Abstract
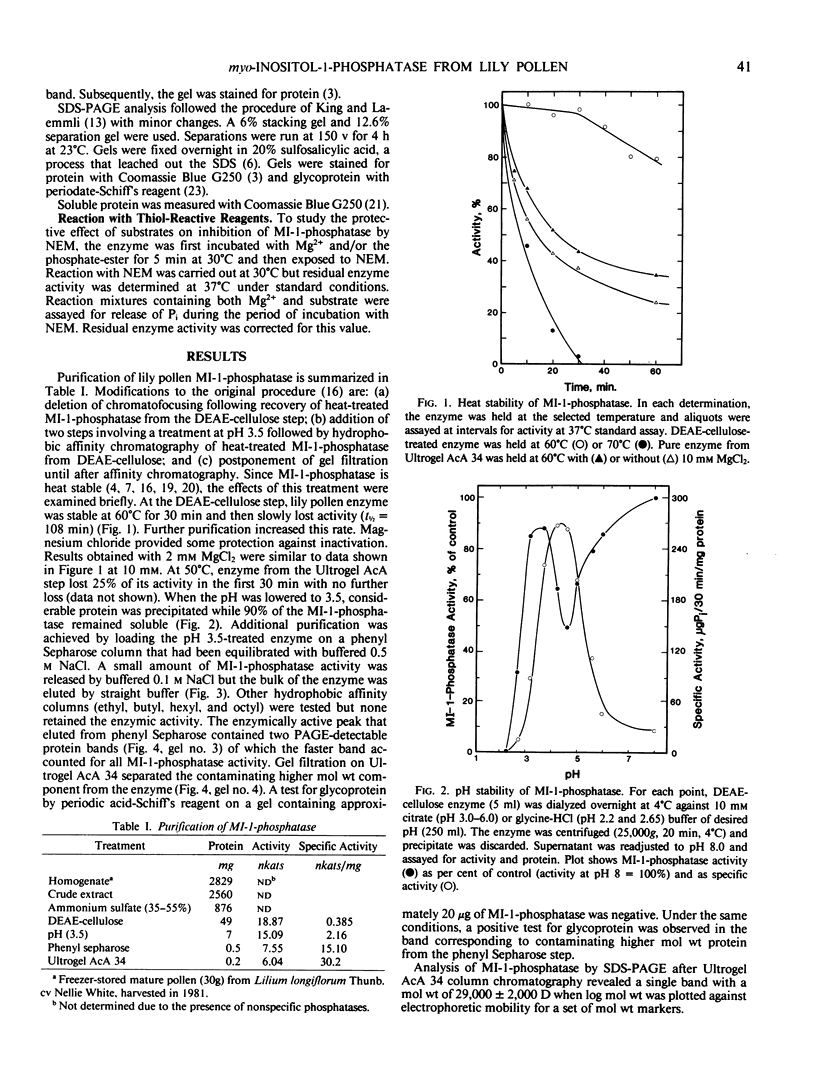
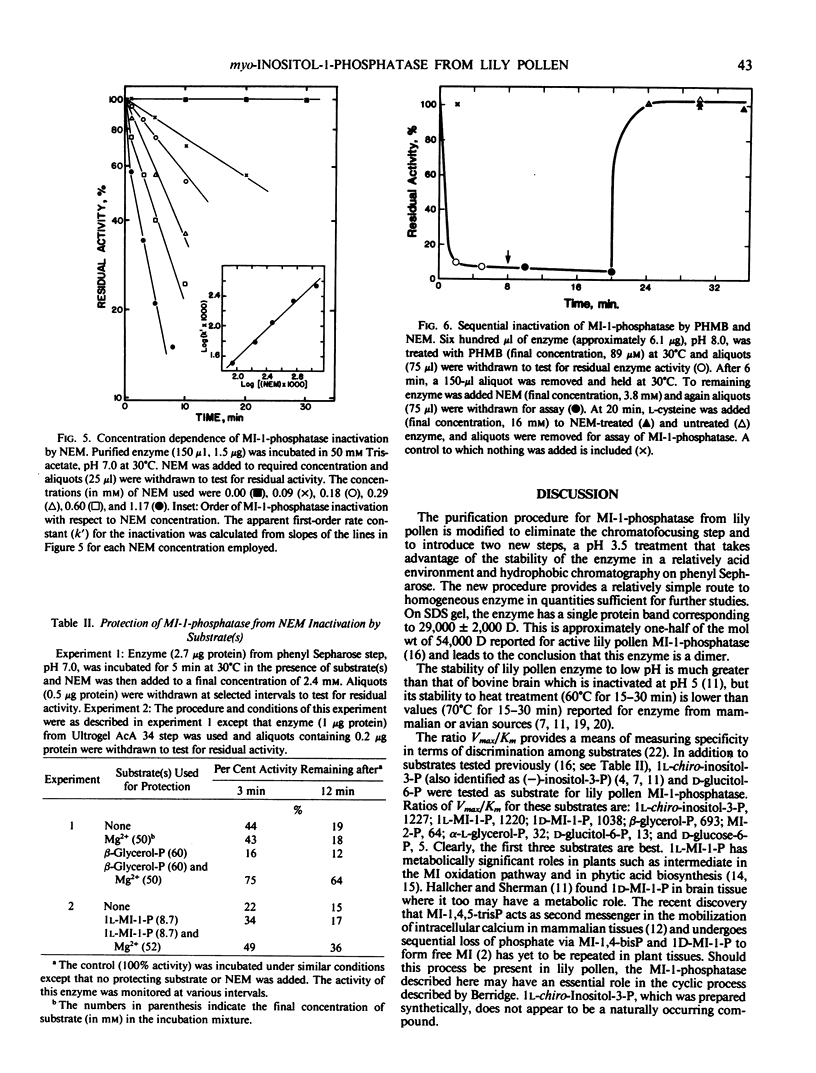
myo-Inositol-1-phosphatase has been purified to homogeneity from Lilium longiflorum pollen using an alternative procedure which includes pH change and phenyl Sepharose column chromatography. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis shows that the enzyme is a dimer (subunit molecular weight, 29,000 daltons). The enzyme is stable at low pH values and is inactivated only below pH 3.0. In addition to 1l-and 1d-myo-inositol-1-phosphate, it shows high specificity for 1l-chiro-inositol-3-phosphate. As observed earlier with other primary phosphate esters, d-glucitol-6-phosphate and d-mannitol-6-phosphate are hydrolyzed very slowly. No activity is observed with inorganic pyrophosphate or myo-inositol pentaphosphate as substrate. The enzyme is inhibited by fluoride, sulfate, molybdate, and thiol-directed reagents. Partial protection against N-ethylmaleimide inhibition by substrate and Mg2+ together suggests sulfhydryl involvement at the active site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baykov A. A., Artjukov A. A., Avaeva S. M. Fluoride inhibition of inorganic pyrophosphatase. I. Kinetic studies in a Mg2+-PPi system using a new continuous enzyme assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):982–992. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakesley R. W., Boezi J. A. A new staining technique for proteins in polyacrylamide gels using coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):580–582. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE GUBAREFF T., FURCHGOTT R. F. The determination of inorganic phosphate and creatine phosphate in tissue extracts. J Biol Chem. 1956 Nov;223(1):377–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg F., Jr D-myoinositol 1-phosphate as product of cyclization of glucose 6-phosphate and substrate for a specific phosphatase in rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1375–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewus M. W., Loewus F. A. myo-Inositol-1-Phosphatase from the Pollen of Lilium longiflorum Thunb. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):765–770. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccarato W. F., Ray R. E., Wells W. W. Biosynthesis of myo-inositol in rat mammary gland. Isolation and properties of the enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. C., Harkness D. R., Isaacks R. E. Studies on avian erythrocyte metabolism: purification and properties of myo-inositol 1-phosphatase form chick erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Sep;210(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



