Abstract
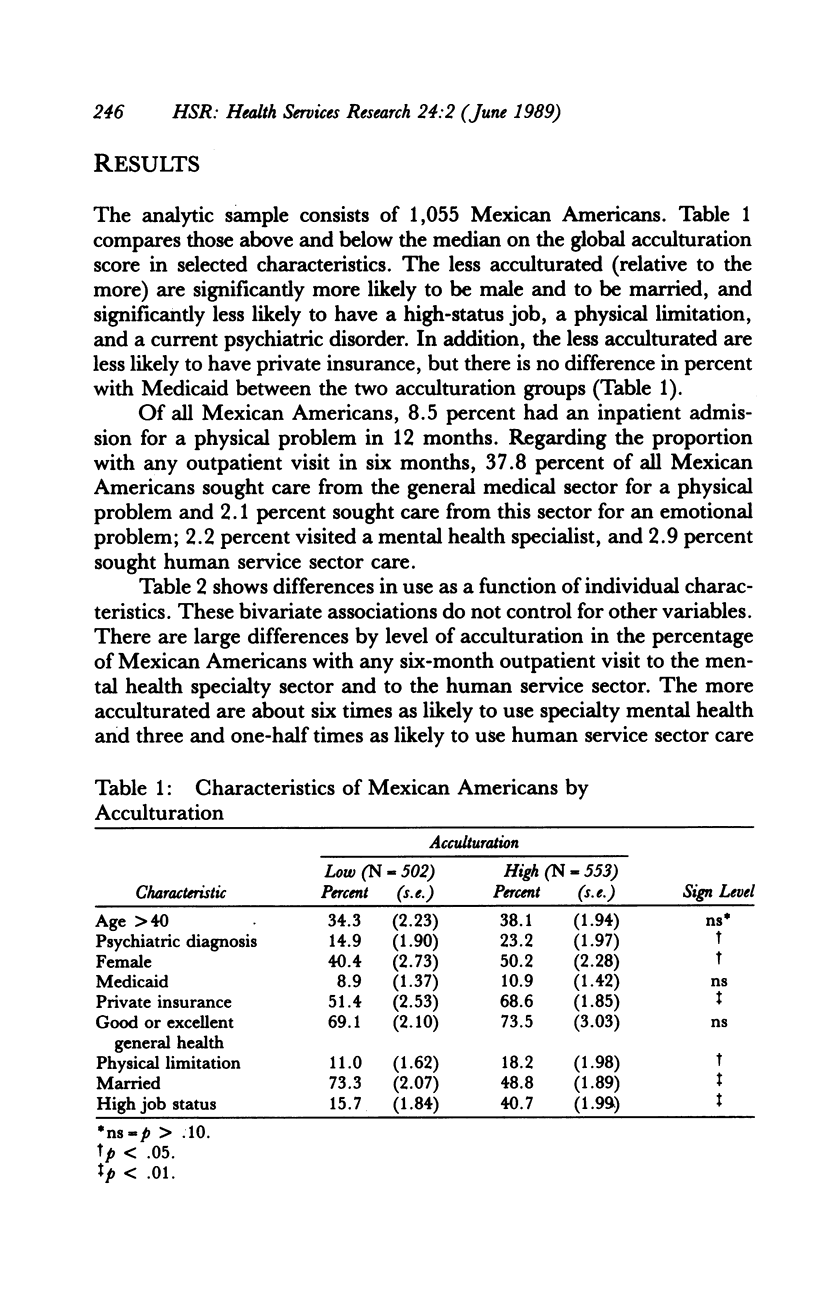
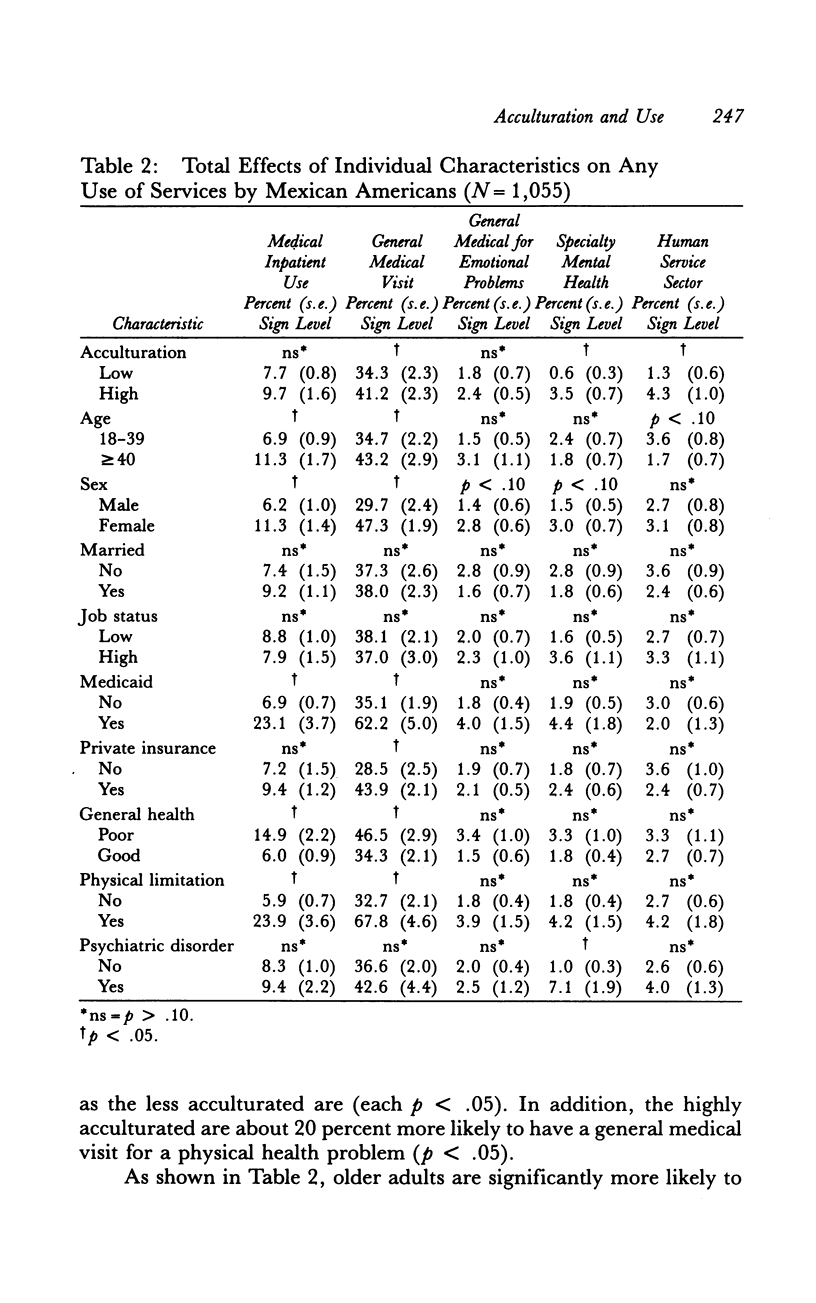
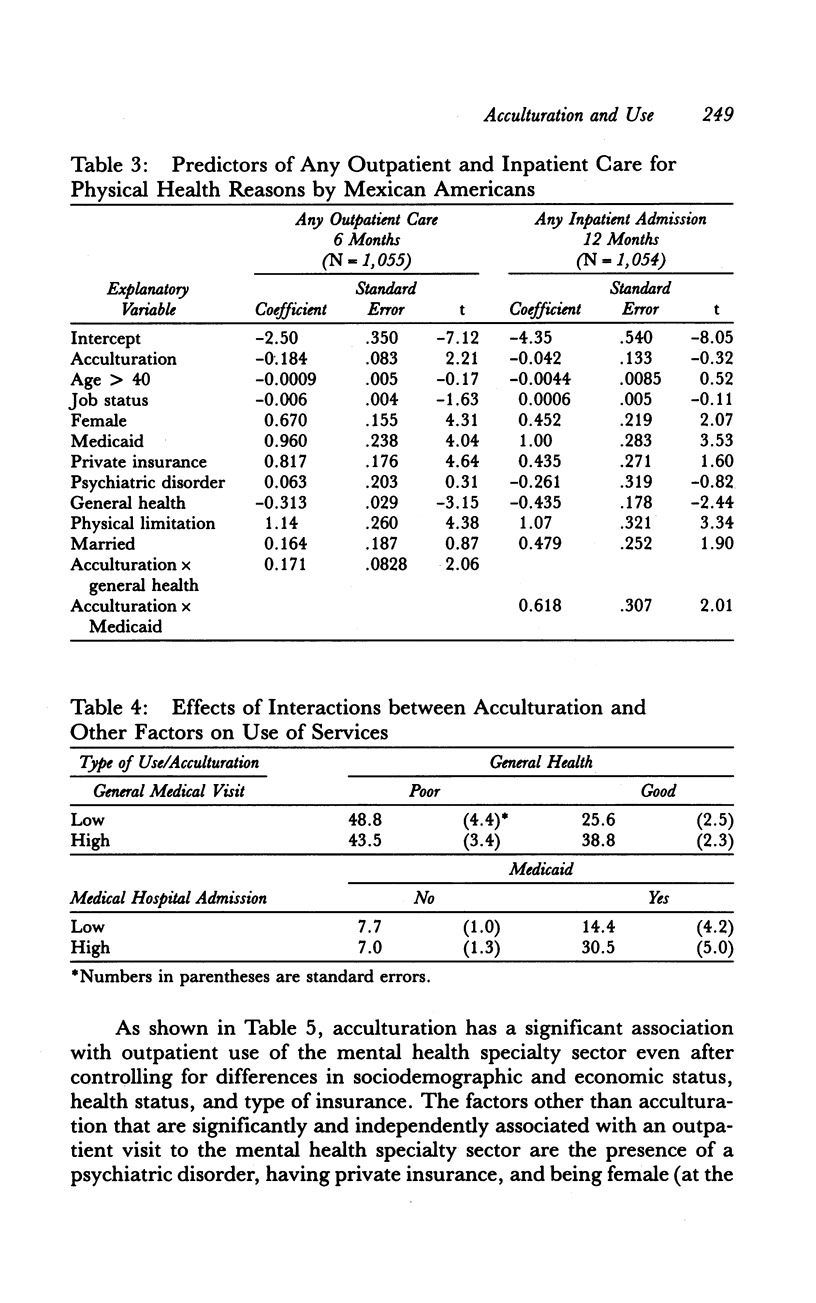
How does level of acculturation affect the probability that Mexican Americans use general health, mental health, and human social services? We studied this question using data from a general population sample of Mexican Americans (N = 1,055). Data were elicited in face-to-face interviews. After controlling for sociodemographic and economic factors, health status, and insurance coverage, Mexican Americans who were less acculturated had significantly lower probabilities of an outpatient medical visit for physical health problems and of a visit to a mental health specialist or human service provider for emotional problems. The less acculturated with good perceived general health were especially unlikely to receive outpatient medical care. Having Medicaid coverage was associated with a larger increase in the probability of an inpatient medical admission for the more acculturated than for the less acculturated. Other individual characteristics had generally similar effects on use of medical and mental health services for both the more and the less acculturated Mexican Americans.
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acosta F. X. Barriers between mental health services and Mexican Americans: an examinations of a paradox. Am J Community Psychol. 1979 Oct;7(5):503–520. doi: 10.1007/BF00894047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aday L. A., Andersen R. A framework for the study of access to medical care. Health Serv Res. 1974 Fall;9(3):208–220. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R., Lewis S. Z., Giachello A. L., Aday L. A., Chiu G. Access to medical care among the Hispanic population of the southwestern United States. J Health Soc Behav. 1981 Mar;22(1):78–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel R., Thoits P. The impact of culture on the cognitive structure of illness. Cult Med Psychiatry. 1987 Dec;11(4):465–494. doi: 10.1007/BF00048494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berki S. E., Kobashigawa B. Education and income effects in the use of ambulatory services in the United States: an analysis of the 1970 National Health Interview Survey data. Int J Health Serv. 1978;8(2):351–365. doi: 10.2190/Y205-GLA2-VD5R-Q1JP. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles R. W., Manga P., Binder D. A., Angus D. E., Charette A. The use of physician services under a national health insurance scheme. An examination of the Canada Health Survey. Med Care. 1983 Nov;21(11):1037–1054. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198311000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnam M. A., Hough R. L., Karno M., Escobar J. I., Telles C. A. Acculturation and lifetime prevalence of psychiatric disorders among Mexican Americans in Los Angeles. J Health Soc Behav. 1987 Mar;28(1):89–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnam M. A., Karno M., Hough R. L., Escobar J. I., Forsythe A. B. The Spanish Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Reliability and comparison with clinical diagnoses. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Nov;40(11):1189–1196. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790100035005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney A. P., Chavira J. A., Hall R. P., Gary H. E., Jr Barriers to medical care of Mexican-Americans: the role of social class, acculturation, and social isolation. Med Care. 1982 Sep;20(9):883–891. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198209000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deyo R. A., Diehl A. K., Hazuda H., Stern M. P. A simple language-based acculturation scale for Mexican Americans: validation and application to health care research. Am J Public Health. 1985 Jan;75(1):51–55. doi: 10.2105/ajph.75.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. W., Holzer C. E., 3rd, Von Korff M., Anthony J. C., Helzer J. E., George L., Burnam A., Boyd J. H., Kessler L. G., Locke B. Z. The design of the Epidemiologic Catchment Area surveys. The control and measurement of error. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Oct;41(10):942–948. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790210024004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgan C. M. Specialty and general ambulatory mental health services. Comparison of utilization and expenditures. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 Jun;42(6):565–572. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790290047005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough R. L., Landsverk J. A., Karno M., Burnam M. A., Timbers D. M., Escobar J. I., Regier D. A. Utilization of health and mental health services by Los Angeles Mexican Americans and non-Hispanic whites. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 Aug;44(8):702–709. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800200028005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karno M., Burnam A., Escobar J. I., Hough R. L., Eaton W. W. Development of the Spanish-language version of the National Institute of Mental Health Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Nov;40(11):1183–1188. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790100029003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karno M., Edgerton R. B. Perception of mental illness in a Mexican-American community. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1969 Feb;20(2):233–238. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1969.01740140105013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning W. G., Jr, Wells K. B., Duan N., Newhouse J. P., Ware J. E., Jr Cost sharing and the use of ambulatory mental health services. Am Psychol. 1984 Oct;39(10):1077–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markides K. S., Levin J. S., Ray L. A. Determinants of physician utilization among Mexican-Americans. A three-generations study. Med Care. 1985 Mar;23(3):236–246. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198503000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nall F. C., 2nd, Speilberg J. Social and cultural factors in the responses of Mexican-Americans to medical treatment. J Health Soc Behav. 1967 Dec;8(4):299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padilla A. M., Ruiz R. A., Alvarez R. Community mental health services for spanish-speaking/surnamed population. Am Psychol. 1975 Sep;30(9):892–905. doi: 10.1037//0003-066x.30.9.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippus M. J. Successful and unsuccessful approaches to mental health services for an urban Hispano American population. Am J Public Health. 1971 Apr;61(4):820–830. doi: 10.2105/ajph.61.4.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regier D. A., Myers J. K., Kramer M., Robins L. N., Blazer D. G., Hough R. L., Eaton W. W., Locke B. Z. The NIMH Epidemiologic Catchment Area program. Historical context, major objectives, and study population characteristics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Oct;41(10):934–941. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790210016003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins L. N., Helzer J. E., Croughan J., Ratcliff K. S. National Institute of Mental Health Diagnostic Interview Schedule. Its history, characteristics, and validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Apr;38(4):381–389. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780290015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S., Skinner E. A., Kessler L. G., Von Korff M., German P. S., Tischler G. L., Leaf P. J., Benham L., Cottler L., Regier D. A. Utilization of health and mental health services. Three Epidemiologic Catchment Area sites. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Oct;41(10):971–978. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790210053007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slesinger D. P., Cautley E. Medical utilization patterns of Hispanic migrant farmworkers in Wisconsin. Public Health Rep. 1981 May-Jun;96(3):255–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon S. W., Roberts R. E. Prevalence of treated and untreated psychiatric disorders in three ethnic groups. Soc Sci Med. 1982;16(17):1575–1582. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(82)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells K. B., Hough R. L., Golding J. M., Burnam M. A., Karno M. Which Mexican-Americans underutilize health services? Am J Psychiatry. 1987 Jul;144(7):918–922. doi: 10.1176/ajp.144.7.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


