Abstract
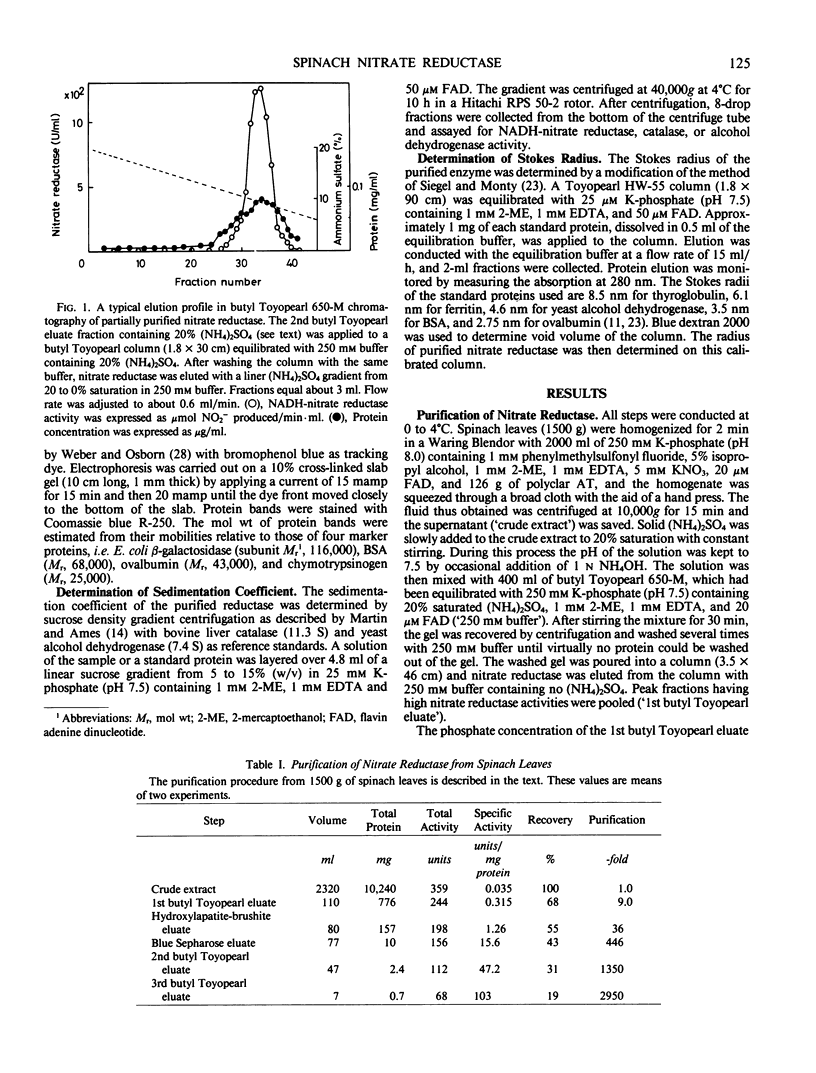
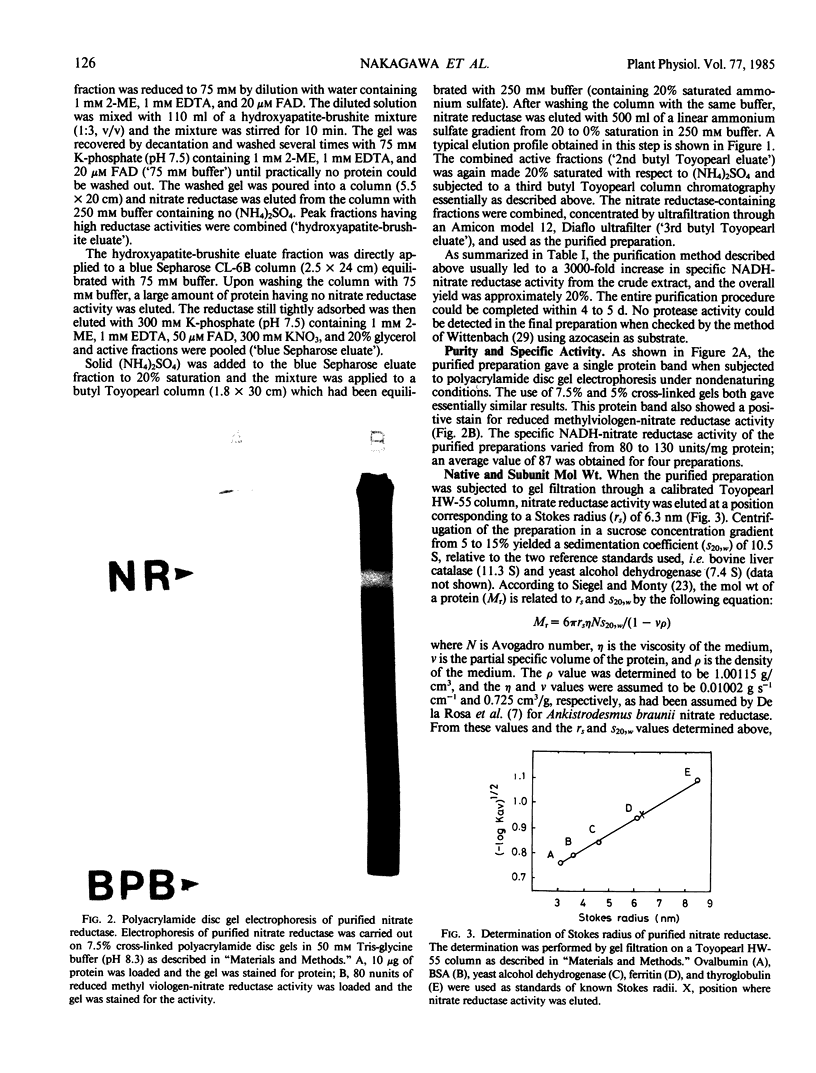
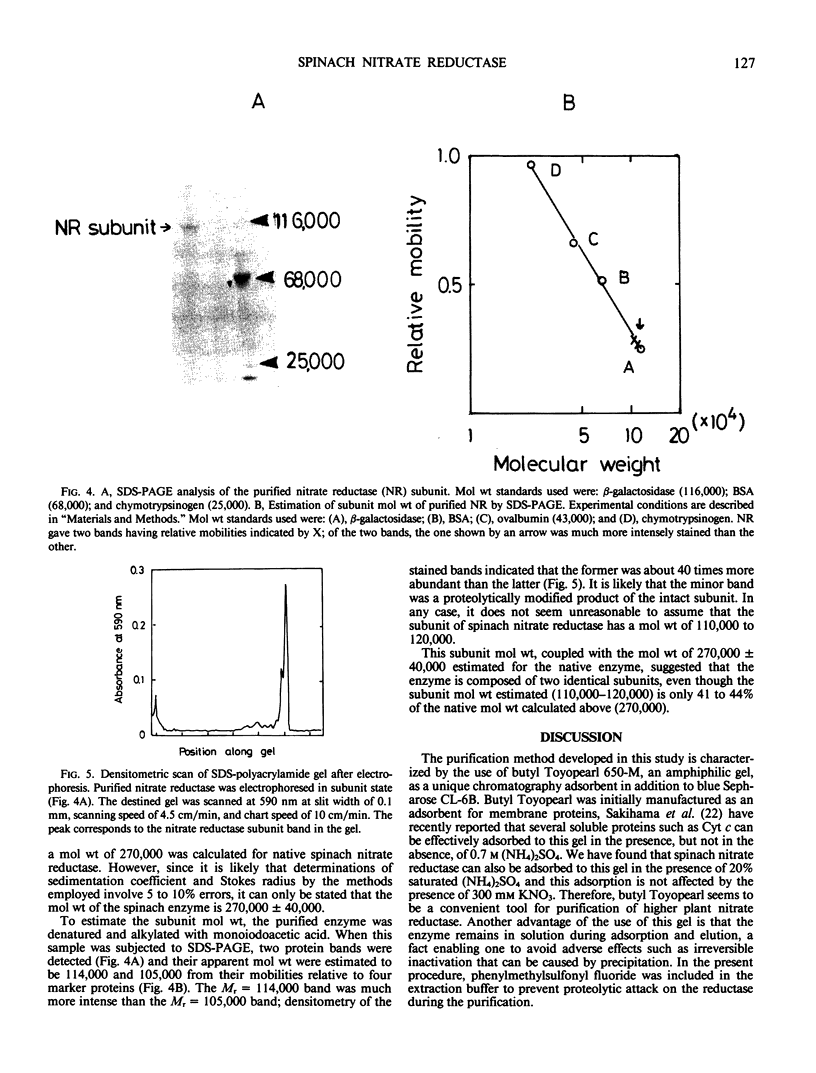
Nitrate reductase was purified about 3,000-fold from spinach leaves by chromatography on butyl Toyopearl 650-M, hydroxyapatite-brushite, and blue Sepharose CL-6B columns. The purified enzyme yielded a single protein band upon polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under nondenaturing conditions. This band also gave a positive stain for reduced methylviologen-nitrate reductase activity. The specific NADH-nitrate reductase activities of the purified preparations varied from 80 to 130 units per milligram protein. Sucrose density gradient centrifugation and gel filtration experiments gave a sedimentation coefficient of 10.5 S and a Stokes radius of 6.3 nanometers, respectively. From these values, a molecular weight of 270,000 ± 40,000 was estimated for the native reductase. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the denatured enzyme yielded a subunit band having a molecular weight of 114,000 together with a very faint band possessing a somewhat smaller molecular weight. It is concluded that spinach nitrate reductase is composed of two identical subunits possessing a molecular weight of 110,000 to 120,000.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. H., Smarrelli J. Purification and Kinetics of Higher Plant NADH:Nitrate Reductase. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):611–616. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Mann K. G., Tanford C. The estimation of polypeptide chain molecular weights by gel filtration in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4989–4994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero M. G., Jetschmann K., Völker W. The stereospecificity of nitrate reductase for hydrogen removal from reduced pyridine nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 12;482(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90349-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard W. D., Solomonson L. P. Quaternary structure of assimilatory NADH:nitrate reductase from Chlorella. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10243–10250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa H., Poulle M., Oaks A. Characterization of Nitrate Reductase from Corn Leaves (Zea mays cv W64A x W182E) : Two Molecular Forms of the Enzyme. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):285–289. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan S. S., Nason A. Purification and characterization of homogeneous assimilatory reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-nitrate reductase from Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 12;523(2):297–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redinbaugh M. G., Campbell W. H. Purification of Squash NADH:Nitrate Reductase by Zinc Chelate Affinity Chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):205–207. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrard J. H., Dalling M. J. In vitro stability of nitrate reductase from wheat leaves: I. Stability of highly purified enzyme and its component activities. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):346–353. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomonson L. P., Lorimer G. H., Hall R. L., Borchers R., Bailey J. L. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-nitrate reductase of Chlorella vulgaris. Purification, prosthetic groups, and molecular properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4120–4127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomonson L. P. Purification of NADH-Nitrate Reductase by Affinity Chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1975 Dec;56(6):853–855. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner F. X., Downey R. J. Isoelectric focusing and two-dimensional analysis of purified nitrate reductase from Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 7;706(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. T., Cass K. H., Stellwagen E. Blue dextran-sepharose: an affinity column for the dinucleotide fold in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):669–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenbach V. A. Breakdown of Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase and Change in Proteolytic Activity during Dark-induced Senescence of Wheat Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):604–608. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa M. A., Diez J., Vega J. M., Losada M. Purification and properties of assimilatory nitrate reductase [NAD(P)H] from Ankistrodesmus braunii. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):249–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]