Abstract
The topic of financial wellbeing is a current concern within the realm of personal and household finance. This study aims to examine the influence of cognitive factors, specifically financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control, on subjective financial wellbeing. While there exist multiple determinants of financial wellbeing, this research focuses on these particular cognitive factors. The present study aims to examine the mediating role of investment decision-making behavior in the association between cognitive factors and financial well-being. The study employed Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) to analyze the data collected from a sample of 449 Chinese university students, with the aim of assessing the empirical associations. The results indicate that financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control exert a favorable and noteworthy influence on an individual’s financial well-being. The results indicate that individuals with a greater degree of financial literacy are more prone to achieving superior financial well-being. Moreover, individuals who practice mental budgeting, a technique that entails mentally classifying and monitoring their expenditures, demonstrate elevated levels of financial well-being. Likewise, the exercise of self-regulation is identified as a pivotal element that impacts an individual’s financial wellbeing. The findings indicate that there is evidence to support the mediator, investment decision-making behavior. This mediator partially mediates the association between the independent variables, namely financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control, and financial well-being. The results suggest that individuals with elevated levels of financial literacy, proficient mental budgeting skills, and self-regulatory abilities are inclined towards demonstrating favorable investment decision-making conduct. Consequently, this contributes to their general financial welfare. In general, the study’s theoretical implications augment the current knowledge repository, while its practical implications provide feasible perspectives for policymakers, financial institutions, and individuals to foster financial wellness and enhance financial results.
1. Introduction
The world’s biggest public health issues are depression, anxiety, and stress. Mental health issues affect 84 million Europeans, or 17.3% of the population, according to the Global Health Data Exchange [1]. Depression and anxiety are the most common mental health problems in society. Public health concerns include anxiety and mood disorder increase [2]. In 2017, Fiksenbaum et al. [3] discovered that 4.4 percent of people worldwide have anxiety disorders, with 3.6 percent exhibiting symptoms. Poor mental health is caused by psychological stress, employment issues [4], and socioeconomic causes [5]. Financial hardship is rising, according to WHO data [6]. The UK survey [7] and PwC’s Employee Financial Wellness Survey [8] in the US reached similar conclusions. Employees reported financial stress higher than any other type of stress in the poll. The Chinese social structure has similar issues. HSBC found that 64% of Chinese are satisfied with their finances in 2019, up from 57% in 2016. The poll found that 36% of Chinese people worry about saving for retirement and 29% about paying unexpected costs [9]. Researching a person’s money management, spending, saving, and investing habits is called "financial well-being" [10]. Lack of financial wellbeing causes financial distress, which lowers physical and mental health and workplace productivity [11–14]. If they think their salary isn’t enough to meet their basic needs, people feel disadvantaged financially [15].
Several things affect and improve financial well-being. Financial literacy helps people make informed and responsible financial decisions, boosting financial stability and reducing financial worries [16]. Financial literacy gives people the information, skills, attitudes, and behaviors to manage their money and reach their goals [17]. It educates people about financial ideas, risks, and decisions [18]. Financial literacy encourages budgeting, saving, and investing, which improves financial health. They can handle complex financial decisions and avoid financial hazards better. Financial literacy helps people manage their income at difficult times like the COVID-19 epidemic [19]. Mental budgeting is also crucial to financial health. Individuals and households utilize cognitive operations to arrange and control their finances [20]. It entails budgeting for several expenditure categories and mentally dividing the monies [21]. Mental budgeting aids in spending tracking, goal setting, and financial decision-making [20]. Many research have shown the benefits of mental budgeting for financial health. According to Chun & Johnson [22], consumers with superior mental budgeting skills are more resistant to store promotions and price fluctuations. This implies that mental budgeting can help people avoid impulse purchases and stay to their budgets. Financial well-being also depends on self-control. Many research have examined the relationship between self-control and financial outcomes like financial assets and financial management behavior. Self-control is the ability to manage ideas, emotions, and actions to attain long-term goals and avoid temptation [23]. It requires the ability to think rationally, control impulses, and manage money [23, 24]. Higher self-control has been linked to improved financial outcomes. Better self-control leads to increased financial assets [24]. They are also more likely to budget, save, and regulate spending [25]. Self-control improves financial planning and saving [26]. Greater self-control is a key predictor of financial security, as persons with it tend to save and avoid debt [27].
Investment decisions are vital to financial well-being. Several elements increase financial well-being through investing decision-making. Financial literacy matters. According to Kamakia et al. [28], financially literate people make better investment decisions and have higher financial stability and well-being. Financial literacy improves investment decisions by helping people understand and analyze information [29]. Investment decision-making mediates mental budgeting and financial well-being [22]. Financial decision-making is influenced by mental budgeting. Credit cards can mix expenditures across budgeted categories and increase temporal distance between purchases and payments, making it harder to remember how much was spent on each [22]. This may lead to overspending or bad budget management, affecting finances. Self-control affects financial well-being through investment decisions. Self-control is the ability to manage behavior and make decisions that support long-term goals [30]. Research shows that self-control improves financial decisions. Higher self-control leads to more wise investment decisions and improved financial wellbeing [31].
Amid the Great Recession and COVID-19 pandemic, individuals, families, legislators, financial service providers, and financial educators need more understanding about financial well-being and how to improve it. This study makes significant literary contributions. First, this study examines the complex interaction between financial literacy, mental budgeting, self-control, and investment decision making, adding to financial wellbeing research. Examination of these structures together provides a more complete knowledge of financial wellbeing variables. Second, study examines mental budgeting and self-control in financial decision making to connect psychological and economic aspects. This integrated approach adds depth to the research by acknowledging that cognitive and behavioral processes affect financial wellbeing as well as economic considerations. Third, investment decision making as a mediator between financial literacy, mental budgeting, self-control, and financial health is another theoretical contribution. This mediation model shows how various factors affect financial well-being. It explains how financial knowledge, mental budgeting, and self-control affect financial outcomes. Financial educators, counselors, and policymakers can apply the study’s conclusions. By recognizing investment decision making as a mediator, it suggests interventions and education to improve financial literacy, mental budgeting, self-control, and financial health. The study emphasizes the need to evaluate many financial wellbeing elements at once. It promotes a holistic approach that emphasizes the interdependence of financial literacy, cognitive processes (mental budgeting), behavioral attributes (self-control), and investment decisions in financial well-being.
Rest of the paper is distributed among four sections: literature and hypotheses, methodology, results and conclusions.
2. Literature and hypotheses
The body of research that is now available on the topic of financial well-being hints that the concept of financial well-being is a subjective evaluation of one’s present and future financial situation [32–35]. The relevance of objective economic measurements, such as a consumer’s income, savings, and investments, credit score, credit card debt, regular mortgage payment, and tax payments, was stressed in much early academic research in the financial wellbeing field [36–38]. The subjective evaluation of financial wellbeing, on the other hand, focuses on the consumer’s self-assessment of his or her disposition, attitude, belief, and behaviors linked to money management [32, 35]. According to this subjective interpretation of financial wellbeing, two people with comparable salaries or debt loads may regard their own financial wellbeing very differently. Due to importance of subjective financial wellbeing for researchers studying consumer behavior, financial institutions (FIs), non-profit organizations, businesses, and decision-makers in the government, study choose to investigate subjective side of this contrast. The relationships described in the study, which examines the impact of financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control on financial wellbeing with the mediating role of investment decision making, can be supported by several theories from the fields of economics, psychology, and behavioral economics, this study uses cognitive dissonance theory. Cognitive Dissonance Theory suggests that individuals strive for consistency in their beliefs and behaviors [39]. Financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control can influence the alignment of an individual’s financial decisions with their overall financial goals and values, reducing cognitive dissonance and enhancing financial wellbeing.
2.1. Financial literacy
Financial literacy refers to the knowledge of basic financial concepts, the ability to apply financial knowledge and skills in managing financial resources effectively, and the ability to make informed financial decisions to achieve financial welfare over a lifetime [40–44]. It involves understanding of financial matters, the ability to make conscious choice of financial products and services, and techniques for making appropriate financial decisions. Financial literacy translates into prosperity and sustainable development and helps in ensuring the financial sustainability of individuals, families, enterprises, and national economies [45]. It also includes a capacity and confidence to handle personal funds appropriately, short-term decision making and solid long-term financial thinking [46]. Moreover, being familiar with finance-related issues and making rational financial decisions based on basic financial knowledge are also crucial components of financial literacy [45, 47]. Subjective financial knowledge, which refers to individuals’ self-evaluation of their financial knowledge, has been found to be a stronger predictor of financial behavior and subjective financial wellbeing than objective financial knowledge [48]. This indicates that individuals who perceive themselves to have higher financial knowledge tend to have higher levels of financial satisfaction and overall financial wellbeing. However, Balasubramnian and Sargent [49] investigate gaps between objective financial literacy and self-reported (perceived) financial literacy and report that individuals with high objective financial literacy make better financial decisions. A study by Joo and Grable [50] sought to identify the variables that affect financial contentment. According to the survey’s findings, financial contentment is directly influenced by factors including education level, financial literacy, risk, financial capability, financial activity, and financial demands. The findings demonstrated that improving financial behaviors increases levels of financial happiness at high knowledge and skill levels. As a result, their research suggested that financial literacy affected financial well-being directly. Another study [51] looked at the connections between 3,121 clients of a financial consulting firm’s financial activity, financial well-being, and health. According to their findings, those who have a greater level of financial well-being are less stressed, more motivated to manage their money, have better family relationships, and are physically and mentally healthier. Due to their advanced age and high level of vulnerability, retirees place a high priority on their financial well-being. They might experience physical or mental health effects from certain financial stress. In a research measuring financial literacy [52], authors found that even those with the information and skills to use that knowledge may not always behave as expected or experience advances in financial well-being due to a variety of factors. Such effects might be caused by cognitive biases, issues with self-control, family, economic, and institutional factors. However, another research [53] discovered that students’ perceptions of their financial well-being were significantly influenced by their financial literacy. Higher financial literacy correlates with greater financial well-being, according to a study [16] on financial literacy, financial well-being, and financial concerns. As a result, financial literacy is required to achieve financial well-being.
2.2. Mental budgeting
Mental budgeting is the cognitive process that people use to organize, evaluate, and keep track of financial activities [54]. It is a financial management technique that involves categorizing and monitoring expenses and income on a mental level [20]. Mental budgeting has an essential role to play in improving financial well-being because it can positively influence personal financial management [21] and consumer budgeting behavior [22]. Studies have shown that mental accounting can aid in monitoring personal spending, consumption, and investments and improve financial self-efficacy and control [55]. It can help socially excluded individuals make better financial decisions [56]. Mental accounting also affects budgeting, investing, and spending decisions [57]. Thus, it plays a central role in improving financial health and helps individuals, communities, and governments in managing their finances [58]. Mental budgeting helps individuals manage their finances better, make informed financial decisions, reducing financial stress, and improving financial self-efficacy. According to [59], financial literacy empowers individuals with knowledge and skills to manage their money effectively. Studies have shown that mental budgeting motivates and positively affects personal financial management [20] and reduces unduly risky personal investment behavior by triggering mental budgeting thoughts [21]. The impact of financial wellbeing and mental health are interlinked, and financial stress is a significant source of stress for many individuals, leading to mental health challenges [22]. Mental budgeting has been identified as a key factor in promoting financial wellbeing and reducing the risk of financial stress impacting an individual’s mental health. Multiple studies have been conducted to explore the relationship between mental budgeting and financial wellbeing in recent years. A systematic review by [60] identified the importance of proactive prevention, such as financial education and literacy, in reducing the burden of mental depression caused by financial stress. Similarly, mental budgeting was highlighted as a significant factor in promoting positive financial management behaviors, reducing financial stress, and improving financial wellbeing [61].
2.3. Self-control
Self-control, often called self-regulation, is the ability to control one’s conduct and reduce impulsivity [62]. Research shows that self-control and financial knowledge improve financial well-being [63]. Self-control, financial understanding, and financial literacy affect financial behavior and decision-making [64]. Self-control is needed to manage finances and prioritize goals in personal financial planning programs. A study on self-control, money attitude, and personal financial planning indicated that self-control affects financial planning [65]. Other research have linked self-control to occupational stress [66], self-directed learning readiness [67], and self-disgust [68].
The financial conduct of all different kinds of economic actors can be influenced by one’s level of self-control. According to Thaler and Shefrin [69], the concept of self-control may be applied to the individual as if they were an organization. According to Baumeister [70], people have a tendency to get confused as a result of conflicts between their behaviors and feelings; yet, inner strength creates self-control. The research conducted by [71] utilized three aspects of self-control: planning, monitoring, and commitment. The researchers came to the conclusion that self-control has a significant correlation with household net wealth and financial hardship. Self-control is beneficial for making decisions, having a strong will, and achieving success in the future, whether that achievement be being wealthy or prominent. The inability to exercise self-control can result in illogical decision making, a lack of confidence, and disastrous behavioral outcomes. The ability of a person to exercise self-control in the present and make sound choices will determine their potential financial well-being in the future. People tend to put their goals off till later, and when they want to improve their performance, they will sometimes try to restrict their behavior by placing stringent restrictions and deadlines on themselves.
According to [72], people who have deadlines that are too stringent tend to have less self-control than those who have deadlines that are not stringent enough. The difficulty of exercising self-control may also be understood through Shefrin and Thaler’s [73] Behavioral Life-Cycle (BLC). According to the BLC theory, the majority of individuals are preoccupied with the challenges and rewards of the now rather than the advantages of the long term. People create mental accounts in order to employ the resources that are accessible to them by categorizing their wealth into three categories, such as their present income, their current assets, and their future income [74]. According to Moffitt et al. [75], individuals lack control over their income and as a result spend more money on their immediate need rather than putting away more money for retirement and other future needs. People who have higher self-control also have better financial conduct and are able to take excellent care of their financial resources. Self-control is a key factor in both of these areas. They invest their resources in the most effective way possible [76]. They do not waste money on activities or products that are not important to their lives. People who have mastered the art of self-control have been at the forefront of society for eons, and they continue to do so now. This is due to the fact that self-control is a prerequisite for making sage choices and enjoying improved material circumstances. Households who have established saving guidelines save significantly more money than households that lack self-control. According to Kahneman [77], people who have cognitive capacities always manage their money in a way that allows them to attain their objectives and pay for their predictable costs. Planners and doers are the two types of people that Thaler and Shefrin [69] have determined people to be based on how well they exercise self-control over their finances. To them, planners are concerned with the utility across a lifetime, whereas doers are self-centered, shortsighted, and only exist for a short period of time. To live a prosperous and healthy life, both financially and emotionally, one of the goals that one must achieve is to have good financial well-being. This can only be accomplished via exercising self-control. Most of the studies measured self-control using Brief Self-Control Scale [78] and Short-Term Future Orientation Scale [59].
2.4. Investment decision making
Investment decision-making behavior refers to the process of making decisions related to finances and investments by individuals, which are influenced by various factors such as financial knowledge, financial attitude, financial behavior, self-control, psychological biases, and external environment. Financial knowledge plays an important role in making informed financial decisions, while financial behavior refers to the habits and behavior of individuals when managing finances. Self-control enables individuals to make rational and informed decisions while managing their finances. Psychological biases such as herding, heuristics, and prospect also affect the financial decision-making behavior of individuals. In summary, financial decision-making behavior is a complex process influenced by various rational and psychological factors that impact an individual’s financial wellbeing [79–82].
Financial or investment decision making behavior is a crucial determinant of financial well-being. It has been established that this behavior has a positive influence on financial well-being [83]. Moreover, financial well-being is directly and indirectly related to financial behavior [83]. Financial behavior is the result of putting expectations and values into action, and it is the link between expectations and financial well-being. Hence, better financial behavior translates to better financial well-being.
Several studies have shown that financial literacy and self-control are significant determinants of financial behavior and financial well-being. Research has found that financial literacy has a significant direct impact on financial well-being, and it affects financial well-being through financial behavior [84]. Similarly, financial self-efficacy and financial literacy positively influence financial well-being through financial behavior mediation [63].
Furthermore, the research has shown a positive relationship between parental financial socialization and financial literacy, financial behavior, and financial well-being. Delafrooz and Paim [85] found that higher levels of financial literacy led to better financial behavior, which in turn resulted in higher financial well-being. Studies have also explored the relationships between financial behavior, financial knowledge, and financial well-being. For instance, research [86, 87] showed that subjective knowledge had stronger relationships with both financial behavior and financial well-being than objective knowledge. Further, it was established that money attitudes and financial knowledge significantly influenced financial behavior. Money attitudes have also been found to have a positive influence on financial management behavior, which in turn impacts financial well-being.
In conclusion, financial decision making behavior has a significant impact on financial well-being. Financial literacy, self-control, parental financial socialization, financial knowledge, and money attitude have been shown to influence financial behavior and thus impact financial well-being. It is crucial, therefore, to educate individuals on the importance of financial behavior and its role in achieving financial security.
Based on previous discussion, following hypotheses are developed:
H1: financial literacy has a significant direct impact on financial wellbeing.
H2: Mental budgeting has a significant direct impact on financial wellbeing.
H3: Self-control has a significant direct impact on financial wellbeing.
H4: Investment decision making has a significant direct impact on financial well-being.
H5: Investment decision making has a significant mediating effect between mental budgeting and financial well-being.
H6: Investment decision making has a significant mediating effect between financial literacy and financial well-being.
H7: Investment decision making has a significant mediating effect between self-control and financial well-being.
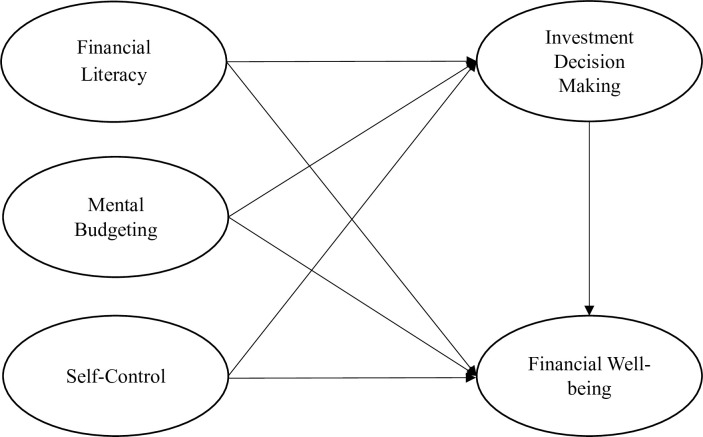
The conceptual model represents the selections of the variables from the critical review of the literature, and we expect their relationship in shape of figure. Moreover, our conceptual model of the study is given in Fig 1.
Fig 1. Research conceptual model.
3. Methodology
3.1. Data
Sample was chosen using the criteria based on number of items. Convenience sampling was used to collect the data. Data was collected from Chinese university students using both physical and electronic channels which resulted in a set of 449 useable observations. Respondents included 245 male (55%) and 204 female (45%) students. 270 (60%) of these respondents belonged to business major. Table 1 shows the distribution of collected data.
Table 1. Data.
| Variable | Indicator | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 245 | 54.6 |
| Female | 204 | 45.4 | |
| Ongoing Qualification Level | Undergraduate | 239 | 53.2 |
| Masters | 112 | 24.9 | |
| Doctor | 98 | 21.8 | |
| Ongoing Qualification Major | Business | 270 | 60.1 |
| Non-Business | 179 | 39.9 |
3.2. Measures
We employed two separate measures to capture the diverse aspects of one’s financial well-being: one, the extent to which one suffered from financial anxiety, and the other is the degree to which one felt financially secure. For the purpose of quantifying anxiety caused by financial concerns, four items from [88] were selected. When calculating the level of financial security, [14] takes into account three different factors. The respondent was asked to rate how strongly they agreed or disagreed on a scale from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree).
Seven items for measuring financial literacy have been adopted from a study [89].
Four items were adopted from a past study of mental budgeting andmanagement of household finance [59].
Self-control is quantified through a general measure which is a smaller version of the Brief Self-Control Scale [78]. It consists of five items, and the four items from the Short-Term Future Orientation Scale [59].
Scale for financial management or investment decision making behavior is adopted [90] and contains four components: overall financial management or decision making behavior, savings and investment, cash management and credit management.
List of the items used for measurement is given in S1 File.
3.3. Ethical statement
The present investigation pertains to the participation of human subjects, and therefore, ethical clearance was obtained subsequent to its evaluation by the research council of Henan Institute of Economics and Trade, located in Zhengzhou, Henan, China. The study was conducted in accordance with the research ethics guidelines of Henan Institute of Economics and Trade. Participants were accurately informed what is being studied, the benefits and risks of the study. Participants were also aware of their right to withdraw from the study at any point, all respondent gave their verbal informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study.
3.4. Analysis
Path analysis and regression are two areas in which Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) excels. SEM is particularly useful when dealing with several variables. The PLS-SEM approach is being utilized throughout this investigation so that Path analysis may be performed. The benefits of utilizing PLS-SEM include the fact that it is more flexible with the sample sizes and is also less vulnerable to the violations of the multivariate data assumptions, such as normality of data. These are only few of the advantages of utilizing PLS-SEM. [91].
4. Results
4.1. Measurement model
Stage one in the estimation of the measurement model included indicator reliability measurement through factor (outer) loadings, internal reliability measurement through composite reliability, convergent validity measurement through average variance extracted. The table shows that all of the indicators have loadings of more than 0.50 (range: 0.637–1.000), which is the value recommended by Nunnally [92] and Hair et al. [93]. All of the constructs obtained composite reliability values (range: 0.714 to 0.845) greater than 0.70, which is the value recommended by [94–96]. Table 2 shows that the Cronbach’s alpha ranges from 0.743 to 0.821; the statistically acceptable minimum value is 0.70 [94–96]. AVE values should be greater than 0.50 [93, 97]. Our results meet these criteria.
Table 2. Factor loadings, composite reliability, Cronbach alpha, and average variance explained.
| Variable | Items | Loadings | CR | Cronbach Alpha | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Wellbeing | FWB1 | 0.823 | 0.845 | 0.821 | 0.773 |
| FWB2 | 0.785 | ||||
| FWB3 | 0.923 | ||||
| FWB4 | 0.812 | ||||
| FWB5 | 0.801 | ||||
| FWB6 | 0.765 | ||||
| FWB7 | 0.873 | ||||
| Financial Literacy | FL1 | 0.772 | 0.791 | 0.743 | 0.764 |
| FL2 | 0.704 | ||||
| FL3 | 0.770 | ||||
| FL4 | 0.818 | ||||
| FL5 | 0.880 | ||||
| FL6 | 0.859 | ||||
| FL7 | 0.737 | ||||
| Mental Budgeting | MB1 | 0.760 | 0.868 | 0.841 | 0.702 |
| MB2 | 0.822 | ||||
| MB3 | 0.855 | ||||
| MB4 | 0.807 | ||||
| Self-Control | SC1 | 0.776 | 0.799 | 0.796 | 0.692 |
| SC2 | 0.804 | ||||
| SC3 | 0.858 | ||||
| SC4 | 0.715 | ||||
| SC5 | 0.769 | ||||
| SC6 | 0.838 | ||||
| SC7 | 0.810 | ||||
| SC8 | 0.770 | ||||
| SC9 | 0.871 | ||||
| Investment Decision Making Behavior | DMB1 | 0.842 | 0.714 | 0.710 | 0.811 |
| DMB2 | 0.855 | ||||
| DMB3 | 0.866 | ||||
| DMB4 | 0.848 | ||||
| DMB5 | 0.857 | ||||
| DMB6 | 0.874 | ||||
| DMB7 | 0.856 | ||||
| DMB8 | 0.809 | ||||
| DMB9 | 0.760 |
4.2. Structural model
The path coefficients were assessed in order to test the hypotheses and determine the association between the psychological characteristics of the young people and their financial conduct as well as their overall financial well-being. The value of a variable’s path coefficient indicates the extent to which that variable was directly influenced by another variable. A value that is closer to 1 indicates that there is a stronger correlation, while a value that is closer to 0 indicates that there is a weaker relationship. Values close to zero are not statistically significant. Path coefficients are listed in the Table 3. Results indicate that all three independent variable (financial literacy, mental budgeting and self-control) are positively affect the dependent variable (financial-wellbeing).
Table 3. Path analysis.
| Paths | Beta | SE | t-stat | p-value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL--> DMB | 0.136 | 0.028 | 4.871 | 0.000 | Supported |
| MB--> DMB | 0.128 | 0.019 | 6.631 | 0.000 | Supported |
| SC--> DMB | 0.152 | 0.024 | 6.399 | 0.000 | Supported |
| DMB--> FWB | 0.126 | 0.067 | 1.892 | 0.059 | Supported |
| FL--> FWB | 0.299 | 0.037 | 8.073 | 0.000 | Supported |
| MB--> FWB | 0.102 | 0.028 | 3.704 | 0.000 | Supported |
| SC--> FWB | 0.182 | 0.033 | 5.494 | 0.000 | Supported |
4.3. Mediation
Baron and Kenny [98] argued for simultaneously considering direct and indirect effects to conclude mediation tests. We found that the direct effects of the independent variables (financial literacy and investment decision making behavior) on the dependent variable (financial well-being) were positive and statistically significant. Similar is the case for other two paths i.e. mental budgeting and investment decision making behavior and self-control and investment decision making behavior. The indirect effects in the presence of the mediator (investment decision making behavior) is also statistically significant. This concludes into partial mediation. The mediation results are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4. Mediation analysis.
| Path | Direct Effect | p-value | Indirect Effect | p-value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FL--> FWB | 0.136 | 0.000 | 0.017 | 0.034 | Partial Mediation |
| MB--> FWB | 0.128 | 0.000 | 0.016 | 0.035 | Partial Mediation |
| SC--> FWB | 0.152 | 0.000 | 0.019 | 0.036 | Partial Mediation |
5. Conclusion
Based on this investigation, it is evident that financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control have a positive and significant impact on subjective financial well-being. The findings suggest that individuals who possess a higher level of financial literacy are more likely to experience better financial well-being. This implies that having a strong understanding of financial concepts, such as budgeting, saving, and investing, can contribute to improved financial outcomes. These findings are consistent to previous literature [45–49]. Furthermore, individuals who engage in mental budgeting, which involves mentally categorizing and tracking their expenses, exhibit higher levels of financial well-being. This practice enables them to have a better grasp of their financial situation and make informed decisions regarding their spending habits and financial goals. Previous literature support this finding [22, 56, 60, 61]. Similarly, self-control emerges as a crucial factor influencing financial well-being. Individuals who exercise self-control, such as resisting impulsive purchases and sticking to their financial plans, are more likely to achieve better financial outcomes. This finding suggests that maintaining discipline and self-restraint in financial matters can significantly contribute to one’s financial well-being. This outcome is also in line with the existing empirical evidence [63, 64, 69]. Results reveal support for the mediator, investment decision-making behavior, which partially mediates the relationship between the independent variables (financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control) and financial well-being. The findings indicate that individuals who possess higher levels of financial literacy, engage in effective mental budgeting, and exercise self-control are more likely to exhibit positive investment decision-making behavior. This, in turn, contributes to their overall financial well-being. The partial mediation suggests that investment decision-making behavior accounts for a portion of the relationship between the independent variables and financial well-being, while other factors may also be involved. These results have important implications for understanding the pathways through which financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control influence financial well-being. The presence of mediation indicates that investment decision-making behavior plays a role in translating the effects of these independent variables into improved financial outcomes. It highlights the significance of making informed investment decisions and aligning them with one’s financial goals [79–82]. Overall, the results of this investigation underscore the importance of financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control in shaping an individual’s financial well-being. To enhance financial well-being, individuals should strive to improve their financial knowledge, develop effective mental budgeting strategies, and cultivate self-control in their financial decision-making processes.
This study has several theoretical and practical implications.
5.1. Theoretical implications
Enriching the understanding of financial well-being: This study contributes to the existing body of knowledge by providing empirical evidence on the impact of financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control on financial well-being. It enhances our theoretical understanding of the factors that influence individuals’ financial well-being and highlights the importance of these variables in achieving positive financial outcomes.
Supporting the importance of financial education: The findings underscore the significance of financial literacy in promoting financial well-being. This emphasizes the need for educational institutions, policymakers, and financial institutions to prioritize and promote financial education programs. It highlights the potential benefits of equipping individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to make informed financial decisions and improve their financial well-being.
Emphasizing the role of behavioral factors: This study highlights the role of behavioral factors, such as mental budgeting and self-control, in shaping financial well-being. It supports the growing body of research that recognizes the impact of psychological and behavioral aspects on financial outcomes. These findings can contribute to the development of theories and frameworks that integrate behavioral economics and finance, providing a more comprehensive understanding of individuals’ financial well-being.
5.2. Practical implications
Policy interventions and financial education programs: Policymakers can utilize these findings to design and implement effective financial education initiatives that focus on improving financial literacy, promoting mental budgeting practices, and enhancing self-control. These programs can be targeted towards various age groups and socio-economic backgrounds to ensure wider accessibility and inclusivity.
Financial counseling and guidance: Financial institutions and professionals can leverage the insights from this study to provide personalized financial counseling and guidance to their clients. By addressing specific areas of financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control, individuals can receive tailored support to enhance their financial well-being and achieve their financial goals.
Development of digital tools and resources: Technology can play a crucial role in improving financial well-being. Based on the findings of this study, the development of digital tools, mobile applications, and online platforms can be tailored to provide financial education, facilitate mental budgeting, and encourage self-control. These resources can provide real-time feedback, personalized recommendations, and practical tips to help individuals manage their finances effectively.
Overall, the theoretical implications of this study contribute to the existing knowledge base, while the practical implications offer actionable insights for policymakers, financial institutions, and individuals to promote financial well-being and improve financial outcomes.
5.3. Limitations
The study’s findings may be limited by the characteristics of the sample used. The investigation has focused on a specific demographic and geographic sample (i.e. students), which could limit the generalizability of the results to a broader population. Future research could consider using larger and more diverse samples to enhance the external validity of the findings. The study employed a cross-sectional design, which captures data at a specific point in time. This design limitation prevents establishing causal relationships between the variables investigated. To address this limitation, future research could employ longitudinal or experimental designs to assess the causal effects of financial literacy, mental budgeting, self-control, and investment decision-making behavior on financial well-being. The study relied on self-reported measures, which may introduce response biases and social desirability effects. Participants might have provided answers that they believed were expected or socially acceptable rather than reflecting their true behaviors or beliefs. Future studies could consider incorporating objective measures or alternative data sources to enhance the validity of the findings.
5.4. Further research directions
Investigating additional mediating and moderating variables could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the relationships between financial literacy, mental budgeting, self-control, investment decision-making behavior, and financial well-being. Factors such as risk tolerance, financial attitudes, social influences, and psychological factors could be explored to uncover their potential impact on the relationships of interest. Future research could explore the long-term effects of financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control on financial well-being. Assessing the sustainability and durability of these effects over time could shed light on the long-term benefits of cultivating these skills and behaviors. Investigating the effectiveness of interventions aimed at improving financial literacy, mental budgeting, and self-control could provide valuable insights. Assessing the impact of educational programs, financial counseling, and interventions on individuals’ financial well-being and investment decision-making behavior would help identify the most effective strategies for promoting positive financial outcomes. Exploring the role of cultural and contextual factors in the relationships of interest could offer valuable insights. Different cultures and socio-economic contexts may influence the impact of financial literacy, mental budgeting, self-control, and investment decision-making behavior on financial well-being. Examining these factors would allow for a more nuanced understanding of how these relationships manifest across diverse populations. Addressing these limitations and pursuing these research directions can further advance the knowledge and understanding of the impact of financial literacy, mental budgeting, self-control, investment decision-making behavior, and their interrelationships on financial well-being.
Supporting information
(DOCX)
Acknowledgments
This paper is a general project of 2021 Henan Higher Education Teaching Reform Research and Practice Project (Research and Practice of "Integration of Competition and Teaching" in Accounting major under the background of National Vocational College Skills Competition 2021SJGLX826)
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
References
- 1.Horackova K, Kopecek M, Machů V, Kagstrom A, Aarsland D, Motlova LB, et al. Prevalence of late-life depression and gap in mental health service use across European regions. European Psychiatry. 2019. Apr;57:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2018.12.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Greenglass ER, Katter JK, Fiksenbaum L, Hughes BM. Surviving in difficult economic times: relationship between economic factors, self-esteem and psychological distress in university students. InThe Multi-generational and Aging Workforce 2015. Jul 31 (pp. 58–77). Edward Elgar Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fiksenbaum L, Marjanovic Z, Greenglass E. Financial threat and individuals’ willingness to change financial behavior. Review of Behavioral Finance. 2017. Jul 10;9(2):128–47. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mo Y, Deng L, Zhang L, Lang Q, Liao C, Wang N, et al. Work stress among Chinese nurses to support Wuhan in fighting against COVID‐19 epidemic. Journal of nursing management. 2020. Jul;28(5):1002–9. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Reiss F. Socioeconomic inequalities and mental health problems in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Social science & medicine. 2013. Aug 1;90:24–31. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2013.04.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Halpern MT, De Moor J, Han X, Zhao J, Zheng Z, Yabroff KR. Associations of employment disruptions and financial hardship among individuals diagnosed with cancer in the United States. 2022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McDaid D, Park AL, Davidson G, John A, Knifton L, McDaid S, et al. The economic case for investing in the prevention of mental health conditions in the UK. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- 8.PwC. (2019). Employee Financial Wellness Survey. Retrieved from https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/private-company-services/library/financial-well-being-retirement-survey.html
- 9.HSBC. HSBC Expat Explorer Survey 2019. London: HSBC. 2019.
- 10.Mishra R. (2022). Financial literacy and financial wellbeing among indian households. International Journal of Business and Management, 17(4), 98. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bagwell DC, Kim J. Financial stress, health status, and absenteeism in credit counseling clients. Journal of Consumer Education. 2003;21:50–8. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Garman ET, Camp P, Kim J, Bagwell D, Baffi C, Redican C. Credit delinquencies: A portrait of pain for employers’ bottom lines—Preliminary findings. Personal finances and worker productivity. 1999;3(1):165–8. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Joo S, Garman ET. The relationship between personal financial wellness and employee productivity: A conceptual model. Personal Finances and Worker Productivity. 1998;2(2):162–71. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Strömbäck C, Skagerlund K, Västfjäll D, Tinghög G. Subjective self-control but not objective measures of executive functions predicts financial behavior and well-being. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance. 2020. Sep 1;27:100339. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mahendru M. Financial well-being for a sustainable society: a road less travelled. Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal. 2021. Nov 3;16(3/4):572–93. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Taft MK, Hosein ZZ, Mehrizi SM, Roshan A. The relation between financial literacy, financial wellbeing and financial concerns. International journal of business and management. 2013. Jun 1;8(11):63. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jayanthi M. and Rau S. (2019). Determinants of rural household financial literacy: evidence from south india. Statistical Journal of the Iaos, 35(2), 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Susanto Y., Setiawan J., & Ariyanto S. (2022). Financial planning for millennials and gen-z (study of millennials and gen-z financial behavior). Ultima Management Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen, 156–168. 10.31937/manajemen.v14i1.2533 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yuesti A., Rustiarini N., & Suryandari N. (2020). Financial literacy in the covid-19 pandemic: pressure conditions in indonesia. Journal of Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues, 8(1), 884–898. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xiao JZ, O’Neill B. Mental accounting and behavioural hierarchy: Understanding consumer budgeting behaviour. Int J Consum Stud. 2018;42(4):380–387. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hoque MZ. Mental budgeting and the financial management of small and medium entrepreneurs. Cogent Economics & Finance. 2017. Jan 1;5(1):1291474. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chun S, Johnson DS. The effects of mental budgeting and pain of payment on the financial decision making of socially excluded people. International Journal of Bank Marketing. 2021. May 5;39(5):886–99. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Siswanti I. (2020). Financial knowledge, financial attitude, and financial management behavior: self–control as mediating. The International Journal of Accounting and Business Society, 28(1), 105–132. 10.21776/ub.ijabs.2020.28.1.5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu F. (2018). Professional financial advice, self‐control and saving behavior. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 43(1), 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Atmaningrum S., Kanto D., & Kisman Z. (2021). Investment decisions: the results of knowledge, income, and self-control. Journal of Economics and Business, 4(1). [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tambun S. and Cahyati E. (2023). Impact of economic literacy and financial management on financial planning with self control as moderation. International Journal of Research in Commerce and Management Studies, 05(01), 164–175. doi: 10.38193/ijrcms.2023.5111 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vuković M. and Pivac S. (2021). Does financial behavior mediate the relationship between self-control and financial security?. Croatian Operational Research Review, 12(1), 27–36. 10.17535/crorr.2021.0003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kamakia M., Mwangi C., & Mwangi M. (2017). Financial literacy and financial wellbeing of public sector employees: a critical literature review. European Scientific Journal Esj, 13(16), 233. 10.19044/esj.2017.v13n16p233 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ratnawati N., Sudarmiatin N., Soetjipto B., & Restuningdiah N. (2022). The role of financial behavior as a mediator of the influence of financial literacy and financial attitudes on msmes investment decisions in indonesia. Journal of Social Economics Research, 9(4), 193–203. 10.18488/35.v9i4.3231 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rahman M. and Gan S. (2020). Generation y investment decision: an analysis using behavioural factors. Managerial Finance, 46(8), 1023–1041. 10.1108/mf-10-2018-0534 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hanopia B., Surasni N., & Hidayati S. (2018). Investment deposits decision-making in bank: a behavioral finance perspective. Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic Sciences, 74(2), 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brüggen EC, Hogreve J, Holmlund M, Kabadayi S, Löfgren M. Financial well-being: A conceptualization and research agenda. Journal of business research. 2017. Oct 1;79:228–37. [Google Scholar]
- 33.CFPB. Financial well-being: The goal of financial education. Retrieved March 13, 2020 from https://files.consumerfinance.gov/f/201501_cfpb_report_financial-well-being.pdf. 2015a.
- 34.CFPB. Measuring financial well-being: A guide to using the CFPB financial well-being scale. Retrieved March 13, 2020 from https://files.consumerfinance.gov/f/201512_cfpb_financial-well-being-user-guide-scale.pdf. 2015b.
- 35.Netemeyer RG, Warmath D, Fernandes D, Lynch JG Jr. How am I doing? Perceived financial well-being, its potential antecedents, and its relation to overall well-being. Journal of Consumer Research. 2018. Jun 1;45(1):68–89. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Browning M, Lusardi A. Household saving: Micro theories and micro facts. Journal of Economic literature. 1996. Dec 1;34(4):1797–855. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schmeiser MD, Seligman JS. Using the right yardstick: Assessing financial literacy measures by way of financial well‐being. Journal of Consumer Affairs. 2013. Jul;47(2):243–62. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Soman D, Cheema A. The effect of credit on spending decisions: The role of the credit limit and credibility. Marketing Science. 2002. Feb;21(1):32–53. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fointiat V. and Pelt A. (2015). Do i know what i’m doing? cognitive dissonance and action identification theory. The Spanish Journal of Psychology, 18 doi: 10.1017/sjp.2015.93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Braunstein S, Welch C. Financial literacy: An overview of practice, research, and policy. Fed. Res. Bull. 2002;88:445. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Abdullah MA, Chong R. Financial literacy: An exploratory review of the literature and future research. Journal of Emerging Economies and Islamic Research. 2014. Sep 30;2(3):32–41. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ouachani S, Belhassine O, Kammoun A. Measuring financial literacy: A literature review. Managerial Finance. 2021. Jan 28;47(2):266–81. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Garg N, Singh S. Financial literacy among youth. International journaL of sociaL economics. 2018. Jan 8. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Goyal K, Kumar S. Financial literacy: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis. International Journal of Consumer Studies. 2021. Jan;45(1):80–105. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Swiecka B, Yeşildağ E, Özen E, Grima S. Financial literacy: The case of Poland. Sustainability. 2020. Jan 18;12(2):700. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Paramitalaksmi R, Astuti W. Personal Financial Planning and Management during Covid-19 Pandemic by Strengthening Financial Literacy for Generation Z in Condongcatur, Kapanewon Depok, Sleman Regency, Special Region of Yogyakarta. Mattawang: Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat. 2022. Sep 1;3(3):307–11. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Aleksandrova A, Ismailov T. IMPROVING FINANCIAL LITERACY AS A PREREQUISITE FOR INCREASING FISCAL CAPACITY: THE BULGARIAN CASE. Proceedings of ADVED. 2021. Oct 18;2021(7th). [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lind T., Ahmed A., Skagerlund K., Strömbäck C., Västfjäll D., & Tinghög G. (2020). Competence, confidence, and gender: the role of objective and subjective financial knowledge in household finance. Journal of Family and Economic Issues, 41(4), 626–638. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Balasubramnian B, Sargent CS. Impact of inflated perceptions of financial literacy on financial decision making. Journal of Economic Psychology. 2020. Oct 1;80:102306. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Joo SH, Grable JE. An exploratory framework of the determinants of financial satisfaction. Journal of family and economic Issues. 2004. Mar;25:25–50. [Google Scholar]
- 51.O’Neill B, Sorhaindo B, Xiao JJ, Garman ET. Financially distressed consumers: Their financial practices, financial well-being, and health. Journal of Financial Counseling and Planning. 2005;16(1). [Google Scholar]
- 52.Huston SJ. Measuring financial literacy. Journal of consumer affairs. 2010. Jun;44(2):296–316. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sabri MF, Cook CC, Gudmunson CG. Financial well‐being of Malaysian college students. Asian education and development studies. 2012. May 25;1(2):153–70. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Thaler R. Mental accounting matters. J Behav Decis Making. 1999;12(3):183–206. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Krishnamurthy P, Prokopec S. Resisting that triple-chocolate cake: Mental budgets and self-control. Journal of Consumer Research. 2010. Jun 1;37(1):68–79. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zhang CY, Sussman AB. The role of mental accounting in household spending and investing decisions. Client Psychology. New York: Wiley, Chicago Booth Research Paper. 2017. Dec 4(19–07). [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhang CY, Sussman AB. Perspectives on mental accounting: An exploration of budgeting and investing. Financial Planning Review. 2018. Mar;1(1–2):e1011. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Elgeka HW, Ma J. Mental budgeting and the malleability of decision making. Psikohumaniora: Jurnal Penelitian Psikologi. 2020. Oct 31;5(2):139–54. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Antonides G, De Groot IM, Van Raaij WF. Mental budgeting and the management of household finance. Journal of Economic Psychology. 2011. Aug 1;32(4):546–55. [Google Scholar]
- 60.bin Hassan MF, Hassan NM, Kassim ES, Said YB. The relationship between financial wellbeing and mental health: A systematic literature reviews. Asia Proceedings of Social Sciences. 2021. Mar 27;7(2):92–95. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rosalina E, Rahim R, Husni T, Alfarisi F. Mental Budgeting dan Motivasi Terhadap Pengelolaan Keuangan Individu. Journal of Applied Accounting and Taxation. 2021. Oct 31;6(2):175–82. [Google Scholar]
- 62.VanBergen N, Laran J. Loss of control and self-regulation: The role of childhood lessons. Journal of Consumer Research. 2016. Dec 1;43(4):534–48. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Younas W, Javed T, Kalimuthu KR, Farooq M, Khalil-ur-Rehman F, Raju V. Impact of self-control, financial literacy and financial behavior on financial well-being. The Journal of Social Sciences Research. 2019;5(1):211–8. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hashmi F, Aftab H, Martins JM, Nuno Mata M, Qureshi HA, Abreu A, et al. The role of self-esteem, optimism, deliberative thinking and self-control in shaping the financial behavior and financial well-being of young adults. Plos one. 2021. Sep 7;16(9):e0256649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Mahapatra MS, Mishra RK. Influence of Financial Parenting and Financial Coping Behaviour on Well-Being of Young Adults: A Study in India. Vision. 2022. Mar 27:09722629221087368. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dhanabhakyam M, Fahad KP, Josep E. A Study on Impact of Compensation Management in Financial Well Being of Employees in Selected It Companies in Kerala. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Gardner DK, Helmes E. Locus of control and self-directed learning as predictors of wellbeing in the elderly. Australian Psychologist. 1999. Jul 1;34(2):99–103. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Lazuras L, Ypsilanti A, Powell P, Overton P. The roles of impulsivity, self-regulation, and emotion regulation in the experience of self-disgust. Motivation and Emotion. 2019. Feb 15;43:145–58. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Thaler RH, Shefrin HM. An economic theory of self-control. Journal of political Economy. 1981. Apr 1;89(2):392–406. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Baumeister RF. Yielding to temptation: Self-control failure, impulsive purchasing, and consumer behavior. Journal of consumer Research. 2002. Mar 1;28(4):670–6. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Biljanovska N, Palligkinis S. Control thyself: Self-control failure and household wealth. Journal of Banking & Finance. 2018. Jul 1;92:280–94. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ariely D, Wertenbroch K. Procrastination, deadlines, and performance: Self-control by precommitment. Psychological science. 2002. May;13(3):219–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Shefrin HM, Thaler RH. The behavioral life‐cycle hypothesis. Economic inquiry. 1988. Oct;26(4):609–43. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Thaler R. Mental accounting and consumer choice. Marketing science. 1985. Aug;4(3):199–214. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Moffitt TE, Arseneault L, Belsky D, Dickson N, Hancox RJ, Harrington H, et al. A gradient of childhood self-control predicts health, wealth, and public safety. Proceedings of the national Academy of Sciences. 2011. Feb 15;108(7):2693–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010076108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.T Kiyosaki R. The business of the 21st century. Manjul Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.; 2012. Jan 1. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Kahneman D. Thinking, fast and slow. macmillan; 2011 Oct 25.
- 78.Tangney JP, Baumeister RF, Boone AL. High self‐control predicts good adjustment, less pathology, better grades, and interpersonal success. Journal of personality. 2004. Apr;72(2):271–324. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3506.2004.00263.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Wachjuni W, Komarudin M, Maulana Y, Azhari A, Astriani R. Analysis of Factors Affecting Financial Behavior. InProceedings of the 2nd Universitas Kuningan International Conference on System, Engineering, and Technology, UNISET; 2021, 2 December 2021, Kuningan, West Java, Indonesia 2022. Aug 18. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Rustan DM. Financial Literacy, Financial Behavior and Financial Attitudes Towards Investment Decisions and Firm Bankruptcy. ATESTASI: Jurnal Ilmiah Akuntansi. 2021. Mar 31;4(1):79–87. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Baihaqqy MR, Disman N, Sari M, Ikhsan S. The effect of financial literacy on the investment decision. Budapest International Research and Critics Institute-Journal (BIRCI-Journal). 2020. Oct 31;3(4):3073–83. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Puspa LW, Mukaram M. Pengaruh Penggunaan Informasi Akuntansi Terhadap Perilaku Keuangan Investor Individual Untuk Pengambilan Keputusan Investasi. Jurnal Riset Bisnis dan Investasi. 2016. Oct 10;2(2). [Google Scholar]
- 83.Riyazahmed DK. Does financial behavior influence financial well-being?. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics, and Business (JAFEB), ISSN. 2021:2288–4637. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Iramani R, Lutfi L. An integrated model of financial well-being: The role of financial behavior. Accounting. 2021;7(3):691–700. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Delafrooz N, Paim LH. Determinants of financial wellness among Malaysia workers. African Journal of Business Management. 2011. Oct 14;5(24):10092. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Robb CA, Woodyard A. Financial knowledge and best practice behavior. Journal of financial counseling and planning. 2011;22(1). [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ghazali MS, Alwi SF, Othman I, Sabri MF, Abd Aziz NN. The Relationship between Subjective Financial Knowledge and Financial Well-Being among Emerging Adults in Malaysia: Mediating Effect of Financial Behaviour. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Fünfgeld B, Wang M. Attitudes and behaviour in everyday finance: evidence from Switzerland. International Journal of Bank Marketing. 2009. Feb 27;27(2):108–28. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Thung CM, Kai CY, Nie FS, Chiun LW, Tsen TC. Determinants of saving behaviour among the university students in Malaysia. Final Year Project, UTAR. Available online at: http://eprints. utar. edu. my/607/1/AC-2011-0907445. pdf. 2012. May. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Dew J, Xiao JJ. The financial management behavior scale: Development and validation. Journal of Financial Counseling and Planning. 2011;22(1):43. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Dash G, Paul J. CB-SEM vs PLS-SEM methods for research in social sciences and technology forecasting. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 2021. Dec 1;173:121092. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Nunnally JC. An overview of psychological measurement. Clinical diagnosis of mental disorders: A handbook. 1978:97–146. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE, Tatham RL. Multivariate data analysis 6th Edition. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Peter JP. Reliability: A review of psychometric basics and recent marketing practices. Journal of marketing research. 1979. Feb;16(1):6–17. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Fornell C, Larcker DF. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH. Psychometric Theory: Nunnally and Bernstein. 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Barclay D, Higgins C, Thompson R. The partial least squares (PLS) approach to casual modeling: personal computer adoption ans use as an Illustration. 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of personality and social psychology. 1986. Dec;51(6):1173. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.51.6.1173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]