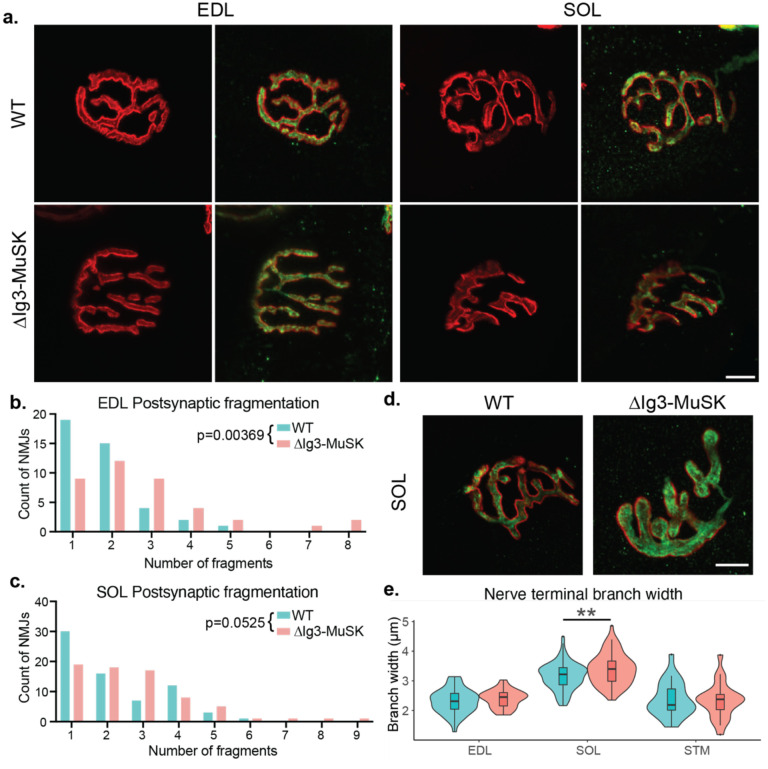
Figure 3. Postsynaptic fragmentation in ΔIg3-MuSK hindlimb muscles.
a. WT and ΔIg3-MuSK EDL and soleus muscles were stained for pre-(green)and post-synaptic (red) elements for morphometric analysis. Both muscles exhibited postsynaptic fragmentation but showed no signs of denervation. b. Quantification of postsynaptic fragmentation observed in EDL. c. Quantification of postsynaptic fragmentation observed in SOL. d. Representative images illustrating wider nerve terminal branches in ΔIg3-MuSK Soleus. e. Quantification of average branch width in EDL, SOL, and STM NMJs from ΔIg3-MuSK and WT animals. Note increased branch width in SOL. (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, generalized linear models, full statistics presented in Tables 3-1 and 3-2, including median and interquartile range for each measurement, n for each age and sex, tests used, and results of statistical testing.)