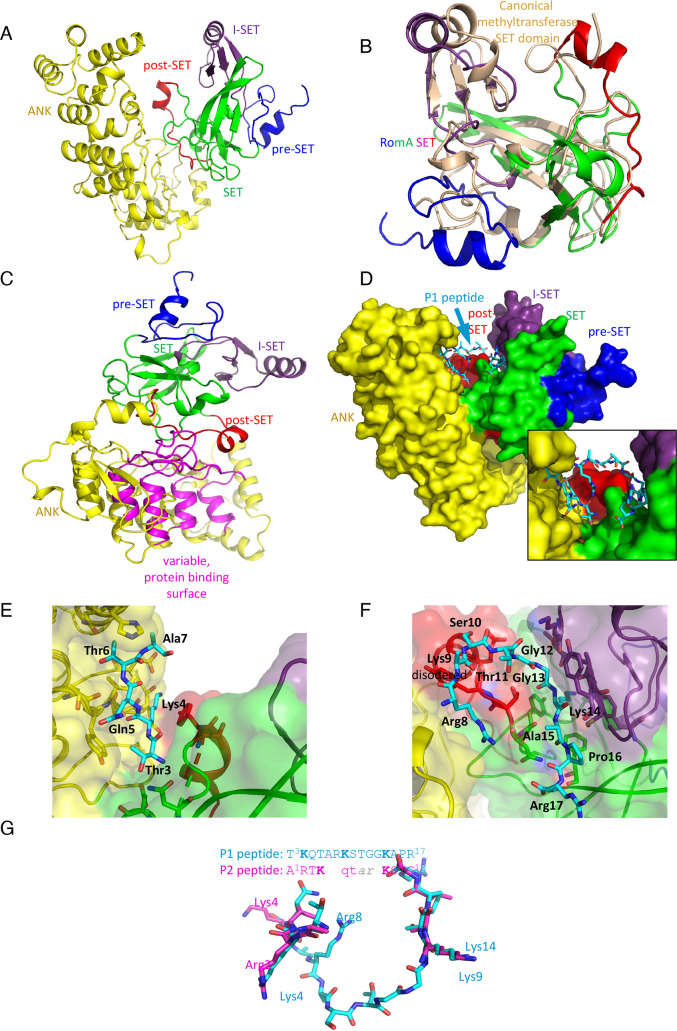
Fig 2.
Crystal structure of LegAS4. (A) Cartoon representation of LegAS4. The segments are individually colored and marked. (B) Superposition of the RomA/LegS4 SET domain (rainbow color) with the canonical SET domain from histone methyltransferase SET7/9 (wheat color). (C) Orientation of LegAS4 showing the interaction between the SET domain (green) and post-SET segment (red) with the ANK domain and, in particular, the top of the loops forming variable protein binding surfaces (magenta). (D) The space filling model of LegAS4 with the P1 peptide bound. P1 is bound in the crevice between the SET and ANK domains making contacts with both. Insert shows a zoomed view on the peptide. (E) The interaction between the N-terminal segment of peptide P1 (blue) and the ANK domain (yellow). (F) The C-terminal segment of peptide P1 (blue) interacts with the post-SET domain (red) and the SET domain (green) and the I-SET segment (magenta). (G) Superposition of peptides P1 and P2. In the absence of Lys 14 in P2 peptide, Lys9 instead enters the active site. The N-terminal segment interacts with the same surface of ANK domain as P1; however, the shorter middle segment is disordered.