Abstract
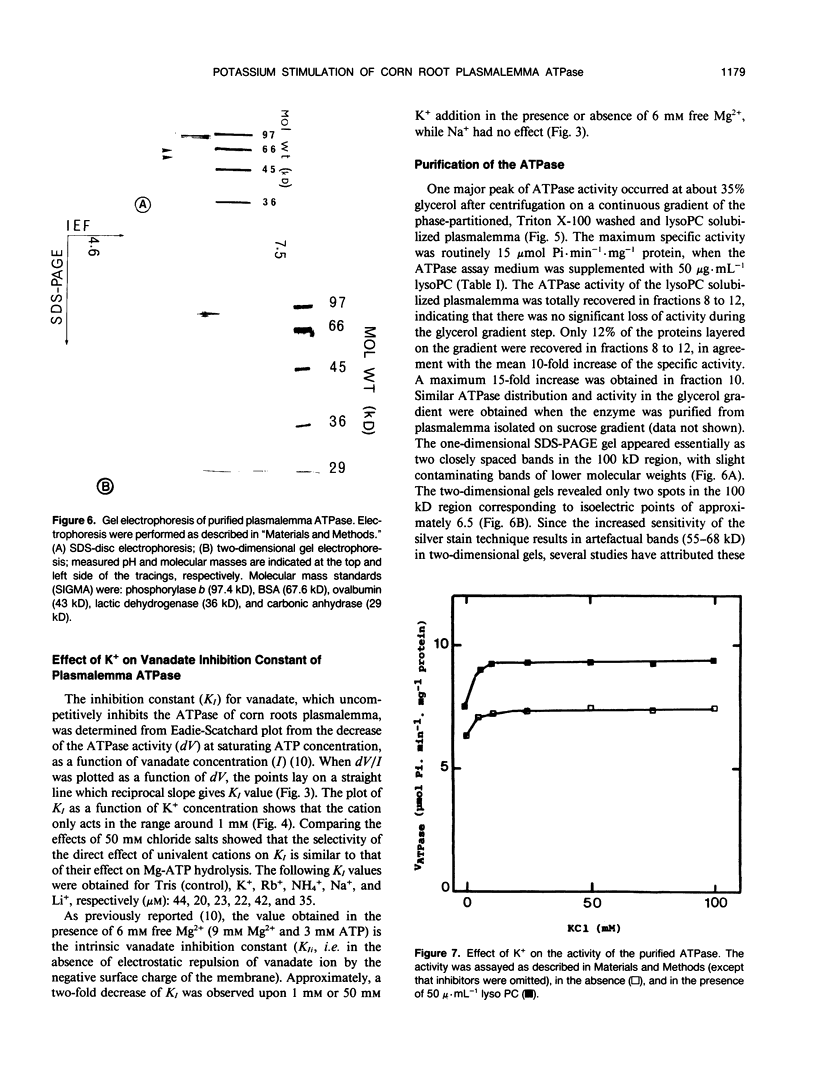
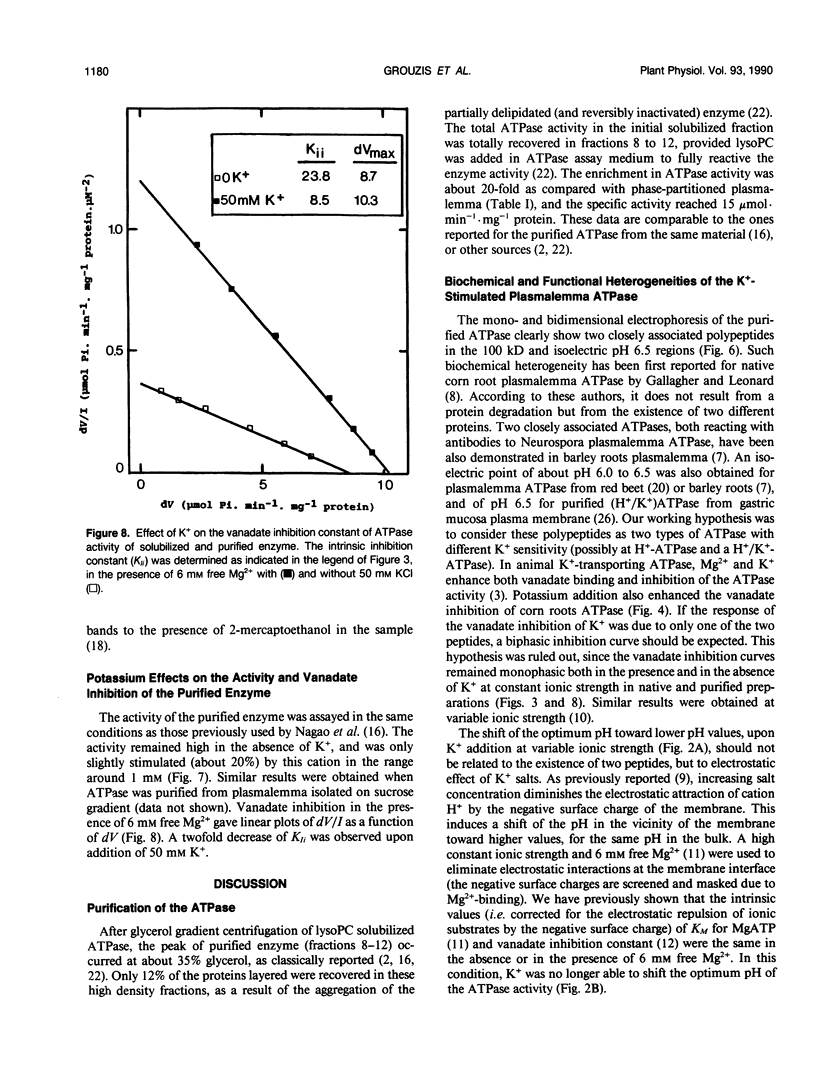
Potassium stimulation of the plasmalemma (Zea mays L. var Mona) was studied by using a constant ionic strength to prevent indirect stimulation by the electrostatic effect of K+ salts. The transmembrane electrochemical H+ gradient was eliminated by using gramicidin. In these conditions, K+ stimulation was attributable to a direct effect of the cation on plasmalemma proteins. We used both native vesicles isolated on a sucrose cushion, and solubilized and purified ATPase from phase-partitioned plasmalemma, according to the method of T. Nagao, W. Sasakawa, and T. Sugiyama ([1987] Plant Cell Physiol 28: 1181-1186). The purified enzyme had a high specific activity (15 micromoles per minute per milligram protein), but was only about 20% stimulated by K+. In both preparations, potassium (in the range around 1 millimolar) specifically decreased two-fold the vanadate inhibition constant, and increased the maximum rate of ATP hydrolysis. In plasmalemma vesicles, the Eadie-Scatchard graph of the K+-dependent ATPase activity as a function of K+ concentration was linear only at constant ionic strength. The purified ATPase preparation appeared as two closely spaced bands in the 100 kilodalton region with isoelectric point about 6.5. Nevertheless, this biochemical heterogeneity seems unlikely to be related to K+ stimulation, since K+ modified neither the pH optimum of the activity (pH 6.5) nor the monophasic kinetics of the vanadate inhibition, in both native plasmalemma and purified enzyme preparation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthon G. E., Spanswick R. M. Purification and properties of the h-translocating ATPase from the plasma membrane of tomato roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Aug;81(4):1080–1085. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.4.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond G. H., Hudgins P. M. Low-affinity Na+ sites on (Na+ +K+)-ATPase modulate inhibition of Na+-ATPase activity by vanadate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 7;687(2):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90560-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation reactions of the red beet plasma membrane ATPase studied in the transient state. Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):84–91. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Michelis M. I., Spanswick R. M. H-pumping driven by the vanadate-sensitive ATPase in membrane vesicles from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):542–547. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Tanaka C. K., Hurkman W. J. separation and Immunological Characterization of Membrane Fractions from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):717–724. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Electrophoretic characterization of a detergent-treated plasma membrane fraction from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1987 Feb;83(2):265–271. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibrat R., Grouzis J. P., Rigaud J., Galtier N., Grignon C. Electrostatic analysis of effects of ions on the inhibition of corn root plasma membrane Mg2+-ATPase by the bivalent orthovanadate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 13;979(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90521-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibrat R., Grouzis J. P., Rigaud J., Grignon C. Potassium Stimulation of Corn Root Plasmalemma ATPase : II. H-Pumping in Native and Reconstituted Vesicles with Purified ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):1183–1189. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. Protein contaminants of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90714-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleski N. A., Bennett A. B. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: IV. N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide Binding and Inhibition of the Plasma Membrane H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):569–572. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Purification of the proton pumping ATPase from plant plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):735–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaya J., Omori K., Taketani S., Kobayashi Y., Tashiro Y. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of (H+, K+)ATPase from hog gastric microsomes. J Biochem. 1987 Oct;102(4):903–911. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibaud J. B., Soler A., Grignon C. H and k electrogenic exchanges in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):847–853. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Partial purification and properties of the proton-translocating ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12826–12830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widell S., Lundborg T., Larsson C. Plasma membranes from oats prepared by partition in an aqueous polymer two-phase system : on the use of light-induced cytochrome B reduction as a marker for the plasma membrane. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1429–1435. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]