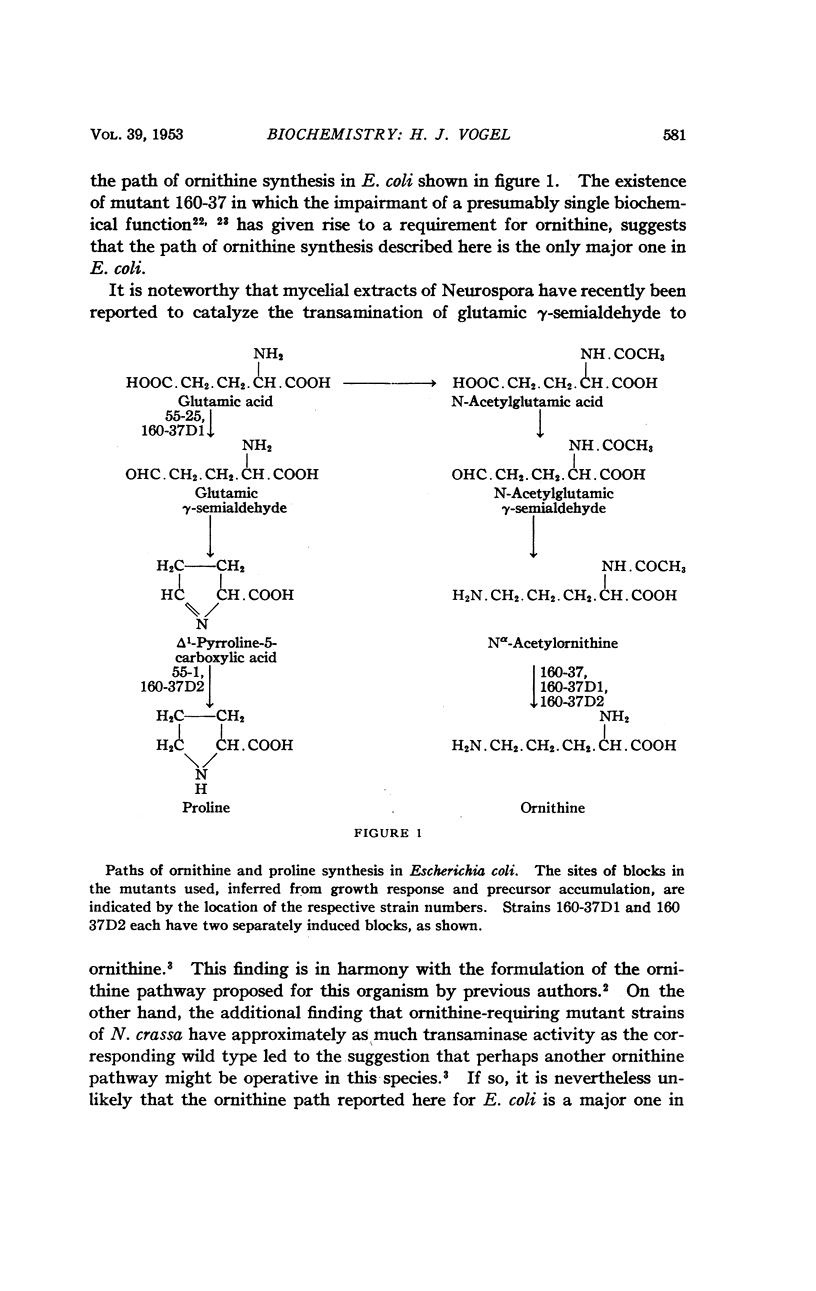
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABELSON P. H., BOLTON E. T., ALDOUS E. Utilization of carbon dioxide in the synthesis of proteins by Escherichia coli. I. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):165–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABELSON P. H., BOLTON E. T., ALDOUS E. Utilization of carbon dioxide in the synthesis of proteins by Escherichia coli. II. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSMAN S. P., ROSSEN J., LAYNE E. C. Gamma-Aminobutyric acid-glutamic acid transamination in brain. J Biol Chem. 1953 Mar;201(1):385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONNER D. M. Gene-enzyme relationships in Neurospora. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:143–157. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCHAM J. R. S. Ornithine transaminase in Neurospora and its relation to the biosynthesis of proline. Biochem J. 1953 Jan;53(2):313–320. doi: 10.1042/bj0530313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISTER A., SOBER H. A., TICE S. V., FRASER P. E. Transamination and associated deamidation of asparagine and glutamine. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;197(1):319–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAO K. R., BIRNBAUM S. M., KINGSLEY R. B., GREENSTEIN J. P. Enzymatic susceptibility of corresponding chloroacetyl- and glycyl-L-amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1952 Oct;198(2):507–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STETTEN M. R. Mechanism of the conversion of ornithine into proline and glutamic acid in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):499–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


