Abstract
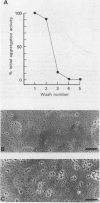
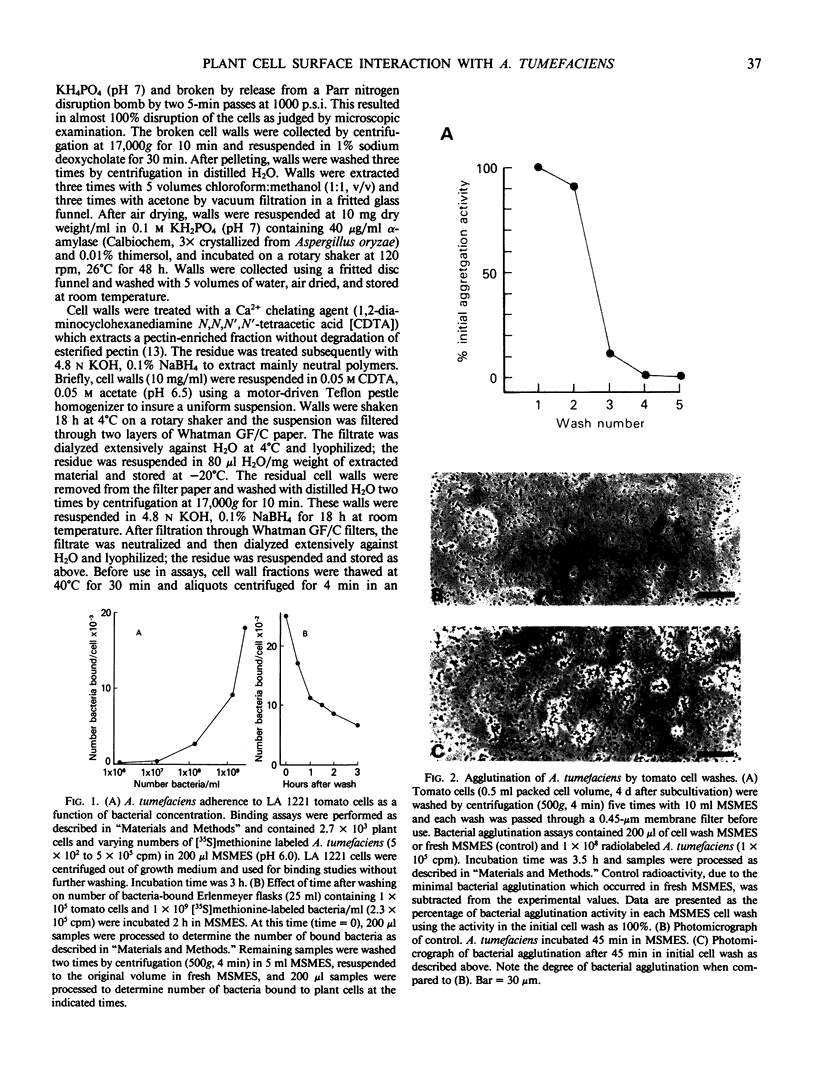
Adherence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to suspension-cultured tomato cells has been characterized using a quantitative binding assay. Saturable binding of radiolabeled A. tumefaciens to plant cells resulted in 100 to 300 bacteria bound per cell. Specificity of A. tumefaciens binding was also inferred from two additional results: (a) an initial incubation of plant cells with A. tumefaciens reduced subsequent binding of radiolabeled A. tumefaciens by 60% to 75%; (b) tomato cells bound less than three E. coli per cell. Protease treatment of plant cells had no effect on subsequent bacterial binding, but prior treatment of plant cells with pectinolytic enzymes increased binding 2- to 3-fold. Pectin-enriched and neutral polymer-enriched fractions were obtained from tomato cell walls. The soluble pectin-enriched fraction inhibited binding of bacteria to plant cells by 85% to 95%, whereas the neutral polymer fraction only partially inhibited binding. Preliminary characterization of the activity showed it is heat stable, partially inactivated by protease treatment, and substantially inactivated by acid hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker G. E., Hui P. A., Albersheim P. Synthesis of Extracellular Polysaccharide by Suspensions of Acer Pseudoplatanus Cells. Plant Physiol. 1964 Nov;39(6):913–920. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.6.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. W., Chilton M. D. T-DNA of the Agrobacterium Ti and Ri plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:357–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A., Herrera-Estrella L., Inzé D., Van Haute E., Van Montagu M., Schell J., Zambryski P. Introduction of genetic material into plant cells. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):815–821. doi: 10.1126/science.222.4625.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. J., Halperin W., Nester E. W. Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutants affected in attachment to plant cells. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1265–1275. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1265-1275.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott B. B., Lippincott J. A. Bacterial attachment to a specific wound site as an essential stage in tumor initiation by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):620–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.620-628.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott B. B., Whatley M. H., Lippincott J. A. Tumor induction by agrobacterium involves attachment of the bacterium to a site on the host plant cell wall. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):388–390. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott J. A., Lippincott B. B. Cell walls of crown-gall tumors and embryonic plant tissues lack agrobacterium adherence sites. Science. 1978 Mar 10;199(4333):1075–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4333.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthysse A. G., Wyman P. M., Holmes K. V. Plasmid-dependent attachment of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to plant tissue culture cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):516–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.516-522.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins D. J., English P. D., Albersheim P. The specific nature of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jul;42(7):900–906. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.7.900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama K., Pelcher L. E., Schaefer A. In Vitro Binding of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to Plant Cells from Suspension Culture. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):382–387. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]