Abstract
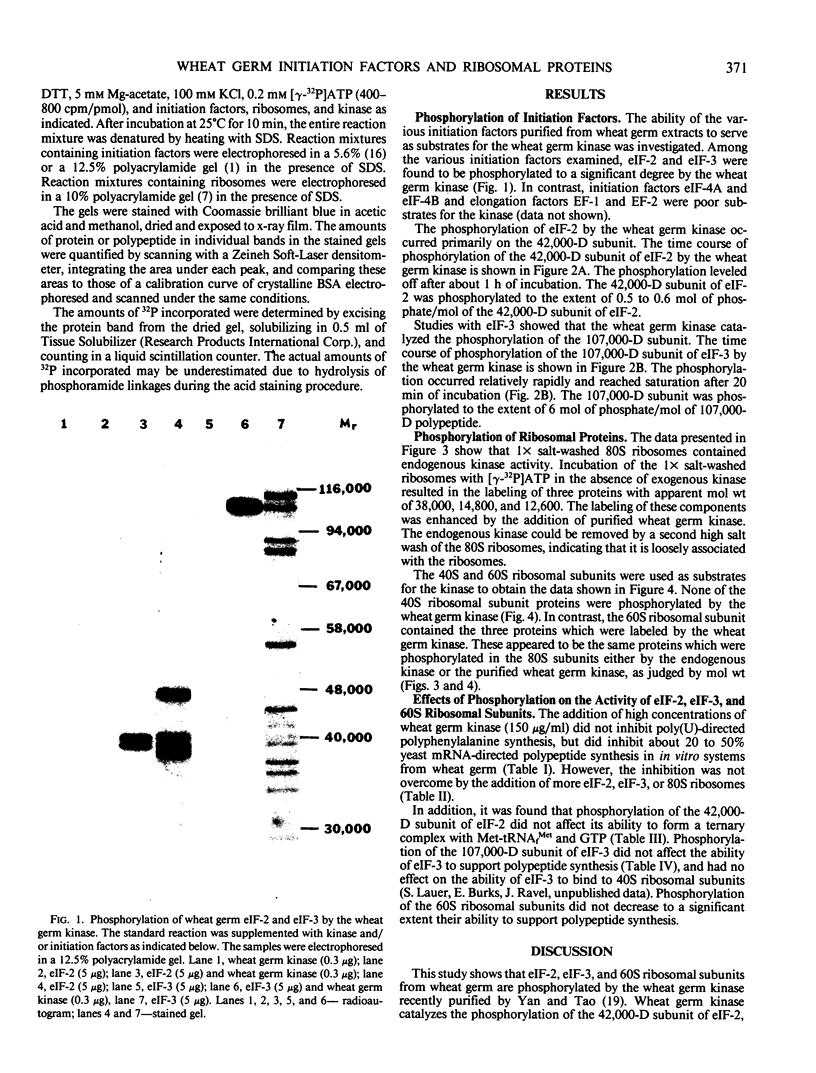
The ability of the wheat germ initiation factors and ribosomes to serve as substrates for a wheat germ protein kinase (Yan and Tao 1982 J Biol Chem 257: 7037-7043) has been investigated. The wheat germ kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of the 42,000 dalton subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF)-2 and the 107,000 dalton subunit of eIF-3. Other initiation factors, eIF-4B and eIF-4A, and elongation factors, EF-1 and EF-2, are not phosphorylated by the kinase. Quantitative analysis indicates that the kinase catalyzes the incorporation of about 0.5 to 0.6 mole of phosphate per mole of the 42,000 dalton subunit of eIF-2 and about 6 moles of phosphate per mole of the 107,000 dalton subunit of eIF-3. Three proteins (Mr = 38,000, 14,800, and 12,600) of the 60S ribosomal subunit are phosphorylated by the kinase, but none of the 40S ribosomal proteins are substrates of the kinase. No effects of phosphorylation on the activities of eIF-2, eIF-3, or 60S ribosomal subunits could be demonstrated in vitro.
Full text
PDF
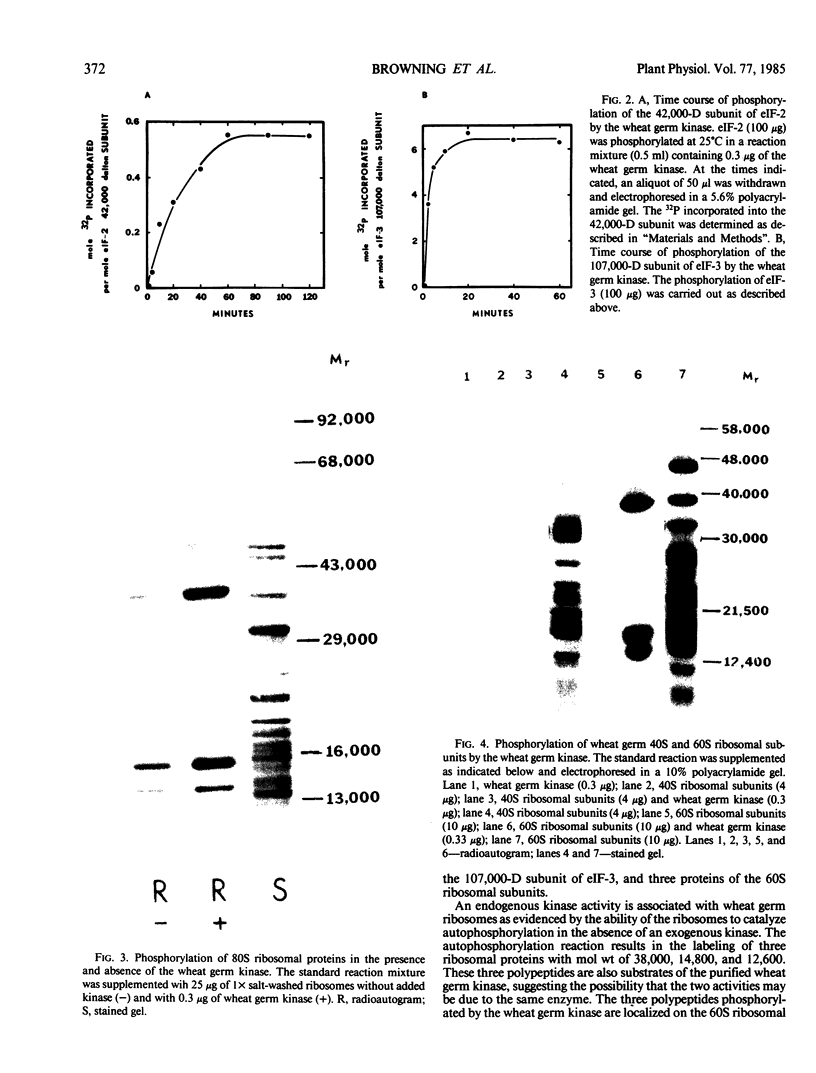
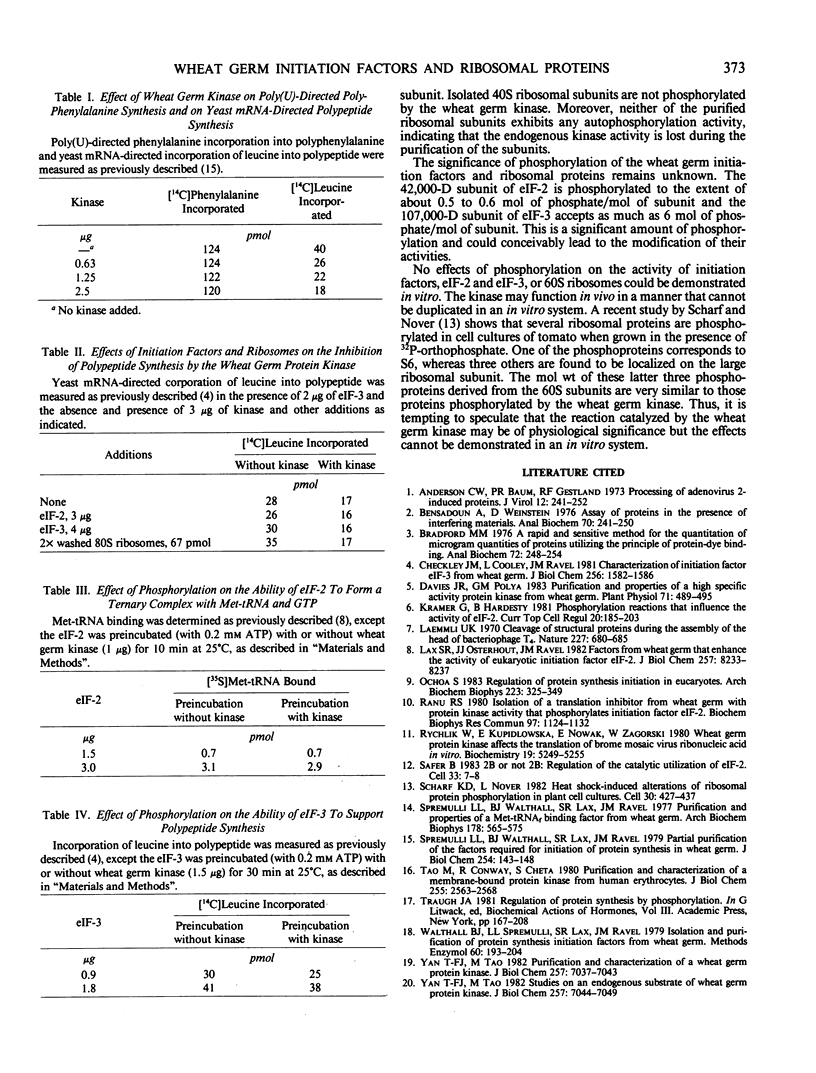
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checkley J. W., Cooley L., Ravel J. M. Characterization of initiation factor eIF-3 from wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1582–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. R., Polya G. M. Purification and properties of a high specific activity protein kinase from wheat germ. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):489–495. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Hardesty B. Phosphorylation reactions that influence the activity of elF-2. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;20:185–203. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152820-1.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax S. R., Osterhout J. J., Ravel J. M. Factors from wheat germ that enhance the activity of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2. Isolation and characterization of Co-eIF-2 beta. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8233–8237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S. Regulation of protein synthesis initiation in eucaryotes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):325–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S. Isolation of a translational inhibitor from wheat germ with protein kinase activity that phosphorylates initiation factor eIF-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 16;97(3):1124–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91492-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Kupidlowska E., Nowak E., Zagórski W. Wheat germ protein kinase affects the translation of Brome Mosaic virus ribonucleic acid in vitro. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5249–5255. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Nover L. Heat-shock-induced alterations of ribosomal protein phosphorylation in plant cell cultures. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):427–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spremulli L. L., Walthall B. J., Lax S. R., Ravel J. M. Partial purification of the factors required for the initiation of protein synthesis in wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spremulli L. L., Walthall B. J., Lax S. R., Ravel J. M. Purification and properties of a Met-tRNAf binding factor from wheat germ. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):565–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Conway R., Cheta S. Purification and characterization of a membrane-bound protein kinase from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2563–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walthall B. J., Spremulli L. L., Lax S. R., Ravel J. M. Isolation and purification of protein synthesis initiation factors from wheat germ. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:193–204. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan T. F., Tao M. Purification and characterization of a wheat germ protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7037–7043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan T. F., Tao M. Studies on an endogenous substrate of wheat germ protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7044–7049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]