Abstract
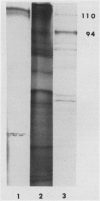
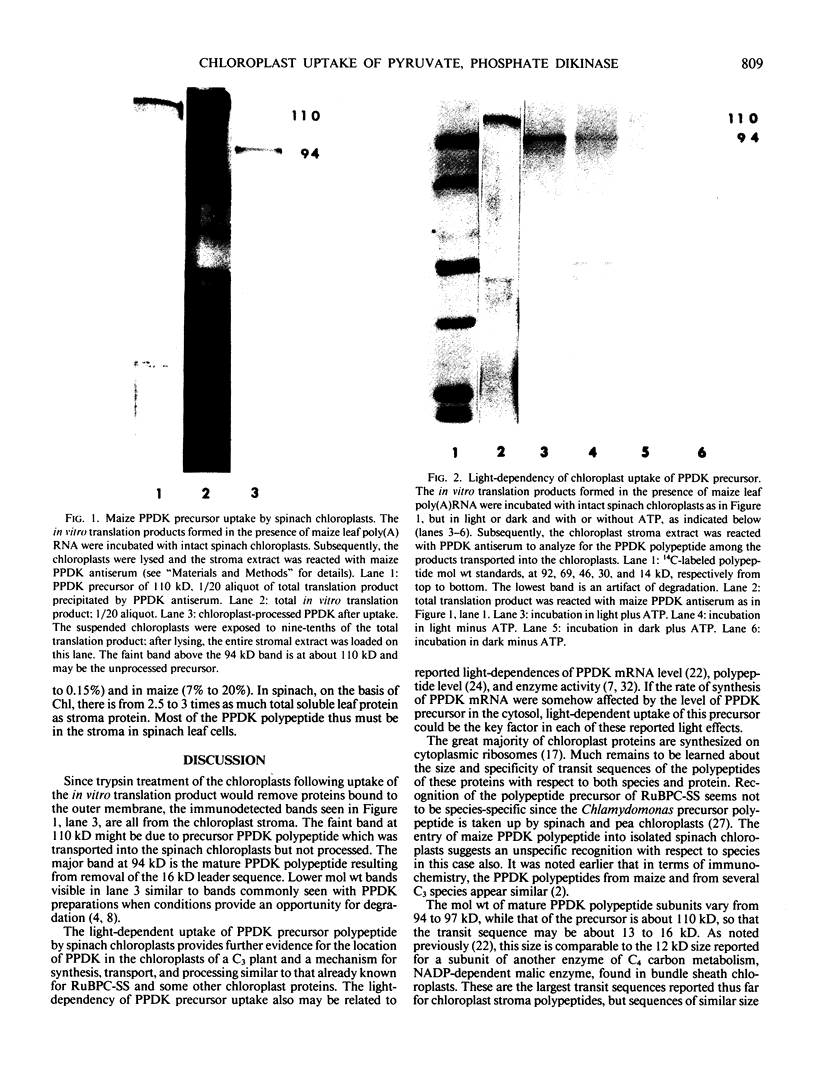
Polyadenylated RNA was isolated from maize leaves and translated in vitro. In agreement with a previous report by others, we found among the translation products a 110-kilodalton pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase (PPDK) precursor that is about 16 kilodaltons larger than the polypeptide isolated from cells. This maize PPDK precursor polypeptide was taken up from the translation product mixture by intact spinach chloroplasts and yielded a mature PPDK polypeptide (94 kilodaltons). The uptake and processing support the proposal that the extra 16-kilodalton size of the polypeptide from in vitro translation of maize leaf mRNA represents a transit sequence which is cleaved after its entry into chloroplasts. Moreover, these results provide additional evidence that in vivo in maize leaf cells PPDK polypeptide is synthesized in the cytoplasm and is transported into the chloroplasts.
Location of PPDK in C3 plant leaves was investigated by immunochemical analysis. Intact chloroplasts were isolated from leaves of spinach, wheat, and maize. A protein blot of stromal protein in each case gave rise to bands corresponding to authentic PPDK polypeptide. This result indicates that PPDK is present in chloroplasts of C3 plant leaves as it is in the case of C4 plants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A., Greene F. C. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase gene expression in developing wheat seeds. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):393–396. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase in wheat leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):853–854. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase mRNA organ specificity in wheat and maize. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):278–280. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase of c(3) seeds and leaves as compared to the enzyme from maize. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):387–392. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apel K., Kloppstech K. The plastid membranes of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Light-induced appearance of mRNA coding for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton A. R., Burnell J. N., Hatch M. D. Regulation of C4 photosynthesis: inactivation of pyruvate, Pi dikinase by ADP-dependent phosphorylation and activation by phosphorolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):492–503. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton A. R., Hatch M. D. Regulation of C4 photosynthesis: regulation of pyruvate, Pi dikinase by ADP-dependent phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90967-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Schmidt G. W. In vitro synthesis, transport, and assembly of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase subunits. Basic Life Sci. 1978;11:325–347. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8106-8_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Hitzeman R., Carbon J. Selection of specific clones from colony banks by screening with radioactive antibody. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:436–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O. Cellular site of opiate dependence. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):625–629. doi: 10.1038/283625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee S. L., Ruzin S., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase: intracellular site of synthesis in maize leaf cells. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):189–191. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. R., Bartlett S. G., Schmidt G. W., Mullet J. E., Chua N. H. Optimal conditions for post-translational uptake of proteins by isolated chloroplasts. In vitro synthesis and transport of plastocyanin, ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase, and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1558–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hague D. R., Uhler M., Collins P. D. Cloning of cDNA for pyruvate, Pi dikinase from maize leaves. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4853–4865. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R. A new enzyme for the interconversion of pyruvate and phosphopyruvate and its role in the C4 dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):141–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1060141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Kobayashi Y., Shibata K., Heber U. Synthesis and hydrolysis of ATP by intact chloroplasts under flash illumination and in darkness. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 11;504(1):142–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkind M. L., Wessler S. R., Schmidt G. W. Functional determinants in transit sequences: import and partial maturation by vascular plant chloroplasts of the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):226–234. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourioux G., Douce R. Slow Passive Diffusion of Orthophosphate between Intact Isolated Chloroplasts and Suspending Medium. Plant Physiol. 1981 Mar;67(3):470–473. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Harpster M. H., Mayfield S. P., Taylor W. C. Light-regulated gene expression during maize leaf development. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):558–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santarius K. A., Heber U. Changes in the intracellular levels of ATP, ADP, AMP and P1 and regulatory function of the adenylate system in leaf cells during photosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 25;102(1):39–54. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack C. R. The photoactivation of a phosphopyruvate synthase in leaves of Amaranthus palmeri. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 12;30(5):483–488. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T. Purification, molecular, and catalytic properties of pyruvate phosphate dikinase from the maize leaf. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 17;12(15):2862–2868. doi: 10.1021/bi00739a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]