Abstract
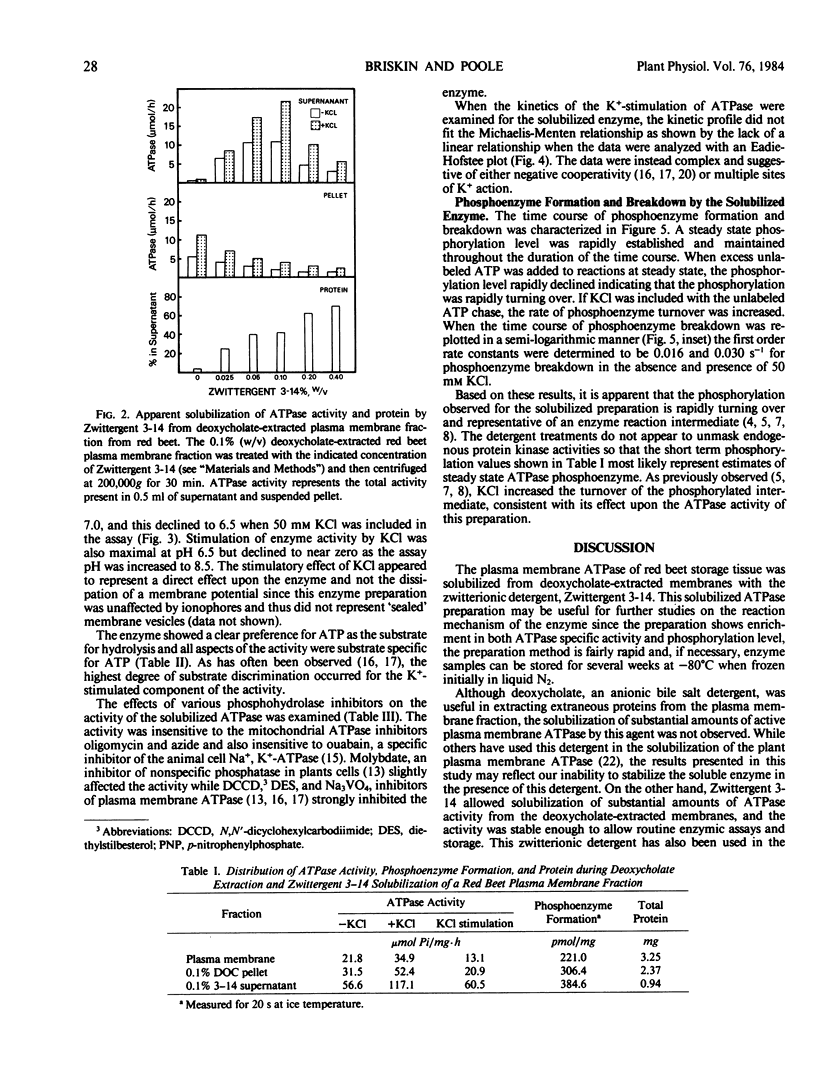
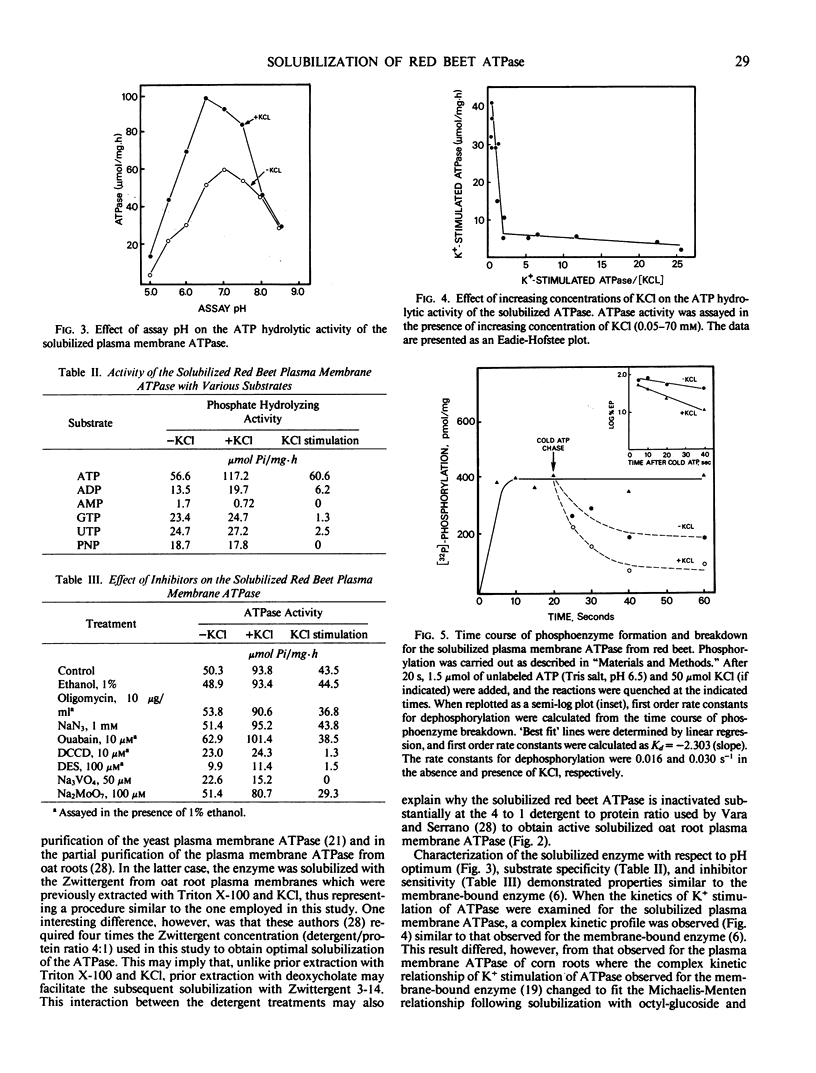
The plasma membrane ATP-phosphohydrolase (ATPase) from red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) storage tissue was solubilized with the zwitterionic detergent Zwittergent 3-14 from a plasma membrane-enriched fraction which was extracted with the anionic detergent, sodium deoxycholate. For both the extraction of extraneous proteins by deoxycholate and the solubilization of active plasma membrane ATPase by Zwittergent 3-14, the optimal concentration of detergent was 0.1% (weight per volume) with a detergent to protein ratio of 1.0 (milligram per milligram). The properties of the solubilized ATPase were found to be similar to the membrane-bound enzyme with respect to pH optimum, substrate specificity, inhibitor sensitivity, and kinetics of K+ stimulation. The solubilized ATPase preparation formed a rapidly turning over phosphoenzyme, the breakdown velocity of which was increased in the presence of 50 millimolar KCl. Solubilization with 0.1% Zwittergent 3-14 following extraction with 0.1% deoxycholate resulted in an increase in both ATPase activity and steady state phosphoenzyme level; however, a direct correspondence between the increase in ATPase activity and phosphorylation level did not exist. It is proposed that this discrepancy may be the result of a detergent-mediated modification of kinetic rate constants in the mechanism of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Leonard R. T. Partial characterization of a phosphorylated intermediate associated with the plasma membrane ATPase of corn roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Leonard R. T. Phosphorylation of the adenosine triphosphatase in a deoxycholate-treated plasma membrane fraction from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1459–1464. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Poole R. J. Characterization of a k-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase associated with the plasma membrane of red beet. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):350–355. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Poole R. J. Evidence for a beta-Aspartyl Phosphate Residue in the Phosphorylated Intermediate of the Red Beet Plasma Membrane ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1133–1135. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Poole R. J. Plasma membrane ATPase of red beet forms a phosphorylated intermediate. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):507–512. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Poole R. J. Role of magnesium in the plasma membrane ATPase of red beet. Plant Physiol. 1983 Apr;71(4):969–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.4.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Burke L. L., Spanswick R. M. Characterization of a partially purified adenosine triphosphatase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):59–63. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Leonard R. T. Solubilization and partial purification of the adenosine triphosphatase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):931–938. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Effect of vanadate, molybdate, and azide on membrane-associated ATPase and soluble phosphatase activities of corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1335–1340. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffeau A., Slayman C. W. The proton-translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):197–223. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. S., Albers R. W. The structure of proteins involved in active membrane transport. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:259–291. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hodges T. K. Characterization of Plasma Membrane-associated Adenosine Triphosphase Activity of Oat Roots. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jul;52(1):6–12. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hotchkiss C. W. Cation-stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity and Cation Transport in Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):331–335. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Koshland D. E., Jr The role of negative cooperativity and half-of-the-sites reactivity in enzyme regulation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:1–40. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida F., Serrano R. Purification of the yeast plasma membrane ATPase solubilized with a novel zwitterionic detergent. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80763-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. J., Briskin D. P., Krátký Z., Johnstone R. M. Density gradient localization of plasma membrane and tonoplast from storage tissue of growing and dormant red beet : characterization of proton-transport and ATPase in tonoplast vesicles. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):549–556. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs G., Berglindh T., Rabon E., Wallmark B., Barcellona M. L., Stewart H. B., Saccomani G. The interaction of K+ with gastric parietal cells and gastric ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;358:118–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalla R., Amory A., Rigaud J., Goffeau A. Phosphorylated intermediate of a transport ATPase and activity of protein kinase in membranes from corn roots. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Partial purification and properties of the proton-translocating ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12826–12830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Phosphorylated intermediate of the ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5334–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


