Abstract
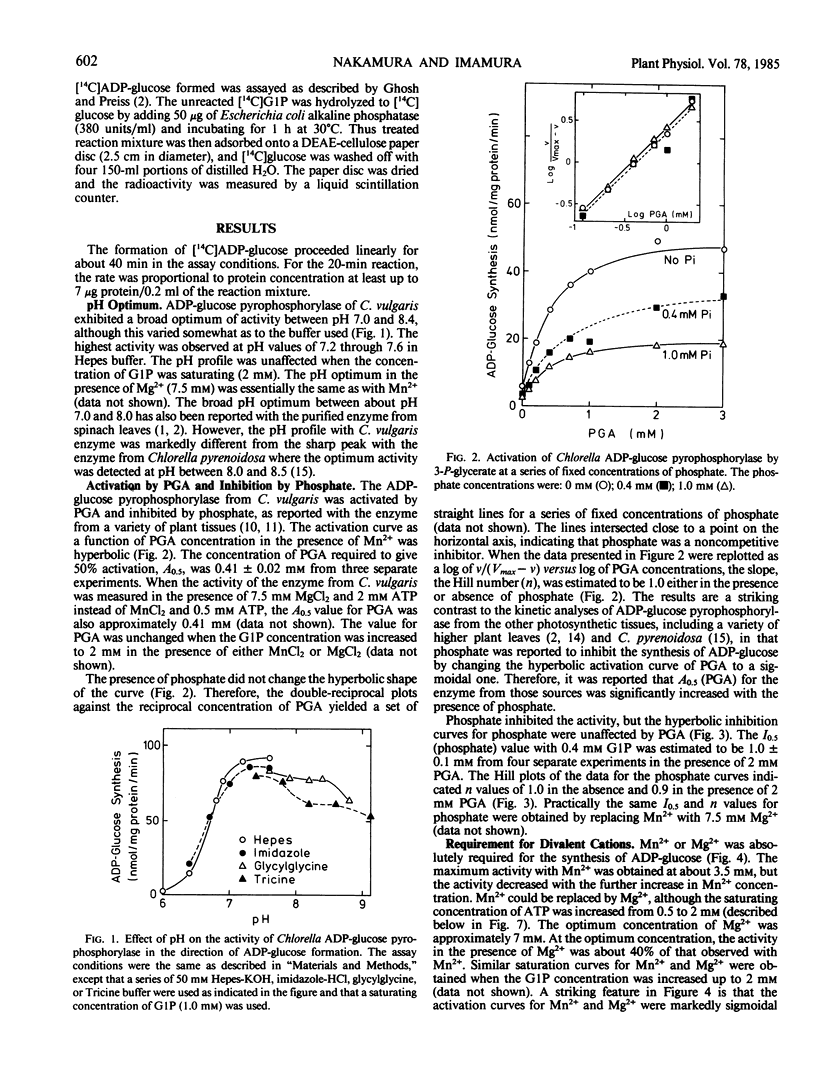
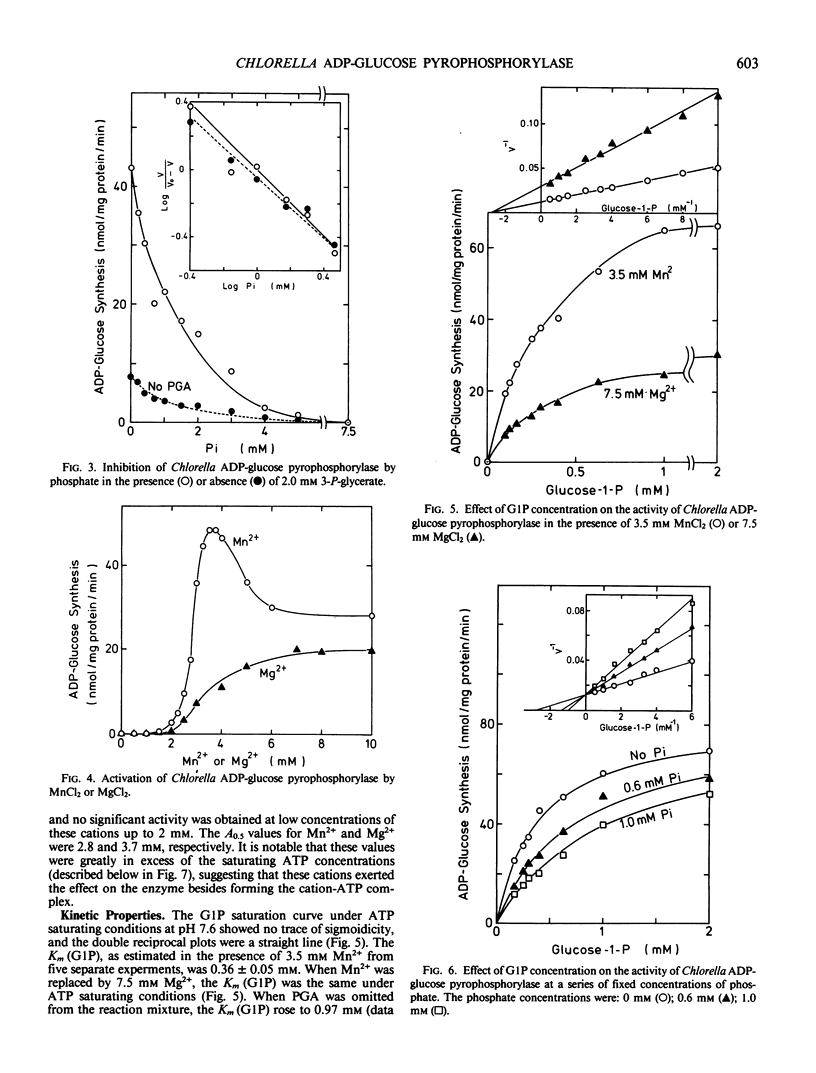
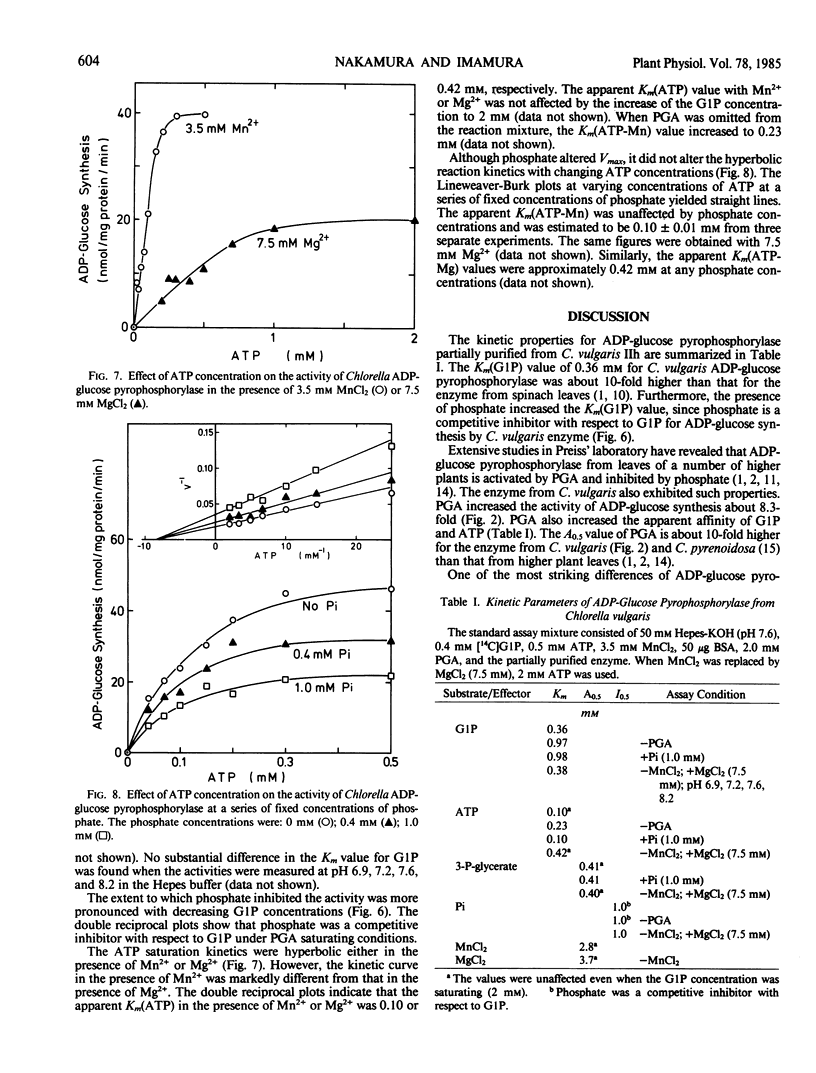
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase was partially purified from Chlorella vulgaris 11h. 3-Phosphoglycerate activated the enzyme by lowering the Michaelis constant for glucose-1-phosphate (from 0.97 to 0.36 millimolar in the presence of 2 millimolar phosphoglycerate) and ATP (from 0.23 to 0.10 millimolar), as well as increasing the Vmax. Saturation curves for 3-phosphoglycerate were hyperbolic and the activator concentration at half Vmax value for 3-phosphoglycerate was 0.41 millimolar either in the presence or absence of phosphate. Phosphate inhibited the enzyme in a competitive manner with respect to glucose-1-phosphate, but did not affect the Michaelis constant value for ATP. 3-Phosphoglycerate changed neither the inhibitor concentration at half Vmax value of 1.0 millimolar for phosphate nor the hyperbolic inhibition kinetics for phosphate. The enzyme required divalent cations for its activity. The activation curves for Mn2+ and Mg2+ were highly sigmoidal. The activator concentration at half Vmax values for Mn2+ and Mg2+ were 2.8 and 3.7 millimolar, respectively. With optimal cations, the Michaelis constant values for ATP-Mn and ATP-Mg were 0.1 and 0.4 millimolar, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Copeland L., Preiss J. Purification of Spinach Leaf ADPglucose Pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):996–1001. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P., Preiss J. Adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase. A regulatory enzyme in the biosynthesis of starch in spinach leaf chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4491–4504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Preiss J. Regulatory Properties of the ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase of the Blue-Green Bacterium Synechococcus 6301. Plant Physiol. 1976 Dec;58(6):753–756. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.6.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Okita T. W., Greenberg E. Characterization of the spinach leaf phosphorylases. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):864–869. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanwal G. G., Greenberg E., Hardie J., Cameron E. C., Preiss J. Regulation of starch biosynthesis in plant leaves: activation and inhibition of ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase. Plant Physiol. 1968 Mar;43(3):417–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.3.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura S., Nagai M., Fukui T. Comparative glucan specificities of two types of spinach leaf phosphorylase. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):703–717. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


