Abstract
In soybean seeds the level of hydroxyproline is regulated in a developmental and tissue-specific manner. The seed coat contains approximately 77% of the total hydroxyproline in the seed at all stages of development. We determined the ratio of hydroxyproline to dry weight in a number of tissues within the seed; however, only the seed coat shows an increase in this ratio during development. Within the many cell layers of the seed coat, hydroxyproline is most abundant in the external layer. The hydroxyproline is present as an hydroxyproline-rich cell wall glycoprotein. The protein is rich in hydroxyproline (36%), lysine (11%), proline (10%), histidine (9%), tyrosine (9%), and serine (8%). The carbohydrate portion is 90 mole% arabinose and 10 mole% galactose. The arabinose residues are attached to hydroxyproline mostly in the form of trisaccharides. The apparent molecular weight of this glycoprotein is 100,000 daltons.
Full text
PDF
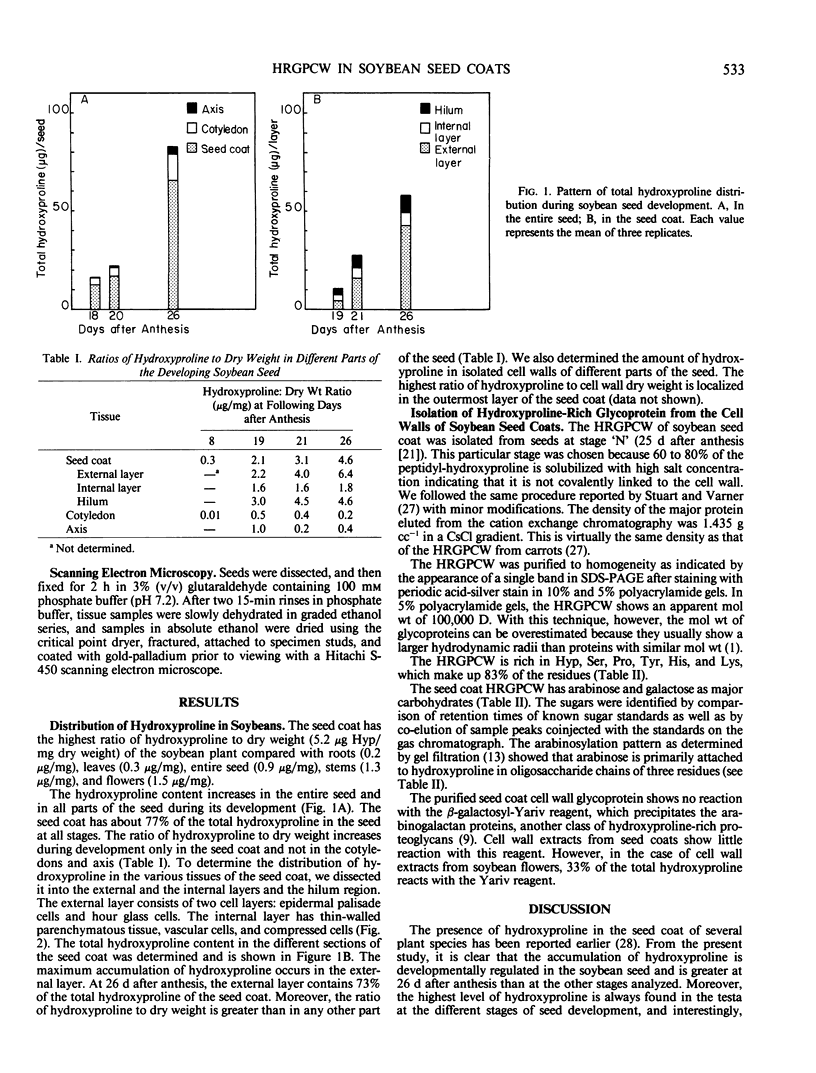
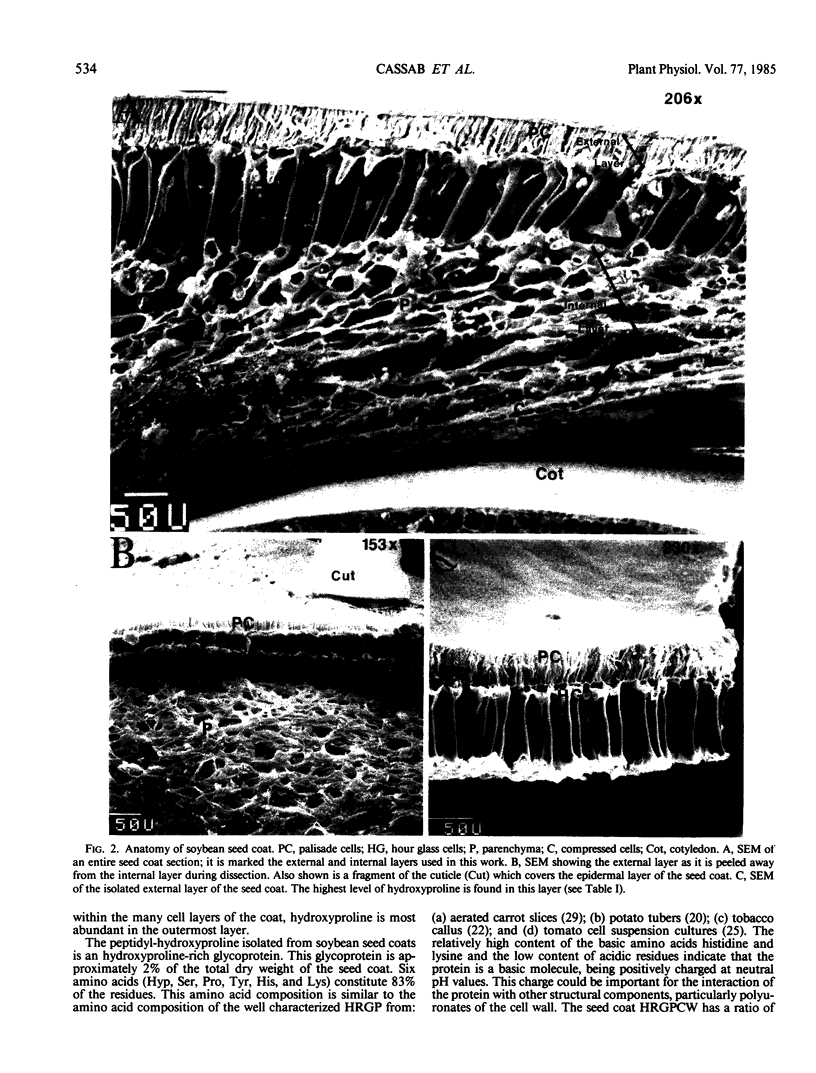

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper J. B., Varner J. E. Insolubilization of hydroxyproline-rich cell wall glycoprotein in aerated carrot root slices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91811-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drózdz M., Kucharz E., Szyja J. A colorimetric micromethod for determination of hydroxyproline in blood serum. Z Med Labortech. 1976 Aug 4;17(4):163–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bezard G. A highly sensitive periodic acid-silver stain for 1,2-diol groups of glycoproteins and polysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquerré-Tugayé M. T., Lafitte C., Mazau D., Toppan A., Touzé A. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions: II. Evidence for the Accumulation of Hydroxyproline-rich Glycoproteins in the Cell Wall of Diseased Plants as a Defense Mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):320–326. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry S. C. Isodityrosine, a new cross-linking amino acid from plant cell-wall glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):449–455. doi: 10.1042/bj2040449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamport D. T., Katona L., Roerig S. Galactosylserine in extensin. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):125–132. doi: 10.1042/bj1330125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach J. E., Cantrell M. A., Sequeira L. Hydroxyproline-rich bacterial agglutinin from potato : extraction, purification, and characterization. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1353–1358. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon J. E., Helgeson J. P. Interaction of a hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein from tobacco callus with potential pathogens. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):401–405. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray D. R. Nutritive Role of the Seedcoats during Embryo Development in Pisum sativum L. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):763–769. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. A., Varner J. E. Purification and Characterization of a Salt-extractable Hydroxyproline-rich Glycoprotein from Aerated Carrot Discs. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):787–792. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holst G. J., Varner J. E. Reinforced Polyproline II Conformation in a Hydroxyproline-Rich Cell Wall Glycoprotein from Carrot Root. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):247–251. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]