Abstract
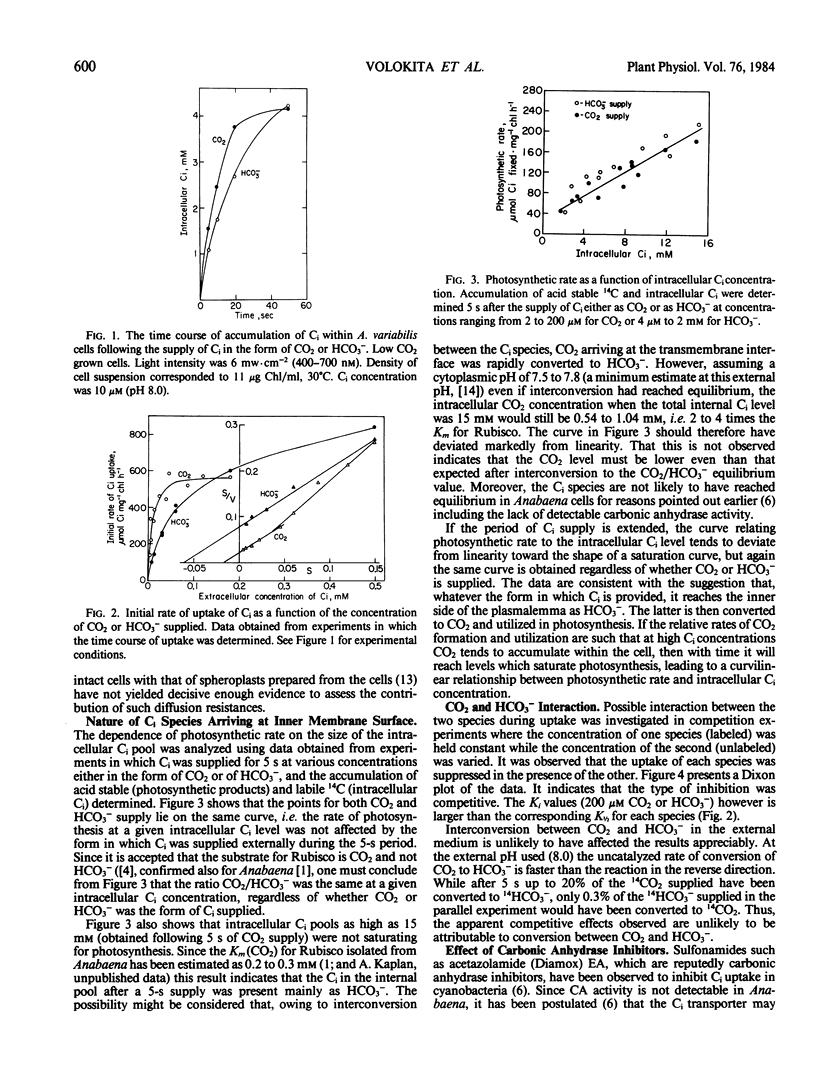
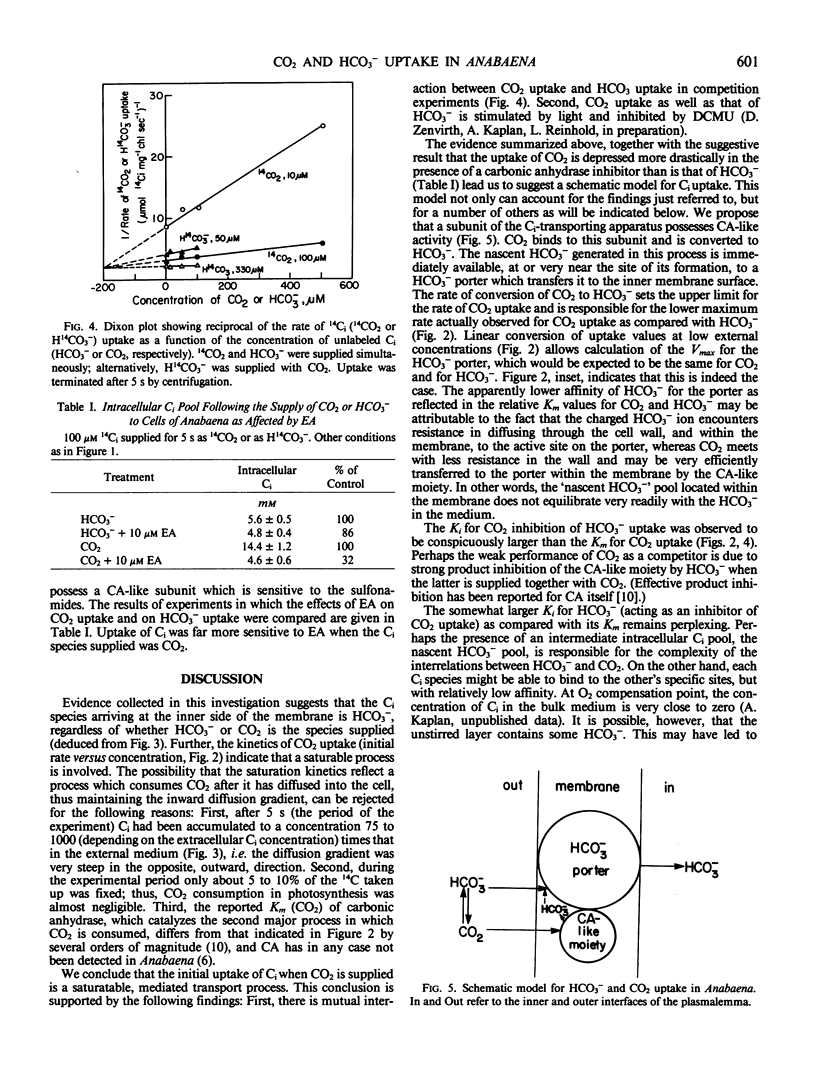
The nature of the inorganic carbon (Ci) species actively taken up by cyanobacteria CO2 or HCO3− has been investigated. The kinetics of CO2 uptake, as well as that of HCO3− uptake, indicated the involvement of a saturable process. The apparent affinity of the uptake mechanism for CO2 was higher than that for HCO3−. Though the calculated Vmax was the same in both cases, the maximum rate of uptake actually observed was higher when HCO3− was supplied. Ci uptake was far more sensitive to the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor ethoxyzolamide when CO2 was the species supplied. Observations of photosynthetic rate as a function of intracellular Ci level (following supply of CO2 or HCO3− for 5 seconds) led to the inference that HCO3− is the species which arrives at the inner membrane surface, regardless of the species supplied. When the two species were supplied simultaneously, mutual inhibition of uptake was observed.
On the basis of these and other results, a model is proposed postulating that a carboic anhydrase-like subunit of the Ci transport apparatus binds CO2 and releases HCO3− at or near a membrane porter. The latter transports HCO3− ions to the cell interior.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. Photosynthesis and Inorganic Carbon Usage by the Marine Cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):517–523. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R. Kinetic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Anabaena variabilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 15;201(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Filmer D. The active species of "CO2" utilized by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1081–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A., Zenvirth D., Reinhold L., Berry J. A. Involvement of a Primary Electrogenic Pump in the Mechanism for HCO(3) Uptake by the Cyanobacterium Anabaena variabilis. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):978–982. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volokita M., Kaplan A., Reinhold L. Nature of the rate-limiting step in the supply of inorganic carbon for photosynthesis in isolated asparagus mesophyll cells. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):886–890. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



