and nicotinamide, histidine, starch and sucrose, pyrimidine, phosphatidylcholine, lysophospholipid, and sphingomyelin pathways. These included metabolites involved in inflammation and immune response, extracellular matrix remodeling, surfactant, and muscle cachexia. There were 75 metabolites significantly different between QIA-predominant and emphysema-predominant phenotypes, with overrepresentation of the phosphatidylethanolamine, nicotinate and nicotinamide, aminoacyl-tRNA, arginine, proline, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate pathways.
Conclusions
Metabolomic correlates may lend insight to the biologic perturbations and pathways that underlie clinically meaningful quantitative CT measurements like QIA in smokers.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12931-023-02576-2.
Keywords: Lung Diseases, Interstitial; Metabolomics; Pulmonary Emphysema; Tomography, X-Ray Computed; Cross-Sectional Studies
Background
Smokers without interstitial lung disease or emphysema may have quantitative interstitial abnormalities (QIA), which are subtle parenchymal changes on chest computed tomography (CT) scans detected by an automated method [1]. The presence and progression of QIA (also called interstitial features in prior work) are associated with worse lung function, reduced exercise capacity, increased respiratory symptoms, and death [1–4]. Risk factors for QIA include advanced age, current smoking status, the MUC5B polymorphism, and female sex [1–4]. Given its shared risk and clinical factors to both idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), QIA may be a precursor to advanced parenchymal diseases in some patients [5, 6], for whom existing therapies slow the future development or decrease symptoms of disease but do not reverse the parenchymal damage [7–10]. QIA may be a useful target for early intervention, but the biomarkers associated with QIA remain unclear.
Metabolomics may be useful for understanding the biochemical perturbations associated with an early stage of lung disease like QIA. Metabolomics is the field of the identification and measurement of small molecules (≤ 1500 Daltons) in a single biological specimen [11]. Endogenous metabolites are end-products of enzymatic reactions and linked by metabolic pathways, making them downstream of genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics; they can also be derived from food, medications, microbiota, and the environment [12, 13]. Metabolism may be perturbed in disease and can directly reflect the underlying pathogenic mechanisms [12].
Prior work has shown that serum and plasma metabolomic analyses are useful in the study of established and advanced lung diseases. Serum and plasma metabolomics have been used to discriminate healthy controls from those with COPD or IPF [14, 15] and to detect the presence and extent of radiographic emphysema and other measures of disease severity [16–18]. Systemic metabolomics may similarly reflect and provide biochemical insight into more subtle parenchymal injury like QIA.
In this study, we used a global metabolomics assay that captures a broad range of chemical classes of metabolites to identify those associated with QIA in a well-characterized cohort of ever-smokers. Additionally, given shared risk factors between QIA and quantitative emphysema, we sought to identify shared and differentiating metabolite profiles in QIA-predominant versus emphysema-predominant CT phenotypes.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional cohort study of metabolomics features associated with QIA. The Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) is a prospective observational study of over 10,000 former and current smokers (ever-smokers) aged 45–80 years with at least a 10 pack-year smoking history and no prior history of bronchiectasis or interstitial lung disease (ILD) [19]. Participants self-reporting as Non-Hispanic White or Black were recruited at 21 study centers across the United States. For this study, we used data from questionnaires, chest CT scans, and blood samples collected at the five-year follow up (visit 2) of the study (2013–2017), as previously described [19]. The COPDGene study (NCT00608764) was approved by the institutional review board for ethical review at all 21 participating centers (Additional file 1). All participants provided written informed consent.
Chest CT measurements
We measured QIA and quantitative emphysema in 4,778 participants using a previously-published automated tool [1]. The tool employs a machine learning classifier using local density histograms and distances from the pleural surface to identify the voxels of total CT lung volume as radiologic features. The percentages of total lung volume of reticulation, subpleural lines, ground glass opacities, honeycombing, linear scarring, centrilobular nodules, and other nodularity features were summed to yield the total QIA percent (Fig. 1); panlobular and centrilobular emphysema features were summed to yield total emphysema percent. We used continuous QIA for the primary analysis.
Fig. 1.
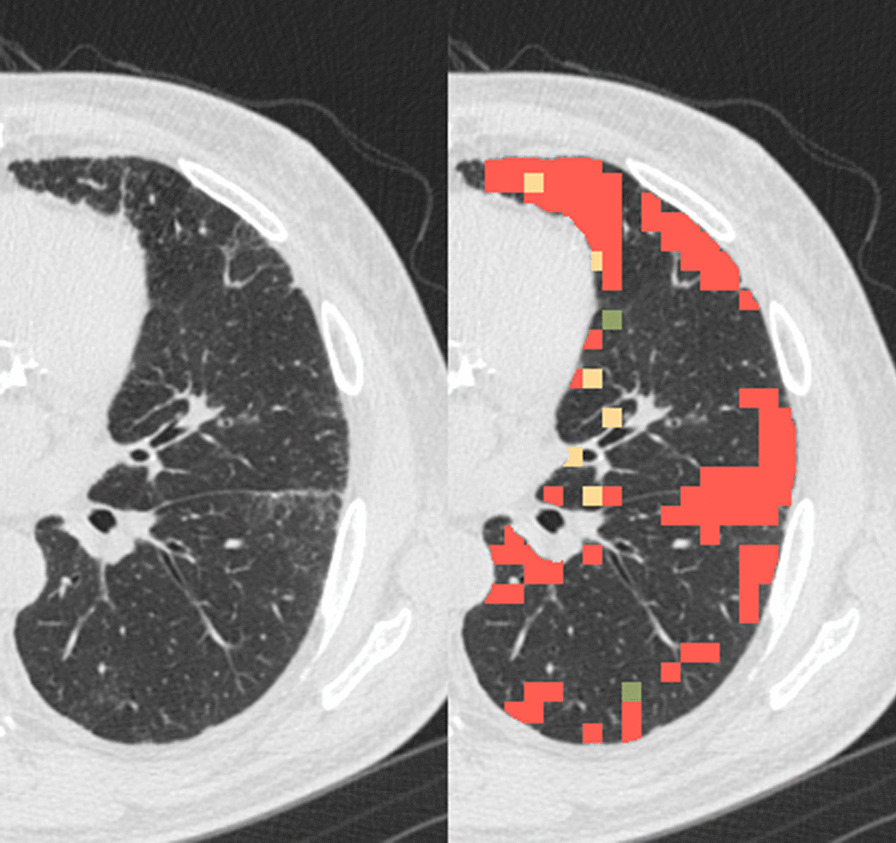
Quantitative interstitial abnormalities (QIA). The left image is an example computed tomography (CT) cut of a left lung, and the right image is the same cut with QIA shaded
Plasma metabolomics measurements
Metabolomics assays were run on plasma samples collected from 1,136 participants from two study centers (National Jewish Health, University of Iowa) at visit 2. This analysis included 928 participants with complete quantitative CT and metabolomics level measurements available (Fig. 2). Plasma samples were profiled using the Metabolon Global Metabolomics Platform (Morrisville, NC), as described previously and in the Additional file 1. [20–22]
Fig. 2.
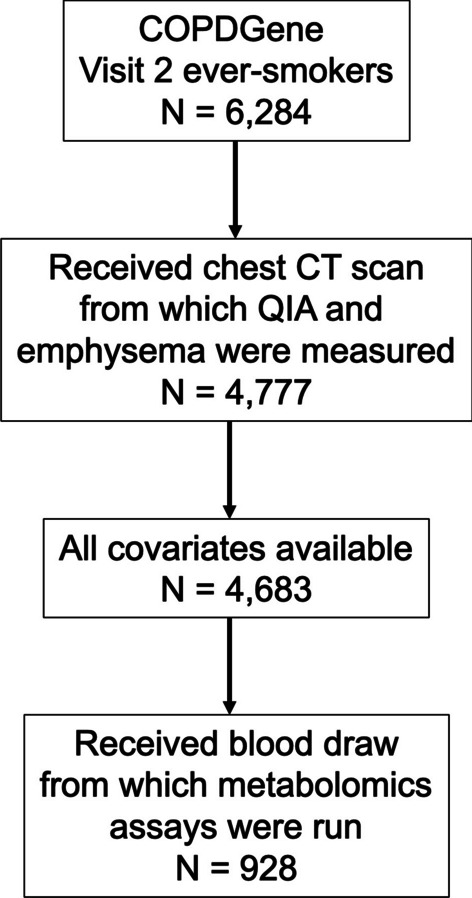
Flow diagram of participants included in the study
Metabolite levels were median scaled within each batch. Of the 1,392 metabolites initially profiled by the Metabolon platform, 397 with > 20% missingness were excluded, as done in prior work, referred as the “80%” rule [23]. Of the remaining 995 metabolites, 237 were quantified but chemically unidentified, and they were not used in our analysis. The remaining 758 named metabolites were used in our analysis. For the 400 metabolites that had ≤ 20% missingness, missing values were imputed using k-nearest neighbor sample imputation (k = 10); 358 metabolites had no values missing. Missingness is an inherent element of metabolomics data, which routinely requires pre-processing such as data reduction and imputation [24]. All values were log2-transformed in preparation for statistical analyses. There were 363 involved in lipid, 180 in amino acid, 32 in nucleotide, 24 in carbohydrate, and 10 in energy metabolism (Additional file 1: Table S1). Additionally, there were 25 cofactors and vitamins, 25 peptides, 96 xenobiotics, and 3 partially-characterized metabolites.
Statistical analyses
We assessed the associations between each metabolite level (individual predictor) and continuous QIA (primary outcome) with univariable linear regression then multivariable linear regression adjusted for age, sex, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, pack-years, and inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) use, using a Benjamini–Hochberg False Discovery Rate (FDR) p-value of ≤ 0.05. Models were adjusted for BMI given obesity perturbs the metabolome, and obesity-related atelectasis may contribute to CT noise [25]. For the secondary analysis, QIA and emphysema were both dichotomized by a cutoff of each measure occupying ≥ 5% or < 5% of the total lung volume; cutoffs were determined based on prior work [1, 26]. We categorized participants into four CT-based phenotypes, defining those with ≥ 5% QIA and < 5% emphysema as QIA-predominant, ≥ 5% QIA and ≥ 5% emphysema as combined-predominant, < 5% QIA and ≥ 5% emphysema as emphysema-predominant, and < 5% QIA and < 5% emphysema as neither-predominant (Additional file 1: Fig. S1). We assessed unadjusted associations between each metabolite level and the CT phenotype (secondary outcome) using analysis of variance (ANOVA), then used multinomial logistic regression adjusted for the covariates listed above, at an FDR of ≤ 0.05, with QIA-predominant used as the reference group. Analyses were performed using R software (version 4.2.2) and implemented using RStudio (version 2022.12.0 + 353). [27, 28]
We performed metabolic pathway enrichment analyses of the significant metabolites using the web platform MetaboAnalyst (V5.0) [29]. L- and D-enantiomer annotations for amino acids were simplified to the L-enantiomer. Metabolites with missing or more than one Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) ID annotations were excluded [30]. The metabolic pathways were mapped to the homo sapiens Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes database (KEGG) [31], then pathway enrichment analyses were performed by global test at an FDR of ≤ 0.05 and topology analyses by relative-betweenness centrality.
Results
The baseline characteristics of the 928 participants in this analysis are shown in Table 1. The participants had mean age of 67.5 ± 8.6 years, were 50.2% male, and were predominantly former smokers. Mean percent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) was 77.8 ± 26.0%, and mean percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC) was 86.6 ± 18.5%. The mean percentage of lung occupied by QIA was 5.0 ± 4.3% and by emphysema was 8.1 ± 16.0%. In the cohort, 223 had QIA-predominant, 109 had combined-predominant, 133 had emphysema-predominant, and 463 had neither-predominant CT phenotypes (Additional file 1: Table S2). The participants in our cohort, when compared to the rest of the COPDGene cohort with CT measurements and covariables but no metabolomics data available, had similar characteristics but were older, with a greater percentage of former smokers and predominantly White in self-reported race (Additional file 1: Table S3).
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics
| N = 928 | |
|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 67.5 ± 8.6 |
| Male | 466 (50.2) |
| Self-reported race | |
| White | 850 (91.6) |
| Black | 78 (8.4) |
| Former Smoker | 688 (74.1) |
| Pack Years, mean ± SD | 44.5 ± 24.3 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 29.0 ± 6.1 |
| Inhaled corticosteroid use | 49 (5.3) |
| Post Bronchodilator FEV1 (L), mean ± SD | 2.0 ± 0.9 |
| Post Bronchodilator FEV1 (percent predicted), mean ± SD | 77.8 ± 26.0 |
| Post Bronchodilator FVC (L), mean ± SD | 3.1 ± 1.0 |
| Post Bronchodilator FVC (percent predicted), mean ± SD | 86.6 ± 18.5 |
| GOLD class | |
| PRISm (reduced FEV1 and FVC, with a FEV1-to-FVC ratio of ≥ 0.7) | 82 (8.8) |
| GOLD 0 | 412 (44.4) |
| GOLD 1 | 97 (10.5) |
| GOLD 2 | 198 (21.4) |
| GOLD 3 | 109 (11.8) |
| GOLD 4 | 29 (3.1) |
| Percentage of Lung Occupied by QIA, mean ± SD | 5.0 ± 4.3 |
| ≥ 5% Percentage of Lung Occupied by QIA | 332 (35.8) |
| Percentage of Lung Occupied by Emphysema, mean ± SD | 8.1 ± 16.0 |
| ≥ 5% Percentage of Lung Occupied by Emphysema | 242 (26.1) |
N(%) unless otherwise specified
FEV1 forced expiratory volume in 1s, FVC forced vital capacity, GOLD Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease, PRISm Preserved ratio impaired spirometry, QIA quantitative interstitial abnormalities
Association of metabolomics with QIA
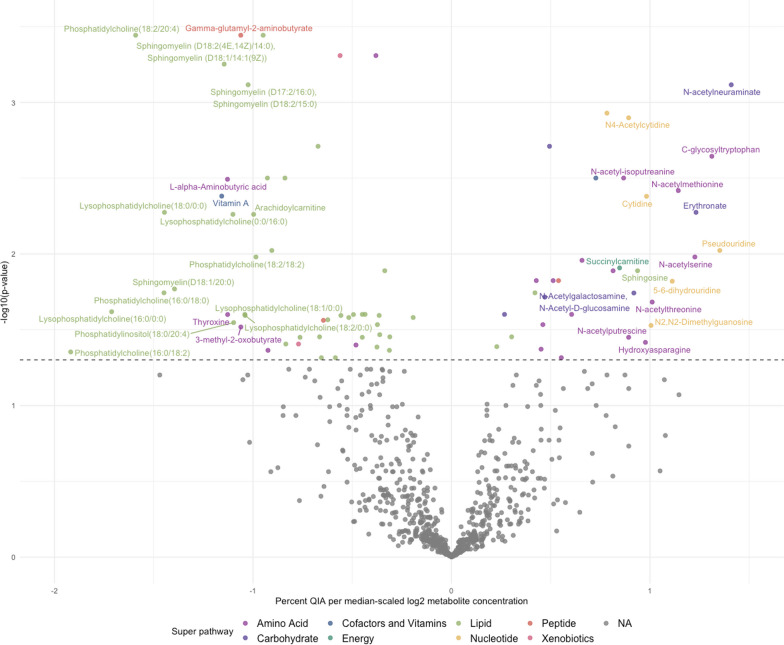
We identified significant associations between 223 metabolites and continuous QIA by univariable linear regression (Additional file 1: Table S4). By multivariable regression, 85 metabolites were significantly associated with QIA (Fig. 3, Additional file 1: Table S5), of which 51 metabolites were negatively-associated and 34 positively-associated with QIA, including 44 (51.8%) lipids and 21 (24.7%) amino acids.
Fig. 3.
Volcano plot of median-scaled, log-transformed metabolites associated with QIA. Metabolites are colored by super pathway if significantly associated with QIA and colored in gray if insignificant (FDR ≤ 0.05)
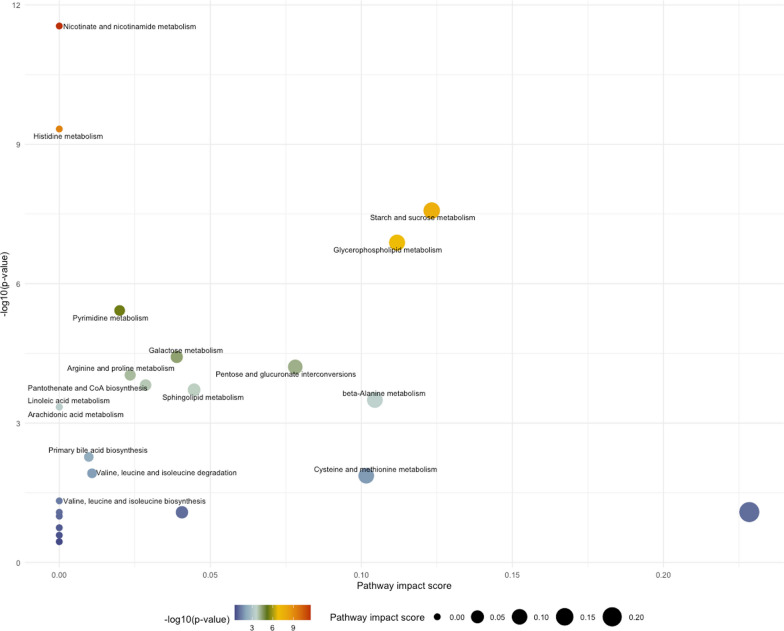
The top 25 positively-associated and 25 negatively-associated metabolites are shown in Table 2. Positively-associated metabolites included the aminosugars N-acetylneuraminate and erythronate, the nucleotide pseudouridine, and the amino acid derivatives C-glycosyl tryptophan and N-acetylserine. Enrichment analysis of these positively-associated metabolites showed overrepresentation of metabolites involved in nicotinate and nicotinamide, histidine, starch and sucrose, and pyrimidine pathways. Negatively-associated metabolites included eight phosphatidylcholines, seven lysophospholipids, and four sphingomyelins; some of these metabolites were represented in the glycerophospholipid and sphingolipid pathways that were significant in the enrichment analysis (Table 3, Fig. 4).
Table 2.
The 25 metabolites that are most positively-associated and 25 metabolites that are most negatively-associated with quantitative interstitial abnormalities in multivariable linear regression models
| Metabolite | HMDB ID* | Percent QIA per unit metabolite, mean [CI]† | FDR p-value | Metabolon class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positively-associated with QIA | ||||
| N-acetylneuraminate | 0000230 |
1.41 [0.80 to 2.02] |
< 0.001 |
Carbohydrate; Aminosugar Metabolism |
| Pseudouridine | 0000767 |
1.35 [0.61 to 2.09] |
0.009 |
Nucleotide; Pyrimidine Metabolism, Uracil containing |
| C-glycosyltryptophan | 0240296 |
1.31 [0.69 to 1.93] |
0.002 |
Amino Acid; Tryptophan Metabolism |
| Erythronate | 0000613 |
1.23 [0.59 to 1.87] |
0.005 |
Carbohydrate; Aminosugar Metabolism |
| N-acetylserine | 0002931 |
1.23 [0.55 to 1.90] |
0.001 |
Amino Acid; Glycine, Serine and Threonine Metabolism |
| N-acetyl-L-methionine | 0011745 |
1.14 [0.57 to 1.72] |
0.004 |
Amino Acid; Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism |
| 5–6-Dihydrouridine | 0000497 |
1.11 [0.46 to 1.76] |
0.015 |
Nucleotide; Pyrimidine Metabolism, Uracil containing |
| N-acetylthreonine | 0062557 |
1.01 [0.40 to 1.62] |
0.021 |
Amino Acid; Glycine, Serine and Threonine Metabolism |
| N2, N2-Dimethylguanosine | 0004824 |
1.01 [0.35 to 1.66] |
0.030 |
Nucleotide; Purine Metabolism, Guanine containing |
| Cytidine | 0000089 |
0.98 [0.48 to 1.48] |
0.004 |
Nucleotide; Pyrimidine Metabolism, Cytidine containing |
| Hydroxyasparagine | 0341329 |
0.98 [0.32 to 1.64] |
0.038 |
Amino Acid; Alanine and Aspartate Metabolism |
| Sphingosine | 0000252 |
0.94 [0.40 to 1.47] |
0.013 |
Lipid; Sphingosines |
|
N-Acetylgalactosamine, N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine‡ |
0000212, 000021‡ |
0.92 [0.37 to 1.47] |
0.018 |
Carbohydrate; Aminosugar Metabolism |
| N4-Acetylcytidine | 0005923 |
0.89 [0.49 to 1.30] |
0.001 |
Nucleotide; Pyrimidine Metabolism, Cytidine containing |
| N-Acetylputrescine | 0002064 |
0.89 [0.30 to 1.49] |
0.035 |
Amino Acid; Polyamine Metabolism |
| N-acetyl-isoputreanine |
0.87 [0.44 to 1.29] |
0.003 |
Amino Acid; Polyamine Metabolism |
|
| Succinylcarnitine | 0061717 |
0.85 [0.37 to 1.32] |
0.012 |
Energy; TCA Cycle |
| 1-Methyl-4-imidazoleacetate | 0002820 |
0.81 [0.35 to 1.28] |
0.013 |
Amino Acid; Histidine Metabolism |
| 3-ureido-Propionate | 0000026 |
0.78 [0.43 to 1.14] |
0.001 |
Nucleotide; Pyrimidine Metabolism, Uracil containing |
| Quinolinate | 0000232 |
0.73 [0.37 to 1.08] |
0.003 |
Cofactors and Vitamins; Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism |
| Acisoga | 0061384 |
0.66 [0.29 to 1.02] |
0.011 |
Amino Acid; Polyamine Metabolism |
| 5-(galactosylhydroxy)-L-lysine |
0.61 [0.23 to 0.98] |
0.025 |
Amino Acid; Lysine Metabolism |
|
| N-acetyltaurine | 0240253 |
0.55 [0.16 to 0.94] |
0.048 |
Amino Acid; Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism |
| Phenylacetylglutamine | 0006344 |
0.54 [0.23 to 0.85] |
0.015 |
Peptide; Acetylated Peptides |
| 1-Carboxyethyltyrosine |
0.51 [0.22 to 0.81] |
0.015 |
Amino Acid; Tyrosine Metabolism |
|
| Negatively-associated with QIA | ||||
| Phosphatidylcholine (18:0/18:2) | 0008039 |
− 2.09 [− 3.26 to − 0.91] |
0.013 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylcholine (PC) |
| Phosphatidylcholine (16:0/18:2) | 0007973 |
− 1.92 [− 3.25 to − 0.59] |
0.044 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylcholine (PC) |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (16:0/0:0) | 0010382 |
− 1.71 [− 2.76 to − 0.66] |
0.024 |
Lipid; Lysophospholipid |
| Phosphatidylcholine (18:2/20:4) | 0008147 |
− 1.59 [− 2.21 to − 0.97] |
< 0.001 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylcholine (PC) |
| Phosphatidylcholine (16:0/18:0) | 0007970 |
− 1.45 [− 2.31 to − 0.59] |
0.018 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylcholine (PC) |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (18:0/0:0) | 0010384 |
− 1.45 [− 2.19 to − 0.70] |
0.005 |
Lipid; Lysophospholipid |
| Sphingomyelin (D18:1/20:0) | 0012102 |
− 1.40 [− 2.22 to − 0.57] |
0.017 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
| Vitamin A | 0000305 |
− 1.16 [− 1.74 to − 0.57] |
0.004 |
Cofactors and Vitamins; Vitamin A Metabolism |
|
Sphingomyelin (D18:2(4E,14Z)/14:0), Sphingomyelin (D18:1/14:1(9Z))‡ |
0240637, 0240612‡ |
− 1.15 [− 1.63 to − 0.66] |
< 0.001 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
| Thyroxine | 0000248 |
− 1.13 [− 1.83 to − 0.42] |
0.025 |
Amino Acid; Tyrosine Metabolism |
| L-alpha-Aminobutyric acid | 0000452 |
− 1.13 [− 1.69 to − 0.57] |
0.003 |
Amino Acid; Glutathione Metabolism |
| Phosphatidylinositol (18:0/20:4) | 0009815 |
− 1.10 [− 1.80 to − 0.39] |
0.028 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylinositol (PI) |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (0:0/16:0) | 0061702 |
− 1.10 [− 1.68 to − 0.53] |
0.005 |
Lipid; Lysophospholipid |
| 3-methyl-2-oxobutyrate | 0000019 |
− 1.06 [− 1.75 to − 0.37] |
0.030 |
Amino Acid; Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine Metabolism |
| Gamma-glutamyl-2-aminobutyrate |
− 1.06 [− 1.48 to − 0.64] |
< 0.001 |
Peptide; Gamma-glutamyl Amino Acid |
|
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (18:1/0:0) | 0002815 |
− 1.04 [− 1.69 to − 0.39] |
0.025 |
Lipid; Lysophospholipid |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (18:2/0:0) | 0010386 |
− 1.04 [− 1.69 to − 0.39] |
0.025 |
Lipid; Lysophospholipid |
|
Sphingomyelin (D17:2/16:0) Sphingomyelin (D18:2/15:0)‡ |
0240677 |
− 1.02 [− 1.47 to − 0.58] |
< 0.001 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
| Arachidoylcarnitine | 0006460 |
− 1.00 [− 1.52 to − 0.48] |
0.005 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Long Chain Saturated) |
| Phosphatidylcholine (18:2/18:2) | 0008138 |
− 0.98 [− 1.53 to − 0.44] |
0.010 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylcholine (PC) |
|
Sphingomyelin (D17:1/14:0), Sphingomyelin (D16:1/15:0)‡ |
− 0.95 [− 1.33 to − 0.57] |
< 0.001 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
|
| Ceramide (D18:2/22:0) |
− 0.93 [− 1.38 to − 0.47] |
0.003 |
Lipid; Ceramides |
|
| Citrulline | 0000904 |
− 0.92 [− 1.56 to − 0.29] |
0.043 |
Amino Acid; Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism |
|
Ceramide (D20:1/18:0), Ceramide (D16:1/22:0), Ceramide (D18:1/20:0)‡ |
0240684, 0240682, 0004951‡ |
− 0.91 [− 1.40 to − 0.41] |
0.009 |
Lipid; Ceramides |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine (24:0/0:0) | 0010405 | − 0.84 [− 1.25 to − 0.43] | 0.003 |
Lipid; Lysophospholipid |
CI 95% confidence interval, FDR Benjamini–Hochberg False Discovery Rate, HMDB Human Metabolome Database, QIA quantitative interstitial abnormalities
*Wishart DS, Guo AC, Oler E, et al., HMDB 5.0: the Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. Jan 7;50(D1):D622–31
†Multivariable regression models adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, pack-years, and inhaled corticosteroid use
‡ Cannot be analytically differentiated
Table 3.
Pathway enrichment analysis of metabolites associated with quantitative interstitial abnormalities
| Pathway* | Total in pathway | Hits | FDR p-value |
Pathway impact value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 15 | 1 | Quinolinate | 6.81E−11 | 0 |
| Histidine metabolism | 16 | 1 | Methylimidazoleacetic acid | 5.61E−09 | 0 |
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | 18 | 2 | Sucrose; Maltose | 2.14E−07 | 0.123 |
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 36 | 2 | Phosphatidylcholine (PC); 1-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (Lysophosphatidylcholine, LPC) | 7.83E−0 | 0.112 |
| Pyrimidine metabolism | 39 | 2 |
3-Ureidopropionate; Cytidine |
1.81E−05 | 0.020 |
| Galactose metabolism | 27 | 1 | Sucrose | 1.50E−04 | 0.039 |
| Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 18 | 1 | D-Xylose | 2.11E−04 | 0.078 |
| Arginine and proline metabolism | 38 | 1 | N-Acetylputrescine | 2.77E−04 | 0.023 |
| Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 19 | 2 |
3-Ureidopropionate; 3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid |
4.05E−04 | 0.029 |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | 21 | 2 | Sphingomyelin; Sphingosine | 4.60E−04 | 0.045 |
| beta-Alanine metabolism | 21 | 1 | 3-Ureidopropionate | 6.93E−04 | 0.104 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | 36 | 1 | Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | 8.32E−04 | 0 |
| Linoleic acid metabolism | 5 | 1 | Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | 8.32E−04 | 0 |
| Primary bile acid biosynthesis | 46 | 1 | Taurochenodeoxycholate | 0.009 | 0.010 |
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | 40 | 1 | 3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid | 0.02 | 0.011 |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 33 | 2 | (S)-2-Aminobutanoate; 2-Oxobutanoate | 0.02 | 0.102 |
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis | 8 | 2 |
3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid; 2-Oxobutanoate |
0.07 | 0 |
| Arginine biosynthesis | 14 | 1 | Citrulline | 0.10 | 0.228 |
| Propanoate metabolism | 23 | 1 | 2-Oxobutanoate | 0.10 | 0.041 |
| Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 33 | 1 | 2-Oxobutanoate | 0.10 | 0 |
| Tyrosine metabolism | 42 | 1 | Thyroxine | 0.12 | 0 |
| alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | 13 | 2 | Phosphatidylcholine (PC); Stearidonic acid | 0.19 | 0 |
| Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 36 | 3 |
Octadecanoic acid; Docosahexaenoic acid; Icosapentaenoic acid |
0.27 | 0 |
| Fatty acid biosynthesis | 47 | 1 | Tetradecanoic acid | 0.36 | 0 |
Abbreviations: FDR = Benjamini–Hochberg False Discovery Rate
*Metabolites with a Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) ID number
Fig. 4.
Scatterplots generated from pathway enrichment analysis in MetaboAnalyst. FDR p-values are on the y-axis and pathway impact values on the x-axis. The size of the plotted point correlates to the pathway impact and color (blue to red) correlates to p-values
Multinomial outcomes of CT phenotypes
Globally amongst the four phenotypes (QIA-predominant, combined-predominant, emphysema-predominant, neither-predominant), 282 metabolites significantly differed by ANOVA. Post-hoc Tukey’s test pairwise comparisons were performed and are shown in Additional file 1: Table S6.
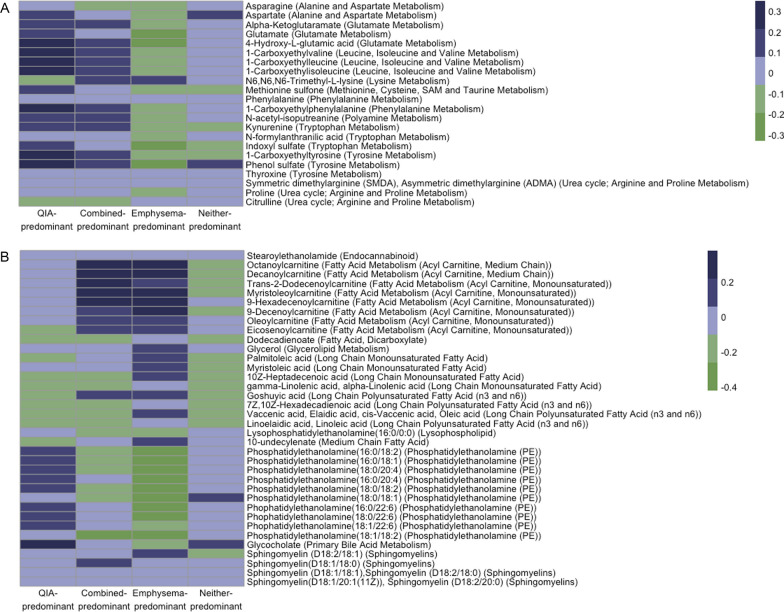
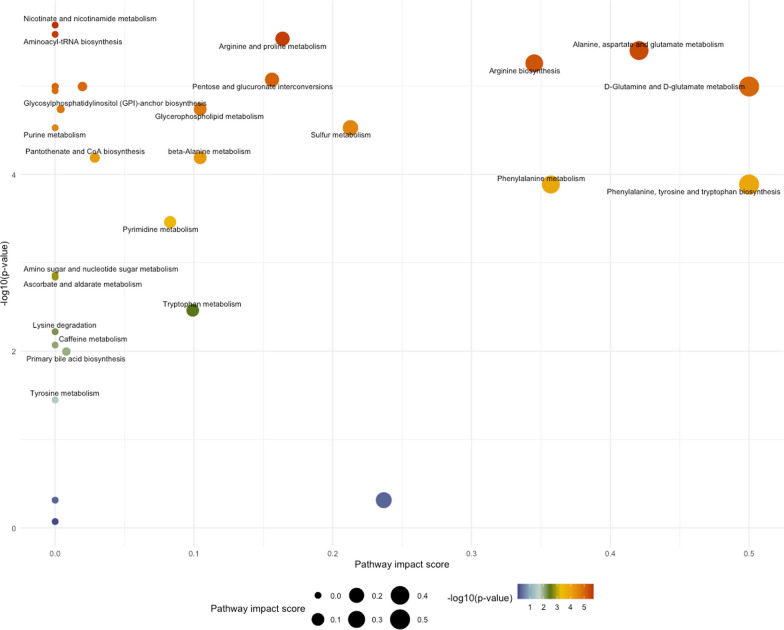
Our adjusted multinomial logistic regression models yielded 75 metabolites that differed significantly between QIA-predominant and emphysema-predominant phenotypes, with 45 associated with higher odds and 30 associated with lower odds of QIA relative to emphysema (Table 4), including 36 (48.0%) lipids and 22 (29.3%) amino acids (Fig. 5, Additional file 1: Table S7). Most of the associations of amino acids with QIA-predominance were positive, and they included dimethylarginine (SDMA, ADMA), phenylalanine, asparagine, proline, and kynurenine. Amongst lipids, phosphatidylethanolamines (PE) were most commonly associated with higher odds of QIA-predominance, whereas sphingomyelins (SM) and acyl carnitines were associated with higher odds of emphysema-predominance. Pathway enrichment analysis showed overrepresentation of metabolites involved in PE metabolism (glycerophospholipid and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor pathways), as well as multiple amino acid pathways including those involving nicotinate and nicotinamide, aminoacyl-tRNA, arginine, proline, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism (Table 5, Fig. 6).
Table 4.
A The 25 metabolites that have highest odds of QIA-predominant phenotype and B 25 metabolites that have the lowest odds of QIA-predominant phenotype compared to emphysema-predominant phenotype in multinomial logistic regression
| Metabolite | HMDB ID* | Odds of QIA-predominant over emphysema-predominant, mean [CI]† |
FDR p-value | Metabolon class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetric dimethylarginine (SMDA), Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)‡ |
0003334, 0001539‡ |
5.19 [2.01–13.40] |
0.021 |
Amino Acid; Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism |
| Phenylalanine | 0000159 |
5.04 [1.73–14.72] |
0.040 |
Amino Acid; Phenylalanine Metabolism |
| Asparagine | 0000168 |
4.79 [1.99–11.54] |
0.018 |
Amino Acid; Alanine and Aspartate Metabolism |
| Sulfate | 01448 |
4.05 [1.79–9.17] |
0.022 |
Xenobiotics; Chemical |
| Proline |
0000162, 0003411 |
3.36 [1.61–7.03] |
0.028 |
Amino Acid; Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism |
| Kynurenine | 0000684 |
2.82 [1.48–5.34] |
0.031 |
Amino Acid; Tryptophan Metabolism |
| Erythronate | 0000613 |
2.71 [1.46–5.04] |
0.031 |
Carbohydrate; Aminosugar Metabolism |
| N-acetyl-isoputreanine |
2.64 [1.73–4.04] |
0.002 |
Amino Acid; Polyamine Metabolism |
|
| Alpha-Ketoglutaramate | 0001552 |
2.57 [1.46–4.50] |
0.026 |
Amino Acid; Glutamate Metabolism |
| Gamma-Glutamylphenylalanine | 0000594 |
2.49 [1.40–4.42] |
0.031 |
Peptide; Gamma-glutamyl Amino Acid |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (16:0/18:2) | 0005322 |
2.37 [1.65–3.40] |
< 0.001 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (16:0/18:1) | 0005320 |
2.31 [1.66–3.23] |
< 0.001 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) |
| Aspartate | 0000191 |
2.25 [1.40–3.61] |
0.022 |
Amino Acid; Alanine and Aspartate Metabolism |
| Lysophosphatidylethanolamine (16:0/0:0) | 0011503 |
2.16 [1.30–3.58] |
0.039 |
Lipid; Lysophospholipid |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (18:0/20:4) | 0009003 |
2.10 [1.39–3.18] |
0.018 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (16:0/20:4) | 0005323 |
2.09 [1.43–3.04] |
0.011 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) |
| 3-Ureidopropionate | 0000026 |
1.99 [1.40–2.83] |
0.011 |
Nucleotide; Pyrimidine Metabolism, Uracil containing |
| N-formylanthranilic acid | 0004089 |
1.97 [1.32–2.95] |
0.026 |
Amino Acid; Tryptophan Metabolism |
| Phosphatidylethanolamine (18:0/18:2) | 0008994 |
1.94 [1.37–2.74] |
0.011 |
Lipid; Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) |
| Succinylcarnitine | 0061717 |
1.92 [1.22–3.01] |
0.049 |
Energy; TCA Cycle |
| Quinolinate | 0000232 |
1.89 [1.35–2.66] |
0.011 |
Cofactors and Vitamins; Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism |
| Gulonate | 0003290 |
1.89 [1.25–2.87] |
0.037 |
Cofactors and Vitamins; Ascorbate and Aldarate Metabolism |
| Methionine sulfone | 0062174 |
1.85 [1.26–2.70] |
0.031 |
Amino Acid; Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism |
| 1-Carboxyethylphenylalanine |
1.81 [1.34–2.43] |
0.011 |
Amino Acid; Phenylalanine Metabolism |
|
| Glutamate | 0000148 |
1.80 [1.25–2.61] |
0.031 |
Amino Acid; Glutamate Metabolism |
|
Sphingomyelin (D18:1/20:1(11Z)), Sphingomyelin (D18:2/20:0)‡ |
0240610, 0240632‡ |
0.31 [0.16–0.63] |
0.026 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
| Thyroxine | 0000248 |
0.32 [0.16–0.64] |
0.028 |
Amino Acid; Tyrosine Metabolism |
|
Sphingomyelin (D18:1/18:1), Sphingomyelin (D18:2/18:0)‡ |
0012101 |
0.32 [0.16–0.66] |
0.031 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
| Sphingomyelin (D18:1/18:0) | 0001348 |
0.33 [0.16–0.68] |
0.038 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
| Citrulline | 0000904 |
0.41 [0.22–0.74] |
0.043 |
Amino Acid; Urea cycle; Arginine and Proline Metabolism |
| Sphingomyelin (D18:2/18:1) |
0.43 [0.26–0.69] |
0.020 |
Lipid; Sphingomyelins |
|
| Eicosenoylcarnitine |
0.47 [0.31–0.70] |
0.011 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Monounsaturated) |
|
| Oleoylcarnitine | 0005065 |
0.49 [0.30–0.80] |
0.049 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Monounsaturated) |
| Stearoylethanolamide | 0013078 |
0.50 [0.31–0.80] |
0.045 |
Lipid; Endocannabinoid |
| Glycerol | 0000131 |
0.53 [0.38–0.74] |
0.011 |
Lipid; Glycerolipid Metabolism |
| N6,N6,N6-Trimethyl-L-lysine | 0001325 |
0.55 [0.38–0.81] |
0.033 |
Amino Acid; Lysine Metabolism |
| Homostachydrine | 0033433 |
0.59 [0.43–0.81] |
0.024 |
Xenobiotics; Food Component/Plant |
| 9-Decenoylcarnitine | 0013205 |
0.61 [0.44–0.84] |
0.037 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Monounsaturated) |
| 9-Hexadecenoylcarnitine | 0013207 |
0.62 [0.45–0.86] |
0.049 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Monounsaturated) |
| 10-undecylenate | 0033724 |
0.63 [0.47–0.85] |
0.037 |
Lipid; Medium Chain Fatty Acid |
| Myristoleoylcarnitine | 0240588 |
0.63 [0.49–0.82] |
0.018 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Monounsaturated) |
| Trans-2-Dodecenoylcarnitine | 13,326 |
0.64 [0.49–0.84] |
0.031 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Monounsaturated) |
| Dodecadienoate |
0.66 [0.52–0.85] |
0.028 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid, Dicarboxylate |
|
| Decanoylcarnitine | 0000651 |
0.67 [0.52–0.87] |
0.034 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Medium Chain) |
| Octanoylcarnitine | 0000791 |
0.68 [0.53–0.88] |
0.037 |
Lipid; Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Carnitine, Medium Chain) |
|
Linoelaidic acid, Linoleic acid‡ |
0006270, 0000673‡ |
0.69 [0.54–0.87] |
0.033 |
Lipid; Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (n3 and n6) |
|
gamma-Linolenic acid, alpha-Linolenic acid‡ |
0003073, 0001388‡ |
0.71 [0.57–0.88] |
0.031 |
Lipid; Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (n3 and n6) |
|
Vaccenic acid, Elaidic acid, cis-Vaccenic acid, Oleic acid‡ |
0003231, 0000573, 0240219, 0000207‡ |
0.71 [0.56–0.90] |
0.049 |
Lipid; Long Chain Monounsaturated Fatty Acid |
| 10Z-Heptadecenoic acid | 0060038 |
0.74 [0.61–0.90] |
0.041 |
Lipid; Long Chain Monounsaturated Fatty Acid |
| 7Z,10Z-Hexadecadienoic acid | 0000477 |
0.74 [0.61–0.89] |
0.031 |
Lipid; Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (n3 and n6) |
CI 95% confidence interval, FDR Benjamini–Hochberg False Discovery Rate, HMDB Human Metabolome Database, QIA quantitative interstitial abnormalities
*Wishart DS, Guo AC, Oler E, et al., HMDB 5.0: the Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. Jan 7;50(D1):D622–31
†Multinomial regression models adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, smoking status, pack-years, and inhaled corticosteroid use. QIA-predominant was initially used as the reference group
‡Cannot be analytically differentiated
Fig. 5.
Heatmaps of mean A amino acid metabolite values and B lipid metabolite values of QIA-predominant, combined-predominant, emphysema-predominant, and neither-predominant groups. Shown are the metabolites that had significant differences in the QIA-predominant and emphysema-predominant groups (FDR p ≤ 0.05)
Table 5.
Pathway enrichment analysis of metabolites associated QIA-predominant versus emphysema-predominant phenotypes from multinomial regression
| Pathway* | Total in pathway | Hits | FDR p-value |
Pathway impact value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 15 | 2 | Aspartate; Quinolinate | 2.71E−05 | 0 |
| Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis | 48 | 5 |
Asparagine; Phenylalanine; Aspartate; Proline; Glutamate |
2.71E−05 | 0 |
| Arginine and proline metabolism | 38 | 2 | Proline; Glutamate | 2.71E−05 | 0.164 |
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | 28 | 4 |
Aspartate; Asparagine; Glutamate; 2-Oxoglutaramate |
2.71E−05 | 0.421 |
| Arginine biosynthesis | 14 | 3 |
Glutamate; Citrulline; Aspartate |
2.71E−05 | 0.345 |
| Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 18 | 2 | Gulonate; D-Xylose | 2.71E−05 | 0.156 |
| D-Glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism | 6 | 1 | Glutamate | 2.71E−05 | 0.500 |
| Glutathione metabolism | 28 | 1 | Glutamate | 2.71E−05 | 0.020 |
| Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 32 | 1 | Glutamate | 2.71E−05 | 0 |
| Butanoate metabolism | 15 | 1 | Glutamate | 2.71E−05 | 0 |
| Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism | 30 | 1 | Glutamate | 2.71E−05 | 0 |
| Nitrogen metabolism | 6 | 1 | Glutamate | 2.71E−05 | 0 |
| Histidine metabolism | 16 | 2 | Glutamate; Aspartate | 2.79E−05 | 0 |
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 36 | 1 | Phosphatidylethanolamine | 3.91E−05 | 0.104 |
| Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis | 14 | 1 | Phosphatidylethanolamine | 3.91E−05 | 0.004 |
| Sulfur metabolism | 8 | 1 | Sulfate | 5.60E−05 | 0.213 |
| Purine metabolism | 65 | 1 | Sulfate | 5.60E−05 | 0 |
| beta-Alanine metabolism | 21 | 2 |
Aspartate; 3-Ureidopropionate |
1.09E−04 | 0.104 |
| Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 19 | 2 |
Aspartate; 3-Ureidopropionate |
1.09E−04 | 0.029 |
| Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 4 | 1 | Phenylalanine | 1.99E−04 | 0.500 |
| Phenylalanine metabolism | 10 | 1 | Phenylalanine | 1.99E−04 | 0.357 |
| Pyrimidine metabolism | 39 | 2 |
Orotidine 5'-phosphate; 3-Ureidopropionate |
5.06E−04 | 0.083 |
| Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 37 | 1 | beta-D-Fructose | 0.002 | 0 |
| Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 8 | 1 | Gulonate | 0.002 | 0 |
| Tryptophan metabolism | 41 | 2 |
Kynurenine; Formylanthranilate |
0.004 | 0.099 |
| Lysine degradation | 25 | 1 | N6,N6,N6-Trimethyl-L-lysine | 0.007 | 0 |
| Caffeine metabolism | 10 | 1 | 7-Methylxanthine | 0.01 | 0 |
| Primary bile acid biosynthesis | 46 | 1 | Glycocholate | 0.01 | 0.008 |
| Tyrosine metabolism | 42 | 1 | Thyroxine | 0.04 | 0 |
| Glycerolipid metabolism | 16 | 1 | Glycerol | 0.50 | 0.237 |
| Galactose metabolism | 27 | 1 | Glycerol | 0.50 | 0 |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | 21 | 1 | Sphingomyelin | 0.85 | 0 |
FDR Benjamini–Hochberg False Discovery Rate
*Metabolites with a Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) ID number
Fig. 6.
Scatterplots generated from pathway enrichment analysis in MetaboAnalyst of multinomial logistic regression analysis of QIA-predominant and emphysema-predominant phenotypes. FDR p-values are on the y-axis and pathway impact values on the x-axis. The size of the plotted point correlates to pathway impact and colors (blue to red) correlate to p-values
One metabolite, tryptophan betaine, was significantly associated with lower odds of QIA-predominant compared to neither-predominant groups. There were no significant metabolites between the QIA-predominant and combined-predominant groups. Intriguingly, despite non-significance, and although the unadjusted mean metabolite levels do not completely reflect the multinomial differences, the combined-predominant group had similar levels of amino acids as the QIA-predominant group but, depending on the metabolite, showed directionality with either the QIA-predominant or the emphysema-predominant group (Fig. 5).
Discussion
To our knowledge, our discovery study was the first global analysis of the metabolomics features of quantitative interstitial abnormalities in a large cohort. Our study of 928 ever-smokers in COPDGene found that 85 plasma metabolites from the Metabolon metabolomics assay were associated with QIA, independent of age, sex, BMI, smoking status, pack-years, and ICS use. These findings highlight the metabolic features of participants with QIA and provide initial insight into the biochemical systemic features associated with these quantitative CT changes. Furthermore, we identified 75 metabolites that differed significantly between participants with QIA-predominant versus emphysema-predominant phenotypes. Such associations of metabolomic differences between participants with shared risk factors but different CT parenchymal findings may be useful as biomarkers that distinguish these smoking-related phenotypes. These associations also help us understand the metabolic processes that may be important in early QIA, but which may be less prominent in later stages of lung injury like emphysema. Lastly, some of the metabolites significant in our analyses were those previously associated with advanced diseases like IPF and COPD, suggesting potential shared pathways in progression that should be studied further.
Amino acids
Circulating amino acids are involved in numerous processes including cell signaling, regulating gene expression, hormone synthesis and secretion, nutrient metabolism, oxidative stress, and immune response regulation [32]. In particular, smokers with COPD can have perturbations in branched chain amino acid levels important in the skeletal muscle, which may reflect systemic changes including impaired immunity or cachexia. [17]
In our analysis, the tryptophan metabolites quinolinate, kynurenine, and N-formylanthranilic acid were associated with higher odds of QIA over emphysema and were notable. These tryptophan derivatives suggest inflammatory activity with QIA and shared overlap with advanced diseases. These three metabolites are downstream in the kynurenine pathway, which normally comprises 95% of tryptophan metabolism and is upregulated in inflammation and immune responses [33]. Quinolinate is also a substrate for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) synthesis, required for normal cell function and energy production, and this pathway has been proposed to be upregulated in physiological stress [34] and was enriched for QIA in our analysis. In COPD, upregulated kynurenine derivatives are associated with reduced FEV1 [35], and reduction in the precursor tryptophan is associated with COPD exacerbations and emphysema [17]. Patients with IPF have been shown to have significant declines in kynurenine after treatment with the anti-fibrotic pirfenidone, thought to be due to its anti-inflammatory effects. [36]
Several glutamine derivatives were associated with higher odds of QIA over emphysema and in pathway enrichment: glutamate, alpha-ketoglutarate, and 4-hydroxyglutamate. The precursor glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the body, found in both plasma and skeletal muscle, and plays roles in immune modulation, ammonia transport, and maintenance of cell integrity and function [37]. The downstream derivatives glutamate and alpha-ketoglutarate are crucial intermediates in the Krebs cycle [37]. In patients with COPD compared to controls, plasma glutamine and glutamate are decreased, thought to be from hypermetabolism and muscle depletion [38]. We found higher odds of higher levels of glutamine derivatives in QIA-predominance compared to emphysema-predominance, which suggests that patients with emphysema may be in a more advanced, catabolic state compared those with QIA. These metabolites should be studied as a potential factor in the progression of QIA to advanced disease.
Lipids
Circulating lipids comprise thousands of individual species with a considerable range of structural diversity and physiological functions, including maintaining the integrity of the lipid bilayer, functional hormones, and cell signaling pathways [39]. In the lungs, lipids are important components of surfactant. [40]
The majority of lipids negatively-associated with QIA were phospholipids, including eight phosphatidylcholines (PCs), significant in enrichment analysis. PCs are the body’s most abundant phospholipids and the major component of surfactant [41]. Some of the PC species negatively-associated with QIA in our analysis were those specifically found in prior studies of IPF and COPD patients demonstrating decreased PC concentrations in the respiratory fluid and blood [18, 42, 43]. Decreased PC levels may also generally reflect oxidative changes in the lungs in the setting of cigarette exposure, as has been demonstrated in mice alveolar cells [44]. Further studies are needed to test the relationship between blood and pulmonary phospholipids in smokers and to understand whether the plasma PC perturbations associated with QIA represent a systemic manifestation of PC dysregulation in surfactant, or another phospholipid perturbation altogether.
Sphingomyelins (SM) were another lipid subclass negatively-associated with QIA, and they were of particular interest given their many roles in fetal lung development and lung inflammation [45]. Patients with IPF have downregulated plasma SM [46], including the SM(D18:1/20:0) species that we identified with QIA. A previous study of COPD phenotypes in the COPDGene cohort found that some SMs were also negatively-associated with emphysema [47]. In our analysis, four SMs were associated with lower odds of QIA-predominance compared to emphysema-predominance. Our findings complement the prior study as it did not account for QIA in the assessment of emphysema, suggesting that both QIA and emphysema CT measures should be considered when studying the metabolomics of smoking-related disease.
Carbohydrates
Amongst carbohydrates, our pathway analyses showed QIA was enriched for certain sugars including maltose, sucrose, and xylose. As these sugars mostly come from the diet and the breakdown of food starches in the digestive system, these metabolites may be related to the gut-lung axis, in which changes in inflammation and microbiota in the gut mucosa cross-talk with lung mucosa [48]. Also positively-associated with QIA was the sialic acid amino sugar N-acetylneuraminate (Neu5Ac), which may be reflective of inflammation. Sialic acids are often the terminal sugars on mucin, and variations in these sugar attachments may indicate regulation by proinflammatory cytokines or modification by bacteria. [49] Higher Neu5Ac levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid have been found to be associated with COPD and with increased bacterial binding in smokers [50, 51]. Lastly, erythronate and its precursor N-acetylglucosamine were also positively-associated with QIA. These extracellular matrix degradation products are associated with pulmonary fibrosis in animal models [52], and they may reflect remodeling during QIA development.
Strengths and limitations
With more patients with a smoking history receiving screening CT scans than before, we need a deeper understanding of the biology that underlies the subtle interstitial changes that are often caught incidentally. The metabolites significant in our exploratory study provide initial insight into the biochemical activity and pathways associated with QIA. We found associations with several metabolomic features previously linked with IPF and COPD, suggestive of shared disease activity between early-stage QIA and later-stage advanced diseases.
We also identified metabolic features that differed between participants with QIA- and emphysema-predominant phenotypes, which provide initial insight into possible common and different underlying pathways. The two smoking-related phenotypes share risk factors and imaging and physiologic features, especially before very advanced disease develops [53]. Since the metabolomic levels of the combined-predominant group did not clearly fall in between those of the QIA- and emphysema-predominant phenotypes, their metabolomic profiles reflect more complicated processes requiring further investigation.
There are several limitations to our study. Although one of the strengths of our study is the large sample size of thoroughly phenotyped ever-smokers, our results need replication in other smoking and population-based cohorts for validation of potential biomarkers. Our analyses can provide insight into, and generate hypotheses for, possible pathogenic pathways of QIA but cannot be used to elucidate exact mechanisms. Furthermore, while the global metabolomics panel captures a broad range of different classes of metabolites, it is not quantitative; in future work aimed at pinpointing mechanisms, targeted assays will be required. Due to the cross-sectional nature of our data, interpretations of causality are limited; longitudinal studies may help elucidate temporal relationships more clearly. We defined CT phenotypes with the predominant CT features occupying at least 5% of the lung volume; although a binary cutoff for emphysema at 5% is well-established as a clinically meaningful value [26], a similar 5% cutoff has been used for QIA but is less robust [1]. Lastly, we used the HMDB identifier and KEGG background database for our pathway analysis because they are widely used, acknowledging the following limitations. Given the novelty of high-throughput metabolomics and rapid accumulation of new data in the field, some metabolites are unclearly notated or not found at all in the databases, other metabolites are redundant in multiple pathways [54]; thus, we may have not been able to detect some pathways that are nonetheless biologically important in QIA.
Conclusions
Lipid, amino acid, and carbohydrate metabolites associated with inflammation and immune response, extracellular matrix remodeling, surfactant, and muscle cachexia may play important roles in the earliest stages of smoking-related lung disease. These metabolic signals provide initial insight into the biochemical associations with QIA as one of the earliest stages of smoking-related lung disease activity. These signals suggest future biomarkers for early detection of disease and potential therapeutic targets before progression to IPF and COPD.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Figure S1. Participants categorized into four CT-based phenotypes, defining those with ≥5% QIA and <5% emphysema as QIA-predominant, ≥5% QIA and ≥5% emphysema as combined-predominant, <5% QIA and ≥5% emphysema as emphysema-predominant, and <5% QIA and <5% emphysema as neither-predominant. Table S1. Distribution of all available metabolites in our analysis, by Metabolon class and sub-class. Table S2. Baseline characteristics, by CT phenotype. Table S3. Baseline characteristic of COPDGene cohort of smokers with CT measurements and exam data, with (our study cohort) and without metabolomics data collected. Table S4: Univariate regression of each metabolite with continuous percent QIA. Table S5: Multivariable regression of each metabolite with continuous percent QIA. Table S6: Analysis of Variance analysis of each metabolite with CT phenotypes, arranged by Metabolon classes and sub-classes. Table S7. Multinomial logistic regression of each metabolite with the CT phenotypes predominant QIA versus predominant emphysema.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the participants of the COPDGene study for their contributions.
COPDGene® Investigators – Core Units: Administrative Center: James D. Crapo, MD (PI); Edwin K. Silverman, MD, PhD (PI); Barry J. Make, MD; Elizabeth A. Regan, MD, PhD. Genetic Analysis Center: Terri H. Beaty, PhD; Peter J. Castaldi, MD, MSc; Michael H. Cho, MD, MPH; Dawn L. DeMeo, MD, MPH; Adel El Boueiz, MD, MMSc; Marilyn G. Foreman, MD, MS; Auyon Ghosh, MD; Lystra P. Hayden, MD, MMSc; Craig P. Hersh, MD, MPH; Jacqueline Hetmanski, MS; Brian D. Hobbs, MD, MMSc; John E. Hokanson, MPH, PhD; Wonji Kim, PhD; Nan Laird, PhD; Christoph Lange, PhD; Sharon M. Lutz, PhD; Merry-Lynn McDonald, PhD; Dmitry Prokopenko, PhD; Matthew Moll, MD, MPH; Jarrett Morrow, PhD; Dandi Qiao, PhD; Elizabeth A. Regan, MD, PhD; Aabida Saferali, PhD; Phuwanat Sakornsakolpat, MD; Edwin K. Silverman, MD, PhD; Emily S. Wan, MD; Jeong Yun, MD, MPH. Imaging Center: Juan Pablo Centeno; Jean-Paul Charbonnier, PhD; Harvey O. Coxson, PhD; Craig J. Galban, PhD; MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS; Eric A. Hoffman, Stephen Humphries, PhD; Francine L. Jacobson, MD, MPH; Philip F. Judy, PhD; Ella A. Kazerooni, MD; Alex Kluiber; David A. Lynch, MB; Pietro Nardelli, PhD; John D. Newell, Jr., MD; Aleena Notary; Andrea Oh, MD; Elizabeth A. Regan, MD, PhD; James C. Ross, PhD; Raul San Jose Estepar, PhD;
Joyce Schroeder, MD; Jered Sieren; Berend C. Stoel, PhD; Juerg Tschirren, PhD; Edwin Van Beek, MD, PhD; Bram van Ginneken, PhD; Eva van Rikxoort, PhD; Gonzalo Vegas Sanchez-Ferrero, PhD; Lucas Veitel; George R. Washko, MD; Carla G. Wilson, MS. PFT QA Center, Salt Lake City, UT: Robert Jensen, PhD. Data Coordinating Center and Biostatistics, National Jewish Health, Denver, CO: Douglas Everett, PhD; Jim Crooks, PhD; Katherine Pratte, PhD; Matt Strand, PhD; Carla G. Wilson, MS. Epidemiology Core, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, CO: John E. Hokanson, MPH, PhD; Erin Austin, PhD; Gregory Kinney, MPH, PhD; Sharon M. Lutz, PhD; Kendra A. Young, PhD. Mortality Adjudication Core: Surya P. Bhatt, MD; Jessica Bon, MD; Alejandro A. Diaz, MD, MPH; MeiLan K. Han, MD, MS; Barry Make, MD; Susan Murray, ScD; Elizabeth Regan, MD; Xavier Soler, MD; Carla G. Wilson, MS. Biomarker Core: Russell P. Bowler, MD, PhD; Katerina Kechris, PhD; Farnoush Banaei-
Kashani, PhD.
COPDGene® Investigators – Clinical Centers: Ann Arbor VA: Jeffrey L. Curtis, MD; Perry G. Pernicano, MD. Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX: Nicola Hanania, MD, MS; Mustafa Atik, MD; Aladin Boriek, PhD; Kalpatha Guntupalli, MD; Elizabeth Guy, MD; Amit Parulekar, MD. Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA: Dawn L. DeMeo, MD, MPH; Craig Hersh, MD, MPH; Francine L. Jacobson, MD, MPH; George Washko, MD. Columbia University, New York, NY: R. Graham Barr, MD, DrPH; John Austin, MD; Belinda D’Souza, MD; Byron Thomashow, MD. Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC: Neil MacIntyre, Jr., MD; H. Page McAdams, MD; Lacey Washington, MD. HealthPartners Research Institute, Minneapolis, MN: Charlene McEvoy, MD, MPH; Joseph Tashjian, MD. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD: Robert Wise, MD; Robert Brown, MD; Nadia N. Hansel, MD, MPH; Karen Horton, MD; Allison Lambert, MD, MHS; Nirupama Putcha, MD, MHS. Lundquist Institute for Biomedical Innovation at Harbor UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA: Richard Casaburi, PhD, MD; Alessandra Adami, PhD; Matthew Budoff, MD; Hans Fischer, MD; Janos Porszasz, MD, PhD; Harry Rossiter, PhD; William Stringer, MD. Michael E. DeBakey VAMC, Houston, TX: Amir Sharafkhaneh, MD, PhD; Charlie Lan, DO. Minneapolis VA: Christine Wendt, MD; Brian Bell, MD; Ken M. Kunisaki, MD, MS. Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA: Eric L. Flenaugh, MD; Hirut Gebrekristos, PhD; Mario Ponce, MD; Silanath Terpenning, MD; Gloria Westney, MD, MS. National Jewish Health, Denver, CO: Russell Bowler, MD, PhD; David A. Lynch, MB. Reliant Medical Group, Worcester, MA: Richard Rosiello, MD; David Pace, MD. Temple University, Philadelphia, PA: Gerard Criner, MD; David Ciccolella, MD; Francis Cordova, MD; Chandra Dass, MD; Gilbert D’Alonzo, DO; Parag Desai, MD; Michael Jacobs, PharmD; Steven Kelsen, MD, PhD; Victor Kim, MD; A. James Mamary, MD; Nathaniel Marchetti, DO; Aditi Satti, MD; Kartik Shenoy, MD; Robert M. Steiner, MD; Alex Swift, MD; Irene Swift, MD; Maria Elena Vega-Sanchez, MD. University of Alabama, Birmingham, AL: Mark Dransfield, MD; William Bailey, MD; Surya P. Bhatt, MD; Anand Iyer, MD; Hrudaya Nath, MD; J. Michael Wells, MD. University of California, San Diego, CA: Douglas Conrad, MD; Xavier Soler, MD, PhD; Andrew Yen, MD. University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA: Alejandro P. Comellas, MD; Karin F. Hoth, PhD; John Newell, Jr., MD; Brad Thompson, MD. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI: MeiLan K. Han, MD MS; Ella Kazerooni, MD MS; Wassim Labaki, MD MS; Craig Galban, PhD; Dharshan Vummidi, MD. University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN: Joanne Billings, MD; Abbie Begnaud, MD; Tadashi Allen, MD. University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA: Frank Sciurba, MD; Jessica Bon, MD; Divay Chandra, MD, MSc; Joel Weissfeld, MD, MPH. University of Texas Health, San Antonio, San Antonio, TX: Antonio Anzueto, MD; Sandra Adams, MD; Diego Maselli-Caceres, MD; Mario E. Ruiz, MD; Harjinder Singh.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
- BMI
Body mass index
- COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CT
Computed tomography
- FEV1
Forced expiratory volume in 1s
- FVC
Forced vital capacity
- HMDB
Human Metabolome Database
- ICS
Inhaled corticosteroid
- IPF
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- KEGG
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- PC
Phosphatidylcholines
- PE
Phosphatidylethanolamines
- QIA
Quantitative interstitial abnormalities
- SM
Sphingomyelins
Author contributions
Study design: BC, WWL, KAS, GRW. Data acquisition: RaSJ, SG, RuSJ, RBP. Analysis: BC, WWL, RaSJ, SG, RuSJ, RBP. Writing: BC, WWL, KAS. Interpretation, revision, and approval of the final manuscript: BC, RaSJ, SG, JLC, JMW, RuSJ, IOR, JRM, BDH, CPH, SYA, MKH, RBP, KAS, GRW, WWL.
Funding
The COPDGene study (NCT00608764) is supported by NHLBI U0 HL089897 and U01HL089856, as well as by the COPD Foundation through contributions made to an Industry Advisory Committee that has included AstraZeneca, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sunovion. Additional funding for this work includes DOD W81XWH1810772 (Rosas, Washko); National Institutes of Health grants: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) R21HL140376, R01HL129937, R01HL095432, R01HL089856, and R01HL089897 (Bowler), F32HL167486 (Choi), R01HL116931 (San José Estépar, Washko), R21HL140422 (San José Estépar, Washko), and P01HL114501 (Washko); NCRR/HIH UL1 RR025680 (Bowler); and K23HL151751 (Labaki).
Availability of data and materials
Data is available from the authors upon request and with permission from the COPDGene study group.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The COPDGene study (NCT00608764) was approved by the institutional review board at all 21 participating centers. All participants provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The following are not directly related to the work in this manuscript. BC reports grant support from the American Lung Association, consulting fees from Quantitative Imaging Solutions. RaSJ reports grant support from Lung Biotechnology, Insmed, BI, fees from Imbio, Leuko Labs, and Chiesi, and is a founder and equity holder for Quantitative Imaging Solutions. JLC reports grant support from NIAID, Department of Veteran Affairs, and Department of Defense, consulting fees from AstraZeneca, CSL Behring, and Novartis. RuSJ reports consulting fees from Quantitative Imaging Solutions. JDH reports grant support from NHLBI, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, and Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Foundation, fees from AstraZeneca. CPH reports grant support from NHLBI, Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Foundation, BI, Vertex. SYA reports grant support from NHLBI and Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation, equity holder for Quantitative Imaging Solutions. MKH reports grant support form NIH, Sanofi, Novartis, Nuvaira, Sunovion, Gala Therapeutics, COPD Foundation, AstraZeneca, American Lung Association, BI, Biodesix, personal fees from BI, GSK, AZ, and Mylan. GRW reports grant support from BI and Janssen Pharmaceuticals, fees from BI, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Vertex, Pulmonix, Novartis, Philips, and is a founder and equity holder for Quantitative Imaging Solutions.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Ash SY, Harmouche R, Ross JC, Diaz AA, Hunninghake GM, Putman RK, et al. The objective identification and quantification of interstitial lung abnormalities in smokers. Acad Radiol. 2017;24(8):941–946. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.08.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ash SY, Harmouche R, Putman RK, Ross JC, Diaz AA, Hunninghake GM, et al. Clinical and genetic associations of objectively identified interstitial changes in smokers. Chest. 2017;152(4):780–791. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.04.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ash SY, Harmouche R, Ross JC, Diaz AA, Rahaghi FN, Vegas Sanchez-Ferrero G, et al. Interstitial features at chest CT enhance the deleterious effects of emphysema in the COPD gene cohort. Radiology. 2018;288(2):600–609. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018172688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Choi B, Adan N, Doyle TJ, San Jose Estepar R, Harmouche R, Humphries SM, et al. Quantitative interstitial abnormality progression and outcomes in the genetic epidemiology of COPD and Pittsburgh lung screening study cohorts. Chest. 2022;163(1):164–175. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2022.06.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(19):1811–1823. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1705751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hogg JC, Senior RM. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease—part 2: pathology and biochemistry of emphysema. Thorax. 2002;57(9):830–834. doi: 10.1136/thorax.57.9.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Raghu G, Rochwerg B, Zhang Y, Garcia CA, Azuma A, Behr J, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline: treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An update of the 2011 clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;192(2):e3–19. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201506-1063ST. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2071–2082. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.King TE, Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(22):2083–2092. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Agusti A, Celli BR, Criner GJ, Halpin D, Anzueto A, Barnes P, et al. Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease 2023 report: GOLD executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2023;61(4). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Bowler RP, Wendt CH, Fessler MB, Foster MW, Kelly RS, Lasky-Su J, et al. New strategies and challenges in lung proteomics and metabolomics. An official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(12):1721–1743. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201710-770WS. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Clish CB. Metabolomics: an emerging but powerful tool for precision medicine. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2015;1(1):a000588. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a000588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gerszten RE, Wang TJ. The search for new cardiovascular biomarkers. Nature. 2008;451(7181):949–952. doi: 10.1038/nature06802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen Q, Deeb RS, Ma Y, Staudt MR, Crystal RG, Gross SS. Serum metabolite biomarkers discriminate healthy smokers from COPD smokers. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(12):e0143937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nambiar S, Tan DBA, Clynick B, Bong SH, Rawlinson C, Gummer J, et al. Untargeted metabolomics of human plasma reveal lipid markers unique to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2021;15(2–3):e2000039. doi: 10.1002/prca.202000039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Paige M, Burdick MD, Kim S, Xu J, Lee JK, Shim YM. Pilot analysis of the plasma metabolite profiles associated with emphysematous Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;413(4):588–593. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Labaki WW, Gu T, Murray S, Curtis JL, Yeomans L, Bowler RP, et al. Serum amino acid concentrations and clinical outcomes in smokers: SPIROMICS metabolomics study. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11367. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47761-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Seeliger B, Carleo A, Wendel-Garcia PD, Fuge J, Montes-Warboys A, Schuchardt S, et al. Changes in serum metabolomics in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and effect of approved antifibrotic medication. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:837680. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.837680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Regan EA, Hokanson JE, Murphy JR, Make B, Lynch DA, Beaty TH, et al. Genetic epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) study design. COPD. 2010;7(1):32–43. doi: 10.3109/15412550903499522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Evans AM, DeHaven CD, Barrett T, Mitchell M, Milgram E. Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Anal Chem. 2009;81(16):6656–6667. doi: 10.1021/ac901536h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dehaven CD, Evans AM, Dai H, Lawton KA. Organization of GC/MS and LC/MS metabolomics data into chemical libraries. J Cheminform. 2010;2(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-2-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Miller MJ, Kennedy AD, Eckhart AD, Burrage LC, Wulff JE, Miller LA, et al. Untargeted metabolomic analysis for the clinical screening of inborn errors of metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2015;38(6):1029–1039. doi: 10.1007/s10545-015-9843-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smilde AK, van der Werf MJ, Bijlsma S, van der Werff-van der Vat BJ, Jellema RH. Fusion of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Anal Chem. 2005;77(20):6729–36. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 24.Wei R, Wang J, Su M, Jia E, Chen S, Chen T, et al. Missing value imputation approach for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):663. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19120-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cirulli ET, Guo L, Leon Swisher C, Shah N, Huang L, Napier LA, et al. Profound perturbation of the metabolome in obesity is associated with health risk. Cell Metab. 2019;29(2):488–500.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Han MK, Tayob N, Murray S, Woodruff PG, Curtis JL, Kim V, et al. Association between emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease outcomes in the COPDGene and SPIROMICS cohorts: a post hoc analysis of two clinical trials. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198(2):265–267. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201801-0051LE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Team R . RStudio: integrated development for R. Boston: RStudio, Inc.; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Team RC. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2020.
- 29.Pang Z, Zhou G, Ewald J, Chang L, Hacariz O, Basu N, et al. Using MetaboAnalyst 5.0 for LC-HRMS spectra processing, multi-omics integration and covariate adjustment of global metabolomics data. Nat Protoc. 2022;17(8):1735–1761. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00710-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wishart DS, Tzur D, Knox C, Eisner R, Guo AC, Young N, et al. HMDB: the human metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:D521–D526. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):27–30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wu G. Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids. 2009;37(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cervenka I, Agudelo LZ, Ruas JL. Kynurenines: Tryptophan's metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health. Science. 2017;357:6349. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf9794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Moffett JR, Blinder KL, Venkateshan CN, Namboodiri MA. Differential effects of kynurenine and tryptophan treatment on quinolinate immunoreactivity in rat lymphoid and non-lymphoid organs. Cell Tissue Res. 1998;293(3):525–534. doi: 10.1007/s004410051145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kim J, Suresh B, Lim MN, Hong SH, Kim KS, Song HE, et al. Metabolomics reveals dysregulated sphingolipid and amino acid metabolism associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022;17:2343–2353. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S376714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fois AG, Sotgiu E, Scano V, Negri S, Mellino S, Zinellu E, et al. Effects of pirfenidone and nintedanib on markers of systemic oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a preliminary report. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(11):1064. doi: 10.3390/antiox9111064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cruzat V, Macedo Rogero M, Noel Keane K, Curi R, Newsholme P. Glutamine: metabolism and immune function, supplementation and clinical translation. Nutrients. 2018;10(11):1564. doi: 10.3390/nu10111564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pouw EM, Schols AM, Deutz NE, Wouters EF. Plasma and muscle amino acid levels in relation to resting energy expenditure and inflammation in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158(3):797–801. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.3.9708097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Quehenberger O, Dennis EA. The human plasma lipidome. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(19):1812–1823. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1104901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dautel SE, Kyle JE, Clair G, Sontag RL, Weitz KK, Shukla AK, et al. Lipidomics reveals dramatic lipid compositional changes in the maturing postnatal lung. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40555. doi: 10.1038/srep40555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Agassandian M, Mallampalli RK. Surfactant phospholipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1831(3):612–625. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schmidt R, Meier U, Markart P, Grimminger F, Velcovsky HG, Morr H, et al. Altered fatty acid composition of lung surfactant phospholipids in interstitial lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;283(5):L1079–L1085. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00484.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cruickshank-Quinn CI, Jacobson S, Hughes G, Powell RL, Petrache I, Kechris K, et al. Metabolomics and transcriptomics pathway approach reveals outcome-specific perturbations in COPD. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35372-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Agarwal AR, Yin F, Cadenas E. Short-term cigarette smoke exposure leads to metabolic alterations in lung alveolar cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014;51(2):284–293. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0523OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tibboel J, Reiss I, de Jongste JC, Post M. Sphingolipids in lung growth and repair. Chest. 2014;145(1):120–128. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-0967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yan F, Wen Z, Wang R, Luo W, Du Y, Wang W, et al. Identification of the lipid biomarkers from plasma in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by Lipidomics. BMC Pulm Med. 2017;17(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12890-017-0513-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bowler RP, Jacobson S, Cruickshank C, Hughes GJ, Siska C, Ory DS, et al. Plasma sphingolipids associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease phenotypes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191(3):275–284. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201410-1771OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Saint-Criq V, Lugo-Villarino G, Thomas M. Dysbiosis, malnutrition and enhanced gut-lung axis contribute to age-related respiratory diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101235. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Angata T, Varki A. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related alpha-keto acids: an evolutionary perspective. Chem Rev. 2002;102(2):439–469. doi: 10.1021/cr000407m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Batson BD, Zorn BT, Radicioni G, Livengood SS, Kumagai T, Dang H, et al. Cystic fibrosis airway mucus hyperconcentration produces a vicious cycle of mucin, pathogen, and inflammatory interactions that promotes disease persistence. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022;67(2):253–265. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0359OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Padra M, Benktander J, Padra JT, Andersson A, Brundin B, Tengvall S, et al. Mucin binding to moraxella catarrhalis during airway inflammation is dependent on sialic acid. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021;65(6):593–602. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0064OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Weckerle J, Picart-Armada S, Klee S, Bretschneider T, Luippold AH, Rist W, et al. Mapping the metabolomic and lipidomic changes in the bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis in young and aged mice. Dis Model Mech. 2022 doi: 10.1242/dmm.049105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kirchner J, Goltz JP, Lorenz F, Obermann A, Kirchner EM, Kickuth R. The, "dirty chest"–correlations between chest radiography, multislice CT and tobacco burden. Br J Radiol. 2012;85(1012):339–345. doi: 10.1259/bjr/62694750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Marco-Ramell A, Palau-Rodriguez M, Alay A, Tulipani S, Urpi-Sarda M, Sanchez-Pla A, et al. Evaluation and comparison of bioinformatic tools for the enrichment analysis of metabolomics data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018;19(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-2006-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Figure S1. Participants categorized into four CT-based phenotypes, defining those with ≥5% QIA and <5% emphysema as QIA-predominant, ≥5% QIA and ≥5% emphysema as combined-predominant, <5% QIA and ≥5% emphysema as emphysema-predominant, and <5% QIA and <5% emphysema as neither-predominant. Table S1. Distribution of all available metabolites in our analysis, by Metabolon class and sub-class. Table S2. Baseline characteristics, by CT phenotype. Table S3. Baseline characteristic of COPDGene cohort of smokers with CT measurements and exam data, with (our study cohort) and without metabolomics data collected. Table S4: Univariate regression of each metabolite with continuous percent QIA. Table S5: Multivariable regression of each metabolite with continuous percent QIA. Table S6: Analysis of Variance analysis of each metabolite with CT phenotypes, arranged by Metabolon classes and sub-classes. Table S7. Multinomial logistic regression of each metabolite with the CT phenotypes predominant QIA versus predominant emphysema.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available from the authors upon request and with permission from the COPDGene study group.