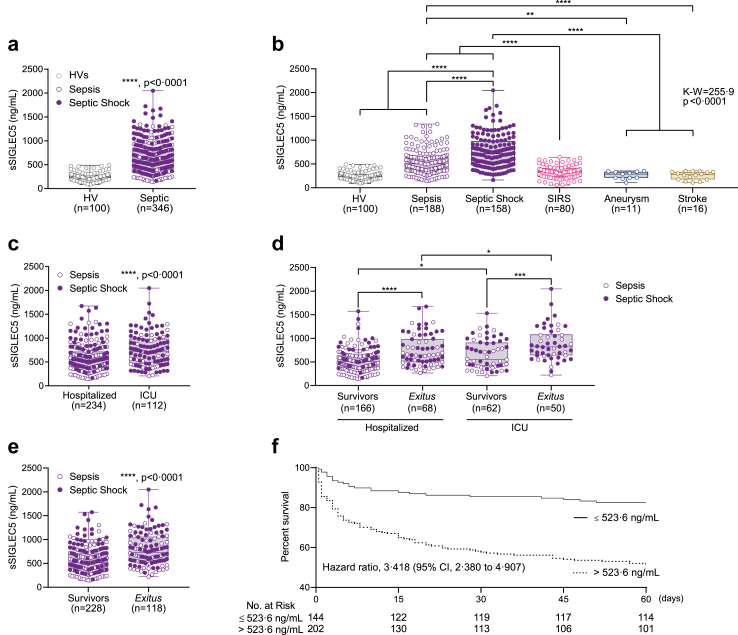
Fig. 6.
Soluble SIGLEC5 classified septic patients on admission. (a) Soluble SIGLEC5 (sSIGLEC5) levels in plasma from HVs (grey clear dots, n = 100) and septic patients (sepsis in violet clear dots and shock septic in purple filled dots, n = 346). (b) sSIGLEC5 levels in plasma from HVs (n = 100) and patients with sepsis (n = 188), septic shock (n = 158), SIRS (n = 80), aneurysm (n = 11) and stroke (n = 16). (c) sSIGLEC5 levels in plasma from septic patients classified according to their hospitalization (n = 234) or their admission to ICU (n = 112). (d) sSIGLEC5 levels in plasma from septic patients hospitalized survivors (n = 166), hospitalized exitus (n = 68), admitted in ICU survivors (n = 62) and admitted in ICU exitus (n = 50). (e) sSIGLEC5 levels in plasma from patients with sepsis (violet clear dots) and septic shock (purple filled dots) classified according to their outcome after 60 days as Survivors (n = 228) and Exitus (n = 118). (f) Septic patients were dichotomized according to the optimal cut-off, estimated by Youden index for plasmatic sSIGLEC5 concentration to be 523.6 ng/mL. Kaplan–Meier survival curves from diagnosis to day 60 according to baseline plasmatic sSIGLEC5 (χ2 = 33.20, p < 0.0001) are shown. Data shown as mean ± SEM. (a and c–e) Unpaired t-test (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). (b) One-way ANOVA test (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). (f) Kaplan–Meier estimation of survival from septic patients according Youden index (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).