Abstract
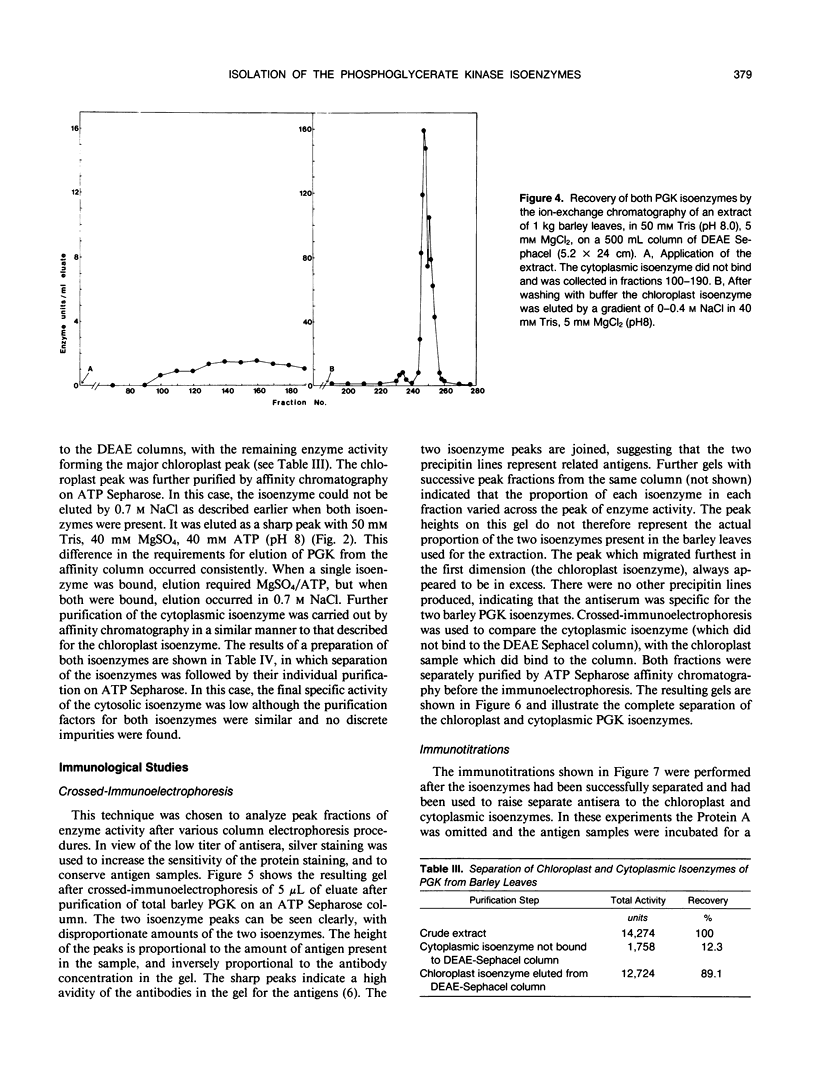
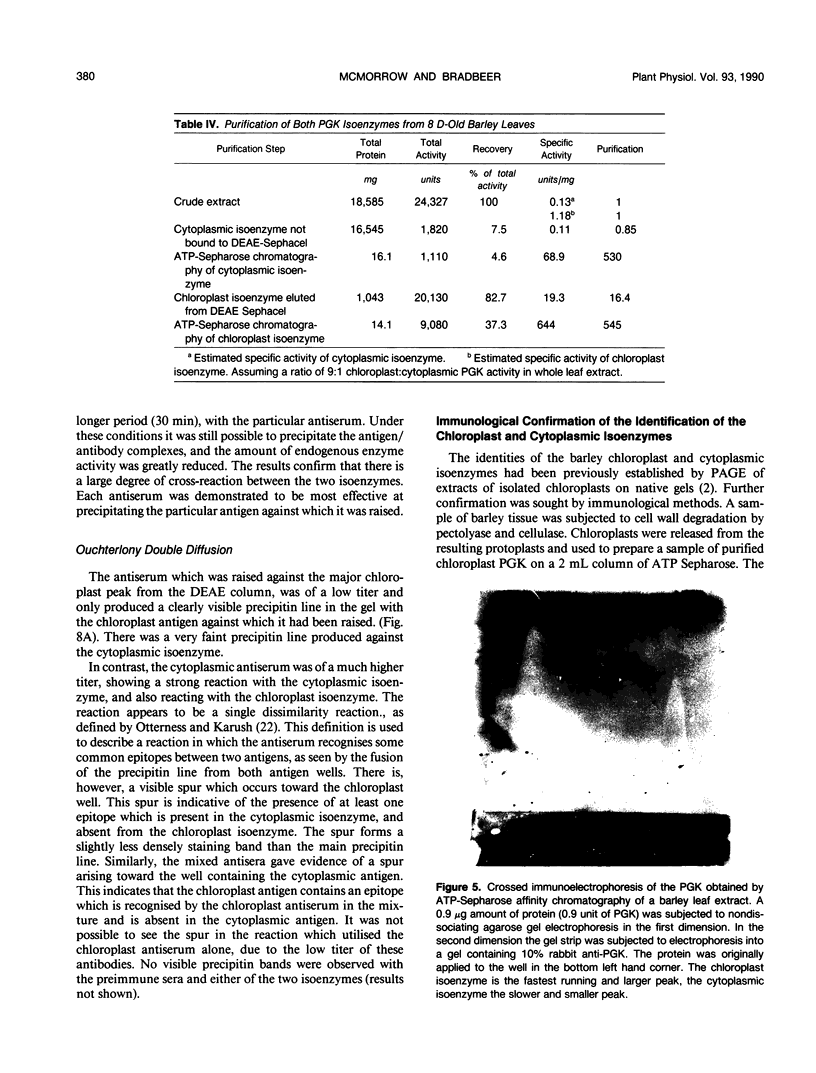
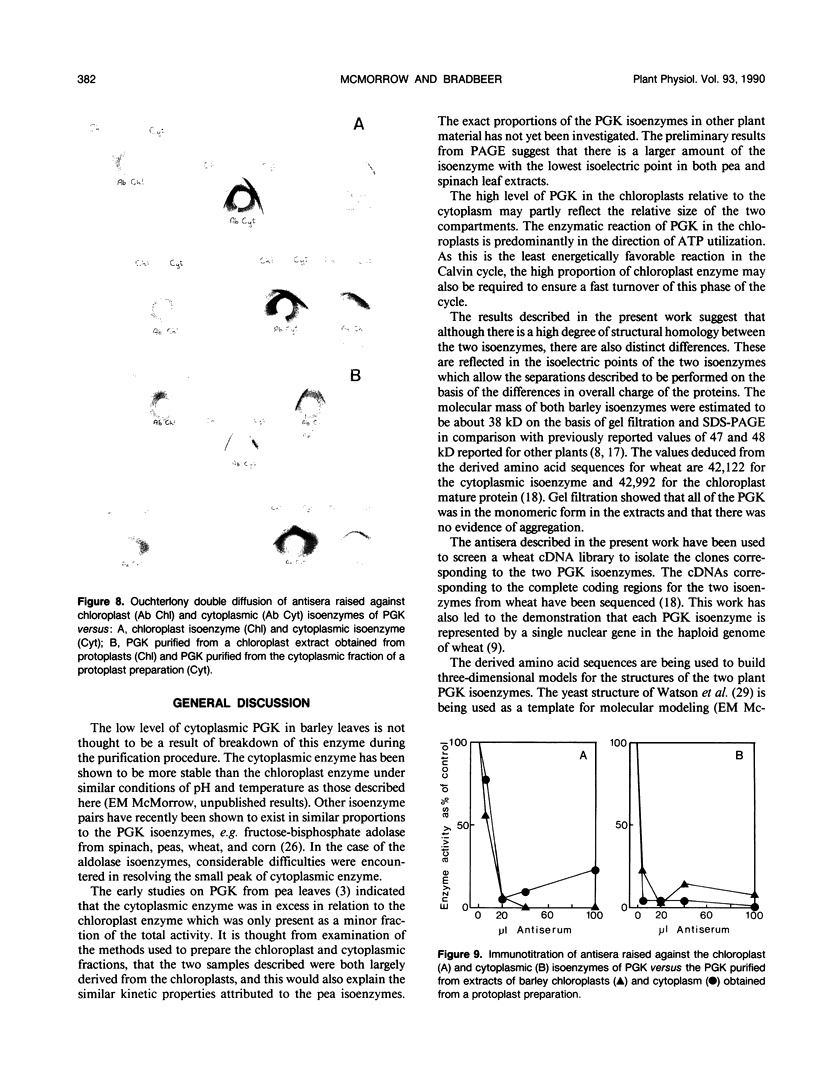
The chloroplast and cytoplasmic isoenzymes of phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) (EC. 2.7.2.3) from Hordeum vulgare leaves have been separated and purified for the first time to apparent homogeneity. The method for purifying the isoenzymes is described here and consists of DEAE Sephacel chromatography followed by affinity chromatography on ATP Sepharose. This consistently provided a 500- to 900-fold purification of each isoenzyme. Most of the total PGK in green barley leaves was found to be in the chloroplasts with only 10% in the cytoplasm. The immunological properties of the two isoenzymes were compared. The antisera raised to the separate isoenzymes showed cross-reactivity, although there is evidence that each isoenzyme possesses some distinct epitopes. The isoenzymes differ in overall charge with isoelectric points at 5.2 and 5.4 for the chloroplast and cytoplasmic isoenzymes, respectively. Molecular mass estimations by gel filtration and sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis provided similar values of approximately 38 kilodaltons for each isoenzyme, some 4 to 5 kilodaltons less than the values calculated from the cDNA sequences of the wheat isoenzymes. The isoenzymes have broadly similar pH optima of pH 7 to 8. The cytoplasmic isoenzyme is more thermally stable than the chloroplast isoenzyme. Further studies are now in progress to compare both the regulatory properties of the isoenzymes and also their three-dimensional structures as compared with the yeast enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD B., BANDURSKI R. S. Phosphoglyceryl kinase in higher plants. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):939–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M., Brownstone Y. S. A study of phosphoglycerate kinase in human erythrocytes. I. Enzyme isolation, purification and assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 12;445(1):74–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. E., Advani V. R. Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes: three distinct isoenzymes associated with the reductive pentose phosphate cycle. Plant Physiol. 1970 May;45(5):583–585. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.5.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H., Bock E., Kroll J. Comparison of antisera. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:101–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavell S., Scopes K. Isolation and characterization of the 'photosynthetic' phosphoglycerate kinase from Beta vulgaris. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):483–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger I., Schnarrenberger C. Purification, subunit structure and immunological comparison of fructose-bisphosphate aldolases from spinach and corn leaves. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):101–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz G. W., Eber S., Kessler W., Krietsch H., Krietsch W. K. Isolation of phosphoglycerate kinases by affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):493–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson-Raźnikiewicz M. Kinetic studies on the reaction catalyzed by phosphoglycerate kinase. II. The kinetic relationships between 3-phosphoglycerate, MgATP2-and activating metal ion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jan 11;132(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longstaff M., Raines C. A., McMorrow E. M., Bradbeer J. W., Dyer T. A. Wheat phosphoglycerate kinase: evidence for recombination between the genes for the chloroplastic and cytosolic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6569–6580. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann A. F., Fentem P. A., Stewart G. R. Identification of two forms of glutamine synthetase in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):515–521. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miernyk J. A., Dennis D. T. Isozymes of the glycolytic enzymes in endosperm from developing castor oil seeds. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):825–828. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacold I., Anderson L. E. Chloroplast and Cytoplasmic Enzymes: VI. Pea Leaf 3-Phosphoglycerate Kinases. Plant Physiol. 1975 Feb;55(2):168–171. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porro M., Viti S., Antoni G., Saletti M. Ultrasensitive silver-stain method for the detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels and immunoprecipitates on agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):316–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radola B. J. Isoelectric focusing in layers of granulated gels. II. Preparative isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;386(1):181–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnarrenberger C., Krüger I. Distinction between Cytosol and Chloroplast Fructose-Bisphosphate Aldolases from Pea, Wheat, and Corn Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):301–304. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. The steady-state kinetics of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. Anomalous kinetic plots and the effects of salts on activity. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):503–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. C., Walker N. P., Shaw P. J., Bryant T. N., Wendell P. L., Fothergill L. A., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F. Sequence and structure of yeast phosphoglycerate kinase. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1635–1640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiksell E., Larsson-Raźnikiewicz M. Affinity labeling of phosphoglycerate kinase by 5'-[p-(fluorosulfonyl)benzoyl]-1,N6-ethenoadenosine. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14472–14478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]