Abstract
A Mg2+-dependent, alkaline phosphatase has been isolated from mature pollen of Lilium longiflorum Thunb., cv. Ace and partially purified. It hydrolyzes 1l- and 1d-myo-inositol 1-phosphate, myo-inositol 2-phosphate, and β-glycerophosphate at rates decreasing in the order named. The affinity of the enzyme for 1l- and 1d-myo-inositol 1-phosphate is approximately 10-fold greater than its affinity for myo-inositol 2-phosphate. Little or no activity is found with phytate, d-glucose 6-phosphate, d-glucose 1-phosphate, d-fructose 1-phosphate, d-fructose 6-phosphate, d-mannose 6-phosphate, or p-nitrophenyl phosphate. 3-Phosphosphoglycerate is a weak competitive inhibitor. myo-Inositol does not inhibit the reaction. Optimal activity is obtained at pH 8.5 and requires the presence of Mg2+. At 4 millimolar, Co2+, Fe2+ or Mn2+ are less effective. Substantial inhibition is obtained with 0.25 molar Li+. With β-glycerophosphate as substrate the Km is 0.06 millimolar and the reaction remains linear at least 2 hours. In 0.1 molar Tris, β-glycerophosphate yields equivalent amounts of glycerol and inorganic phosphate, evidence that transphosphorylation does not occur.
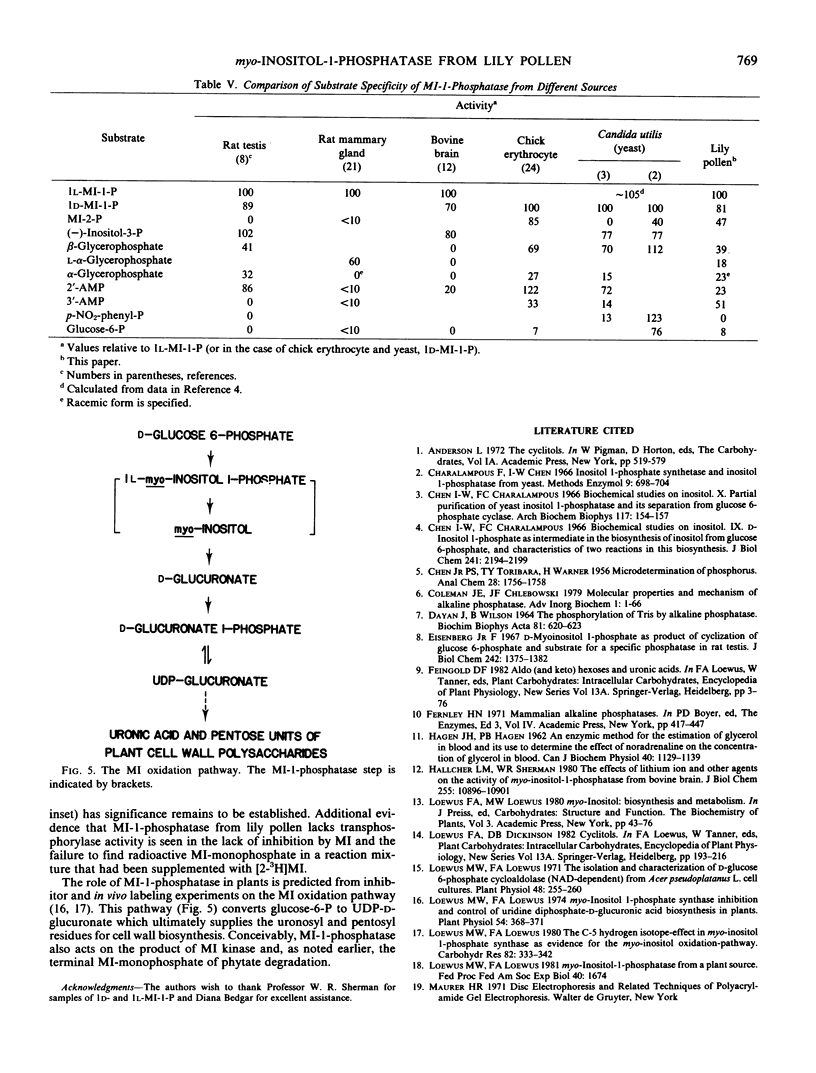
In higher plants this myo-inositol-1-phosphatase links myo-inositol biosynthesis to the myo-inositol oxidation pathway to produce an alternative path from d-glucose 6-phosphate to UDP-d-glucuronate that bypasses UDP-d-glucose dehydrogenase. myo-Inositol-1-phosphatase also furnishes free myo-inositol for reactions that lead to other cyclitols and cyclitol-containing compounds of biosynthetic and/or regulatory significance in plant growth and development.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen I. W., Charalampous C. F. Biochemical studies on inositol. IX. D-Inositol 1-phosphate as intermediate in the biosynthesis of inositol from glucose 6-phosphate, and characteristics of two reactions in this biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2194–2199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAYAN J., WILSON I. B. THE PHOSPHORYLATION OF TRIS BY ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 9;81:620–623. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg F., Jr D-myoinositol 1-phosphate as product of cyclization of glucose 6-phosphate and substrate for a specific phosphatase in rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1375–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEN J. H., HAGEN P. B. An enzymic method for the estimation of glycerol in blood and its use to determine the effect of noradrenaline on the concentration of glycerol in blood. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Aug;40:1129–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewus M. W., Loewus F. A. The C-5 hydrogen isotope-effect in myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase as evidence for the myo-inositol oxidation-pathway. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Jul;82(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85707-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewus M. W., Loewus F. The Isolation and Characterization of d-Glucose 6-Phosphate Cycloaldolase (NAD-Dependent) from Acer pseudoplatanus L. Cell Cultures: Its Occurrence in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1971 Sep;48(3):255–260. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewus M. W., Loewus F. myo-Inositol 1-Phosphate Synthase Inhibition and Control of Uridine Diphosphate-d-glucuronic Acid Biosynthesis in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):368–371. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccarato W. F., Ray R. E., Wells W. W. Biosynthesis of myo-inositol in rat mammary gland. Isolation and properties of the enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAO N. A., CAMA H. R., KUMAR S. A., VAIDYANATHAN C. S. Alkaline beta-glycerophosphatase of green gram (Phaseolus radiatus). J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3353–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., MAPSON L. W. Uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase of pea seedlings. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):567–572. doi: 10.1042/bj0660567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Loewus F. A. Redistribution of Tritium during Germination of Grain Harvested from myo-[2-H]Inositol- and scyllo-[R-H]Inositol-Labeled Wheat. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jan;69(1):220–225. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


