Abstract
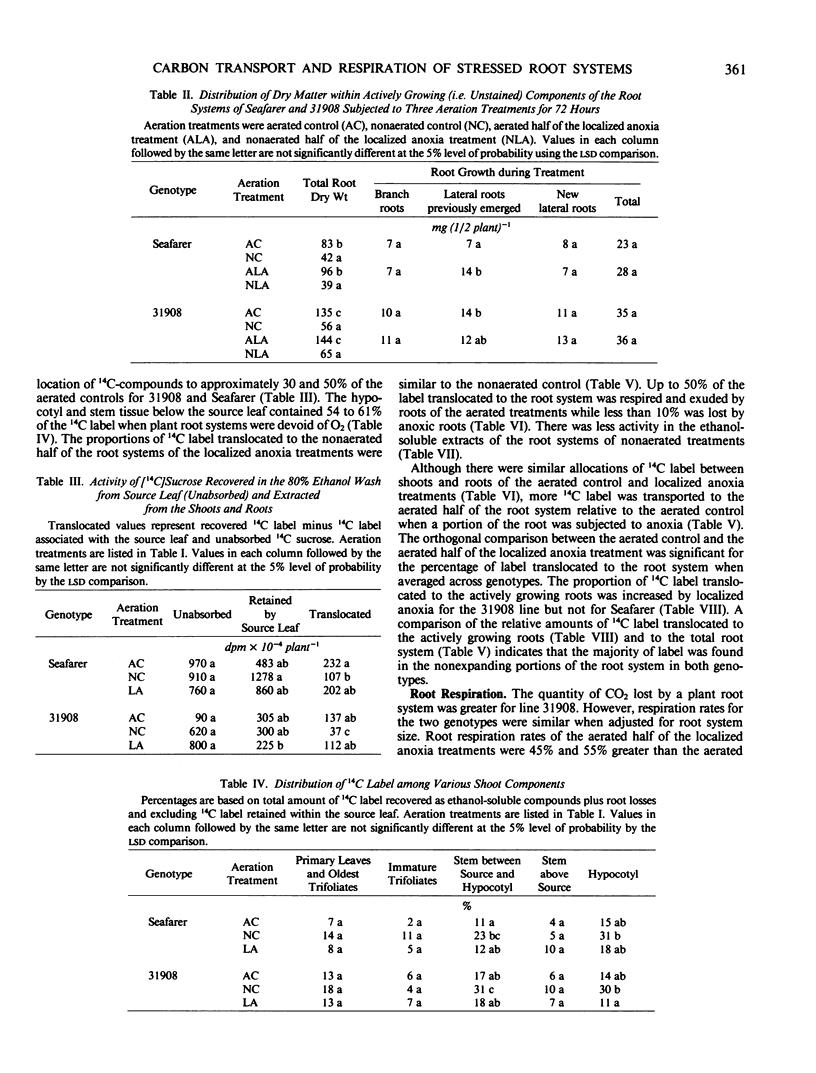
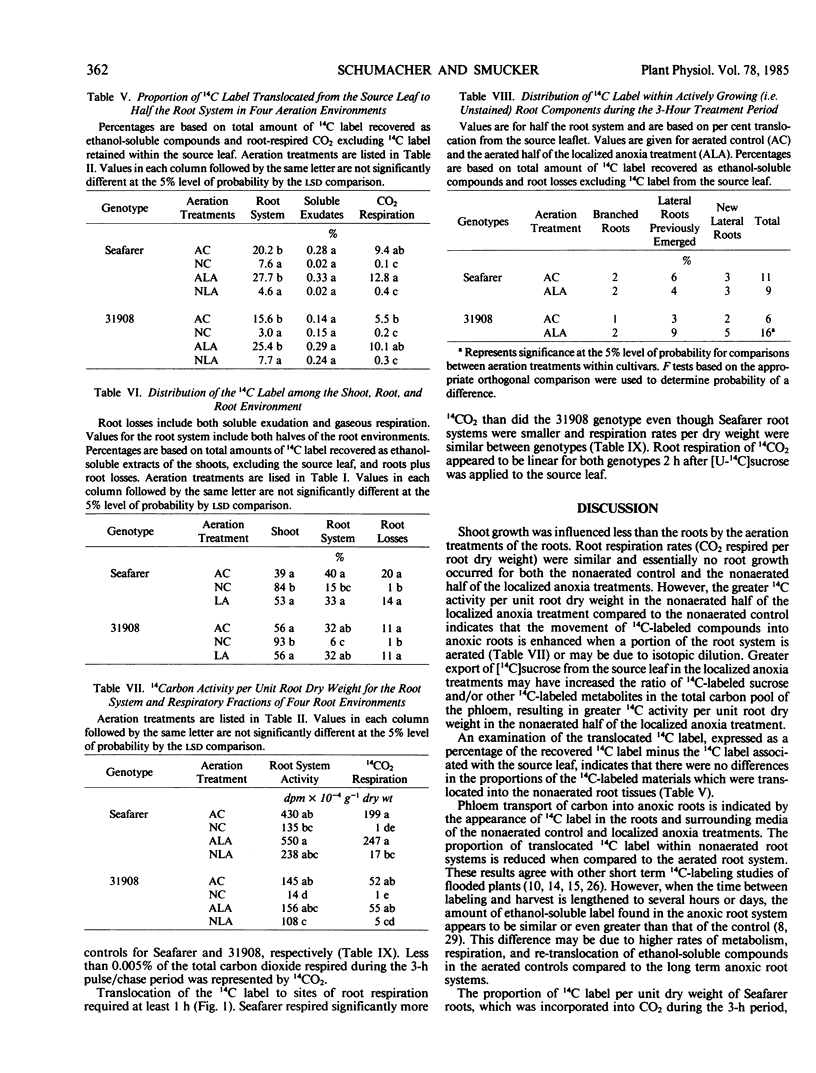
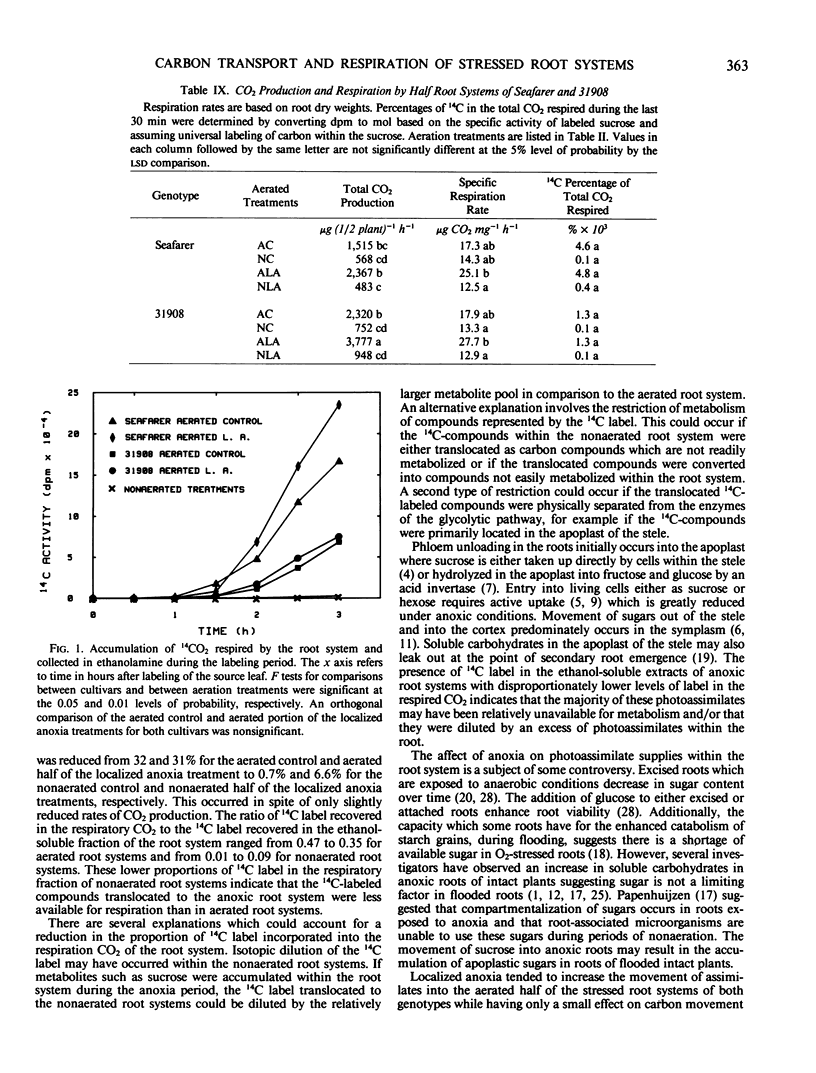
The influence of anoxia on carbon transport and root respiration was evaluated by applying [U-14C]sucrose to the foliage. Translocation patterns to the root systems of two dry edible bean genotypes (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) were examined after a 3-day exposure to aerated and nonaerated environments. Localized anoxia of root systems was simulated by growing roots in split configurations and exposing half of the system to anoxic conditions. Anoxia of the root system for 72 hours reduced the movement of 14C label into the roots with concurrent accumulations in the hypocotyl region. The translocation of 14C label to anoxic roots was less than 50% of the aerated controls of both genotypes. Most of the 14C label translocated to anoxic root systems was excluded from respiratory metabolism during the 3-hour pulse/chase period and was an order of magnitude less than the aerated controls. These observations suggest that the bulk of 14C label which entered the root during the anoxic period was unavailable for metabolism by the enzymes of glycolysis and/or was diluted by a relatively large metabolite pool. A higher percentage of 14C label was translocated to the aerated half of the localized anoxia treatment relative to the half of the aerated controls. The proportion of 14C label translocated to the root system in the aerated control was 20 and 16% compared to 28 and 25% in the aerated localized anoxia treatment for the genotypes Seafarer and line 31908, respectively. Line 31908 partitioned a greater percentage of 14C-labeled compounds to the actively growing fraction of the root system in the localized anoxia treatment than did Seafarer. This suggests a greater reliance on previously stored carbohydrate for immediate root growth in Seafarer than in line 31908.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Giaquinta R. T., Lin W., Sadler N. L., Franceschi V. R. Pathway of Phloem unloading of sucrose in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jun;72(2):362–367. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglio P. H., Raymond P., Pradet A. Metabolic Activity and Energy Charge of Excised Maize Root Tips under Anoxia: CONTROL BY SOLUBLE SUGARS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1053–1057. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher T. E., Smucker A. J. Measurement of CO(2) Dissolved in Aqueous Solutions Using a Modified Infrared Gas Analyzer System. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):212–214. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


