Abstract
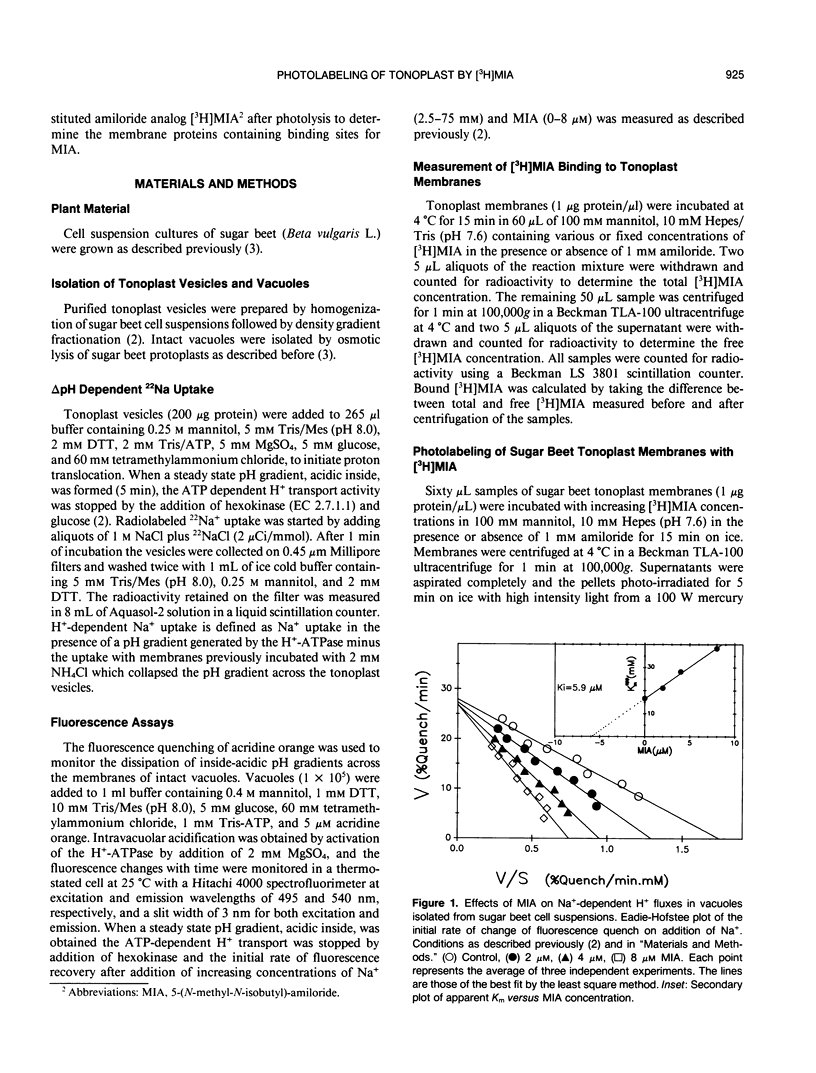
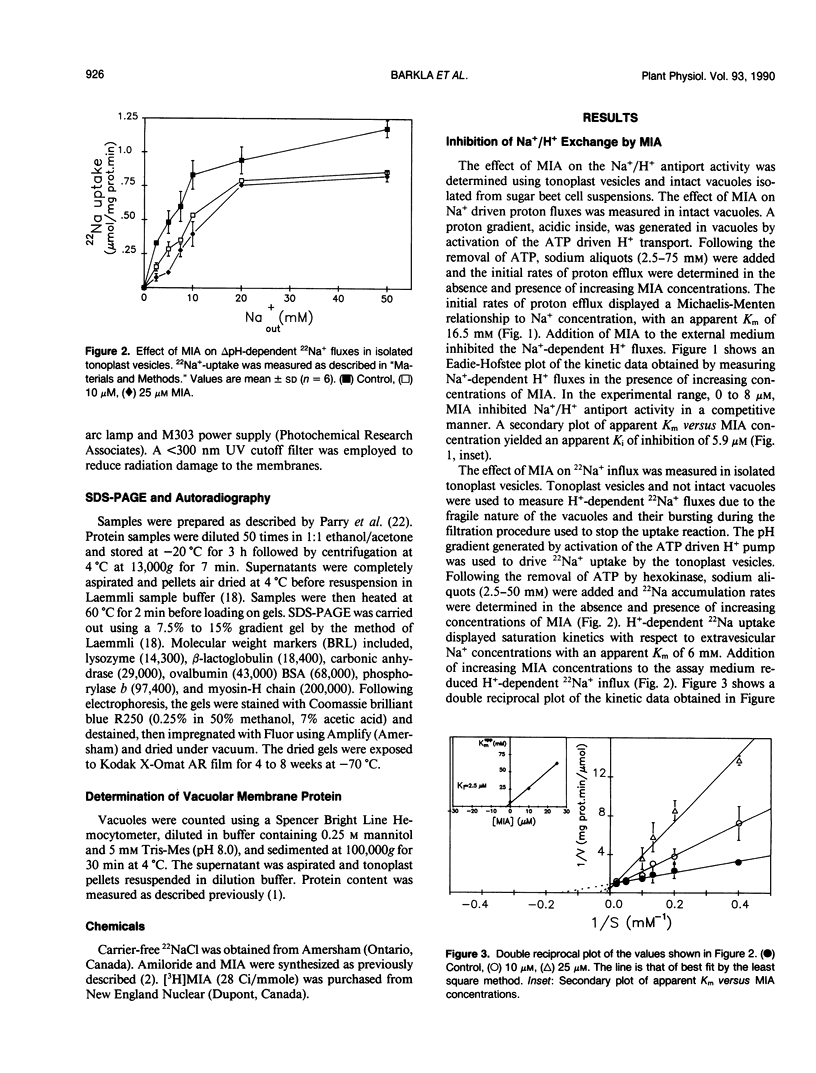
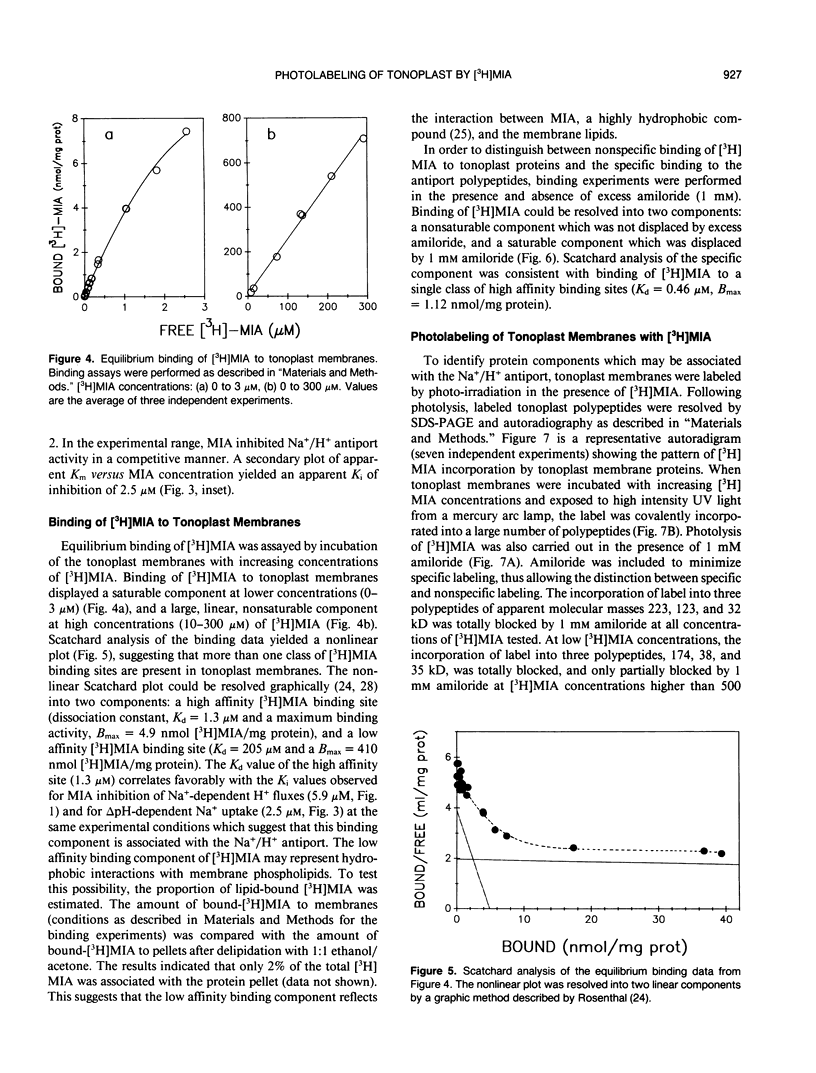
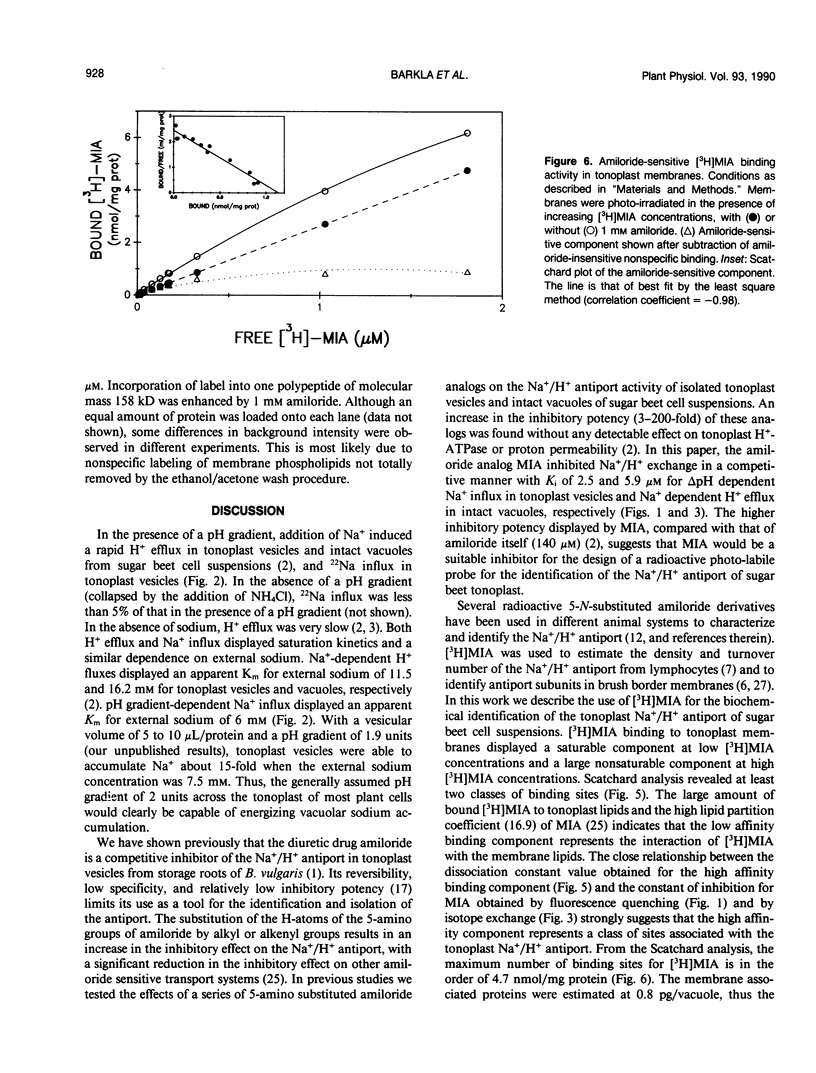
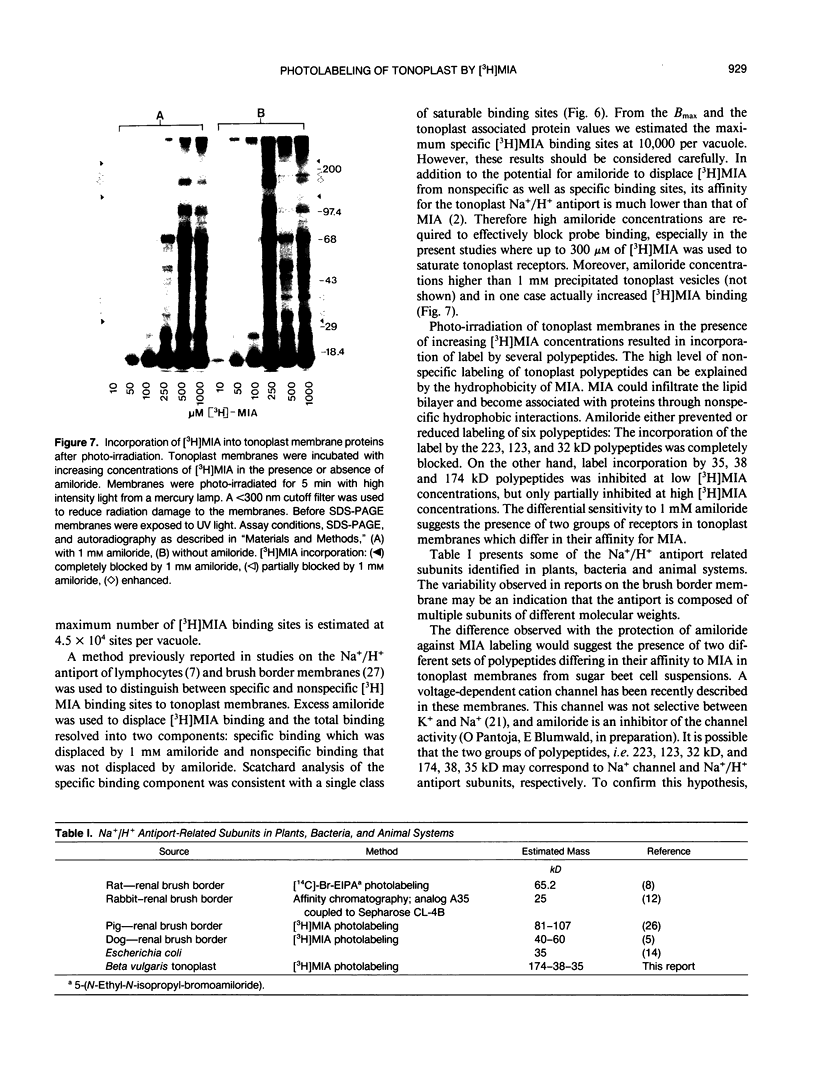
The effects of 5-(N-methyl-N-isobutyl)-amiloride (MIA), an amiloride analog, was tested on the Na+/H+ antiport activity of intact vacuoles and tonoplast vesicles isolated from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) cell suspension cultures. MIA inhibited Na+/H+ exchange in a competitive manner with a Ki of 2.5 and 5.9 micromolar for ΔpH-dependent 22Na+ influx in tonoplast vesicles and Na+-dependent H+ efflux in intact vacuoles, respectively. Scatchard analysis of the binding of [3H]MIA to tonoplast membranes revealed a high affinity binding component with a Kd of 1.3 micromolar. The close relationship between the dissociation constant value obtained and the constants of inhibition for MIA obtained by fluorescence quenching and isotope exchange suggests that the high affinity component represents a class of sites associated with the tonoplast Na+/H+ antiport. Photolabeling of the tonoplast with [3H]MIA revealed two sets of polypeptides with a different affinity to amiloride and its analog.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumwald E., Cragoe E. J., Poole R. J. Inhibition of na/h antiport activity in sugar beet tonoplast by analogs of amiloride. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):30–33. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Poole R. J. Na/H Antiport in Isolated Tonoplast Vesicles from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):163–167. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Poole R. J. Salt tolerance in suspension cultures of sugar beet : induction of na/h antiport activity at the tonoplast by growth in salt. Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):884–887. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun Y., Hassidim M., Lerner H. R., Reinhold L. Evidence for a Na/H Antiporter in Membrane Vesicles Isolated from Roots of the Halophyte Atriplex nummularia. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):104–108. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon S. J., Cohen S., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Grinstein S. Estimation of the number and turnover rate of Na+/H+ exchangers in lymphocytes. Effect of phorbol ester and osmotic shrinking. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3626–3632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett W. F., Dunn M. F. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Phytopathogenic Pseudomonas syringae Pathovars in Infected Leaves of Susceptible Hosts. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):5–9. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich T., Sablotni J., Burckhardt G. Identification of the renal Na+/H+ exchanger with N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) and amiloride analogues. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(3):253–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01869721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. NaCl Induces a Na/H Antiport in Tonoplast Vesicles from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):231–236. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. Rapid induction of na/h exchange activity in barley root tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huot S. J., Cassel D., Igarashi P., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Slayman C. W., Aronson P. S. Identification and purification of a renal amiloride-binding protein with properties of the Na+-H+ exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):683–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpel R., Olami Y., Taglicht D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Sequencing of the gene ant which affects the Na+/H+ antiporter activity in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10408–10414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinoia E., Schramm M. J., Kaiser G., Kaiser W. M., Heber U. Transport of anions in isolated barley vacuoles : I. Permeability to anions and evidence for a cl-uptake system. Plant Physiol. 1986 Apr;80(4):895–901. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry R. V., Turner J. C., Rea P. A. High purity preparations of higher plant vacuolar H+-ATPase reveal additional subunits. Revised subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20025–20032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Cragoe E. J., Jr Inhibition of chemotactic factor-activated Na+/H+ exchange in human neutrophils by analogues of amiloride: structure-activity relationships in the amiloride series. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;30(2):112–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watad A. E., Pesci P. A., Reinhold L., Lerner H. R. Proton Fluxes as a Response to External Salinity in Wild Type and NaCl-Adapted Nicotiana Cell Lines. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):454–459. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Lever J. E. Photoaffinity labeling by [3H]-N5-methyl-N5-isobutylamiloride of proteins which cofractionate with Na+/H+ antiport activity. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2980–2984. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K. Misuse of nonlinear Scatchard plots. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):314–317. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]