Figure 5. GABAergic interneurons receive descending input from the brain.
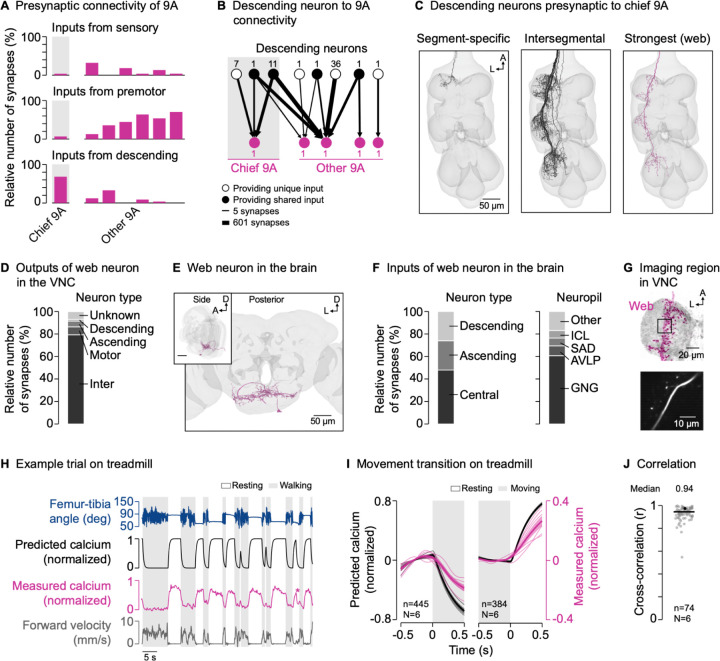
(A) Inputs from sensory neurons, premotor neurons, and descending neurons onto individual 9A neurons presynaptic to hook axons in the front leg neuromere (FANC connectome).
(B) Connectivity between descending neurons and the 9A neurons presynaptic to hook axons (FANC connectome). Numbers next to nodes indicate the number of neurons with the same connectivity motif. Lines indicate the log10 of the number of synapses.
(C) Segment-specific and intersegmental descending neurons presynaptic to chief 9A, including the most strongly connected descending neuron (web; FANC connectome). A: anterior; L: lateral.
(D) Outputs of the descending web neuron in the VNC (MANC connectome).
(E) Posterior and side view of the descending web neuron in the brain (FlyWire connectome). A: anterior; D: dorsal; L: lateral.
(F) Inputs to the descending web neuron in the brain (FlyWire connectome). GNG: gnathal ganglia; AVLP: anterior ventrolateral protocerebrum; SAD: saddle; ICL: inferior clamp.
(G) Top: Confocal image of web neuron in the VNC. The black box indicates the imaging region. Magenta: GFP; gray: neuropil stain (nc82). A: anterior; L: lateral. Bottom: Mean tdTomato signal within the imaging region during an example trial.
(H) Example trial of two-photon calcium imaging of the web neuron in the neuromere of the left front leg and behavior tracking on the treadmill. The asterisk highlights part of a front leg resting bout during which the hind legs were grooming.
(I) Predicted and measured calcium signals aligned to the transitions into and out of movement. Movement includes walking and grooming. Thin lines show animal means, thick lines show mean of means, shadings show standard error of the mean. n: number of transitions; N: number of flies.
(J) Cross-correlation coefficient between predicted and measured calcium signals per trial at a time lag of zero. The black line shows the median. The black dot marks the trial shown in (H). n: number of trials; N: number of flies.