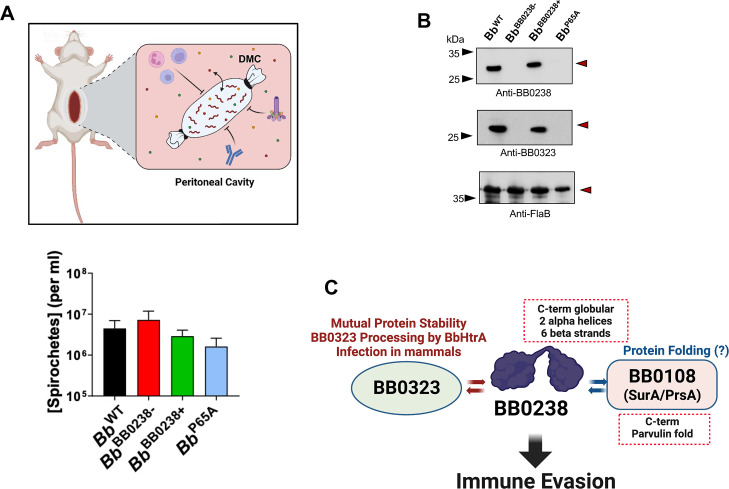
Fig 7.
BB0238 contributes to evasion of host cellular immunity. (A) Spirochete survival within dialysis membrane chambers (DMCs). Schematic diagram (upper panel) shows the DMC experimental design, which allows spirochetes to access host nutrients (small circles) while maintaining separation from the cellular host innate immune cells, complement, and antibodies. Lower panel denotes comparable bacterial concentrations within the DMC, as determined after two weeks within the rat peritoneal cavity (two rats/group). No statistical difference was recorded (P > 0.05). (B) Immunoblot analysis of DMC-cultivated spirochetes. Lysates from each of the DMCs were collected and analyzed via western analysis with antisera for BB0238 (upper panel), BB0323 (center panel), and FlaB (lower panel). Arrows indicate migration of proteins. Images represent similar western analysis from two rats of three independent DMC experiments, totaling six animals per group. (C) A diagram summarizing BB0238 structure and functions. BB0238 features a two-domain organization and is involved in multifaceted interactions with BB0323 and BB0108 that ultimately support immune evasion in mammals, promoting spirochete infectivity. Crystallization results are indicated by dotted callout boxes.