Abstract
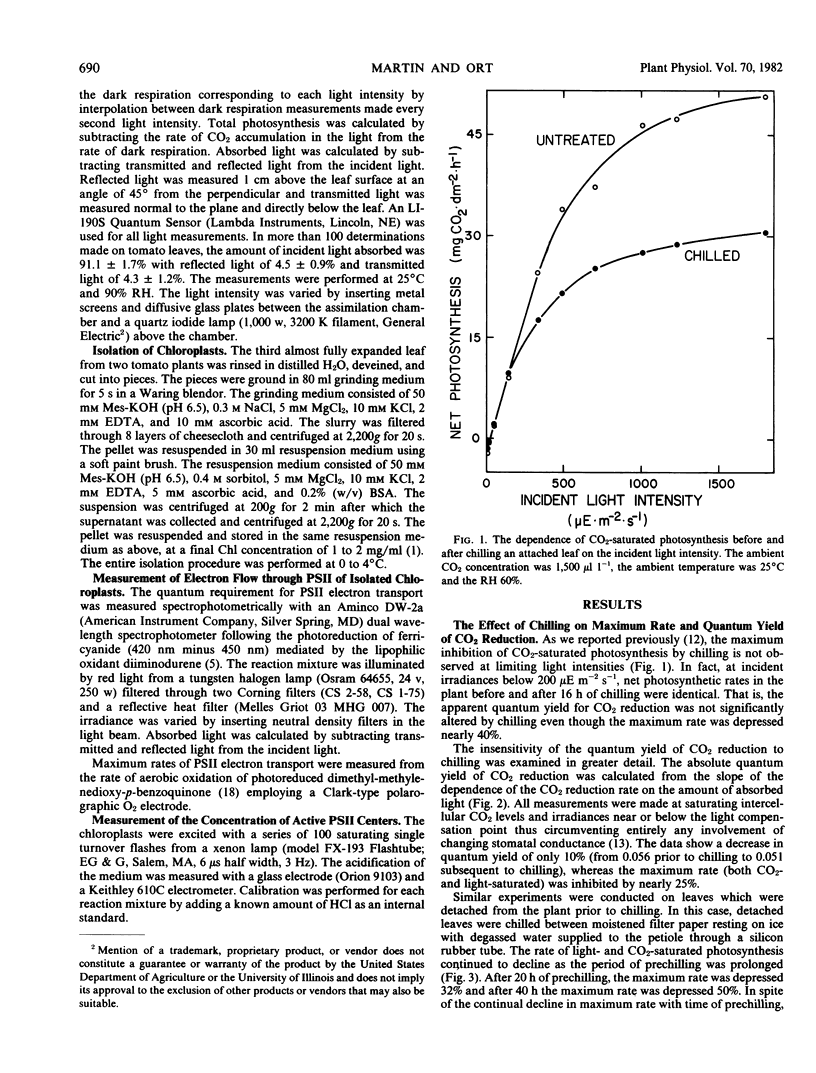
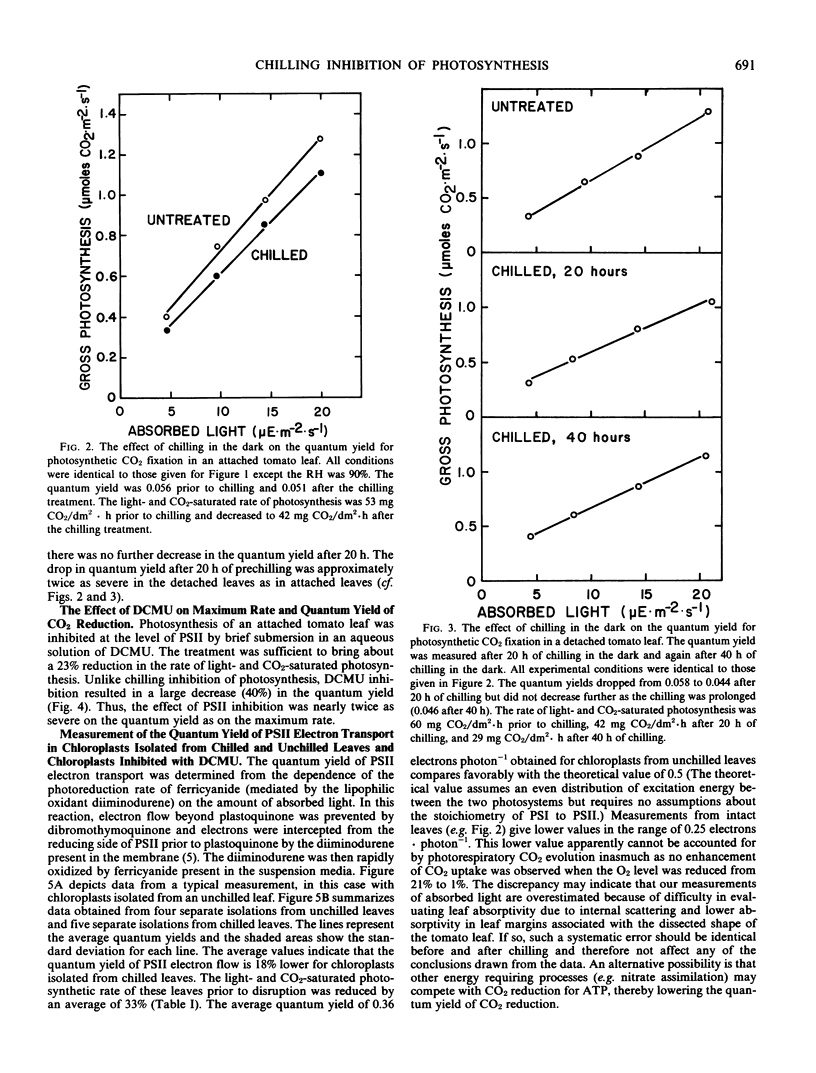
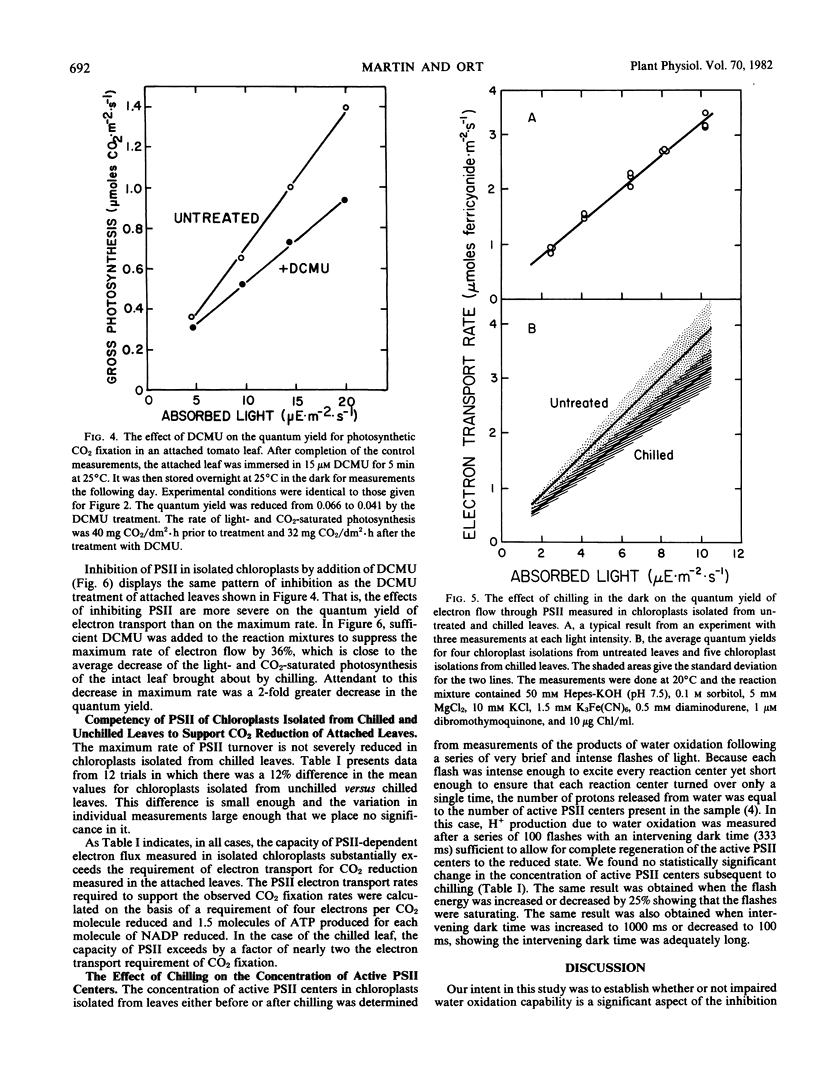
Chilling tomato plants (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. cv. Rutgers and cv. Floramerica) in the dark resulted in a sizable inhibition in the rate of light- and CO2-saturated photosynthesis. However, at low light intensity, the inhibition disappeared and the absolute quantum yield of CO2 reduction was diminished only slightly. The quantum yield of photosystem II (PSII) electron flow was 18% lower when measured in chloroplasts isolated from chilled leaves than in chloroplasts isolated from unchilled leaves. Even though the maximum rate of PSII turnover in these chloroplasts was 12% lower subsequent to chilling, it was in all cases two or more times that required to support the light- and CO2-saturated rate of photosynthesis measured in the attached leaf. The concentration of active PSII centers in chloroplasts isolated from leaves either before or after chilling was determined by measurement of the products of water oxidation from a series of saturating flashes short enough to turnover the electron transport carriers only a single time. There was no significant change in the concentration of active PSII centers due to dark chilling.
It was concluded that PSII activity and water oxidation capacity are not significantly impaired in tomato by chilling in the dark and therefore are not primary aspects of the inhibition of CO2 reduction observed in attached leaves.
Full text
PDF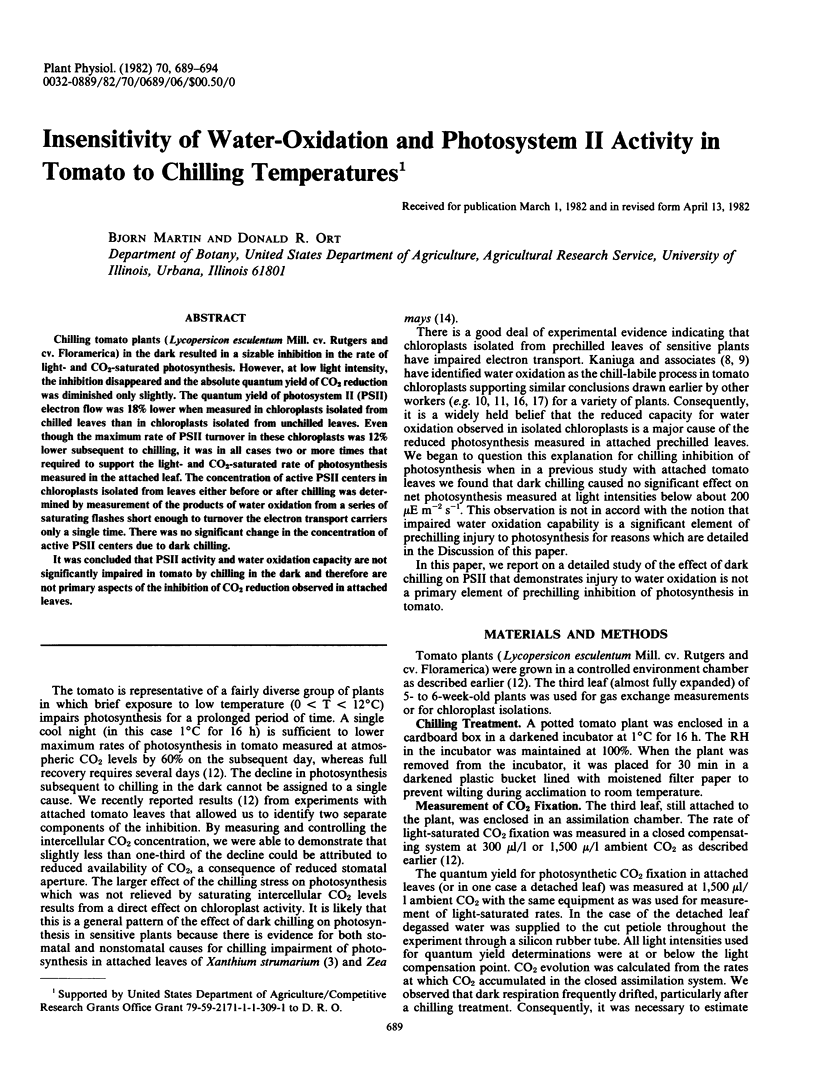

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diner B. A., Wollman F. A. Isolation of highly active photosystem II particles from a mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(2):521–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Raschke K. Prechilling of Xanthium strumarium L. Reduces Net Photosynthesis and, Independently, Stomatal Conductance, While Sensitizing the Stomata to CO(2). Plant Physiol. 1974 Jun;53(6):808–812. doi: 10.1104/pp.53.6.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izawa S., Gould J. M., Ort D. R., Felker P., Good N. E. Electron transport and photophosphorylation in chloroplasts as a function of the electron acceptor. 3. A dibromothymoquinone-insensitive phosphorylation reaction associated with photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 27;305(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joliot P., Bennoun P., Joliot A. New evidence supporting energy transfer between photosynthetic units. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):317–328. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGULIES M. M., JAGENDORF A. T. Effect of cold storage of bean leaves on photosynthetic reactions of isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Oct;90:176–183. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90565-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M. Effect of cold-storage of bean leaves on photosynthetic reactions of isolated chloroplasts. Inability to donate electrons to photosystem II and relation to manganese content. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 20;267(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B., Ort D. R., Boyer J. S. Impairment of photosynthesis by chilling-temperatures in tomato. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):329–334. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty P., Boyer J. S. Chloroplast Response to Low Leaf Water Potentials: IV. Quantum Yield Is Reduced. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):704–709. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Butler W. L. Low temperature spectral properties of subchloroplast fractions purified from spinach. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):373–379. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie R. M., Nott R. Assay of chilling injury in wild and domestic tomatoes based on photosystem activity of the chilled leaves. Plant Physiol. 1979 May;63(5):796–801. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.5.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


