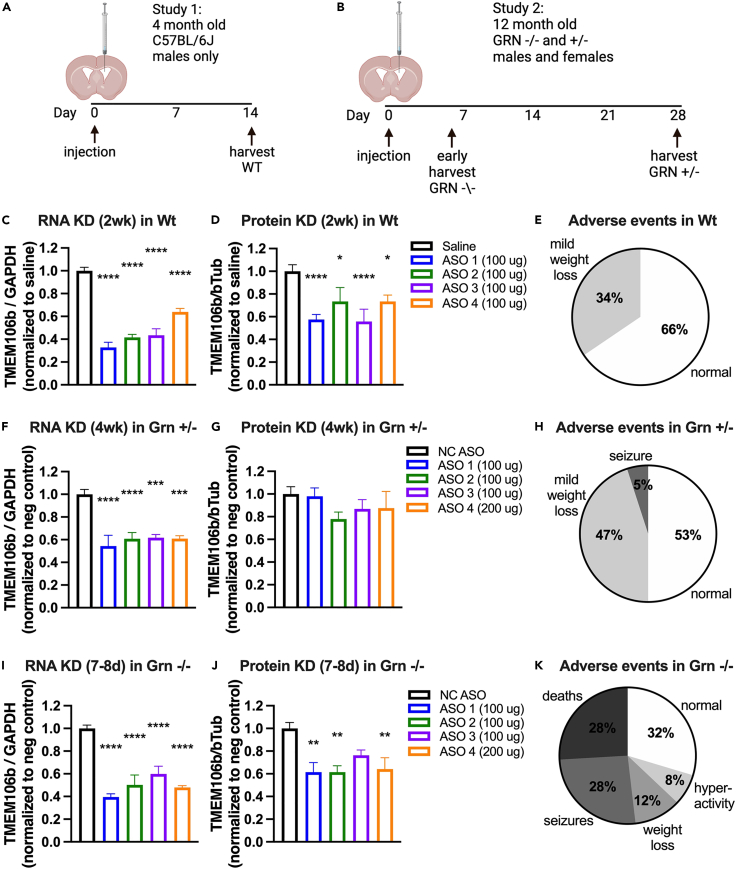
Figure 7.
Partial reduction of Tmem106b with ASO treatment is toxic in Grn −/− mice
(A and B) Study designs for Tmem106b ASO dosing experiments in Wt (A) and Grn +/− and Grn −/− mice (B).
(C and D) Significant knockdown of Tmem106b RNA and protein observed in brains of Wt mice with an overall effect of ASO by one-way ANOVA for mRNA, p < 0.001 and protein, p < 0.0074. When compared to saline, all 4 ASOs significantly reduced Tmem106b RNA and protein levels.
(E) Little to no adverse events observed in Wt mice after ASO dosing. n = 6 Wt mice/group.
(F and G) Significant knockdown of Tmem106b RNA was observed in brains of Grn +/− mice with an overall effect of ASO by one-way ANOVA for RNA p < 0.001 but not for protein. When compared to NC ASO, all 4 Tmem106b ASOs significantly reduced Tmem106b mRNA levels but not protein levels.
(H) Little to no adverse event observed in Grn +/− mice after ASO dosing. n = 4–5 Grn +/− mice/group.
(I and J) Significant knockdown of Tmem106b mRNA and protein was observed in brains of Grn −/− mice with an overall effect of ASO by one-way ANOVA for RNA p < 0.001 and protein p = 0.0088. When compared to NC ASO, all 4 Tmem106b ASOs significantly reduced Tmem106b RNA levels with 3/4 ASOs also significantly reducing protein levels. n = 3–5 Grn −/− mice/group.
(K) At 5–7 days of age many of the Grn −/− mice dosed with Tmem106b targeting ASO developed adverse events including death, seizures, and significant weight loss. Post-hoc Student’s t test ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. All error bars represent S.E.M.