Abstract
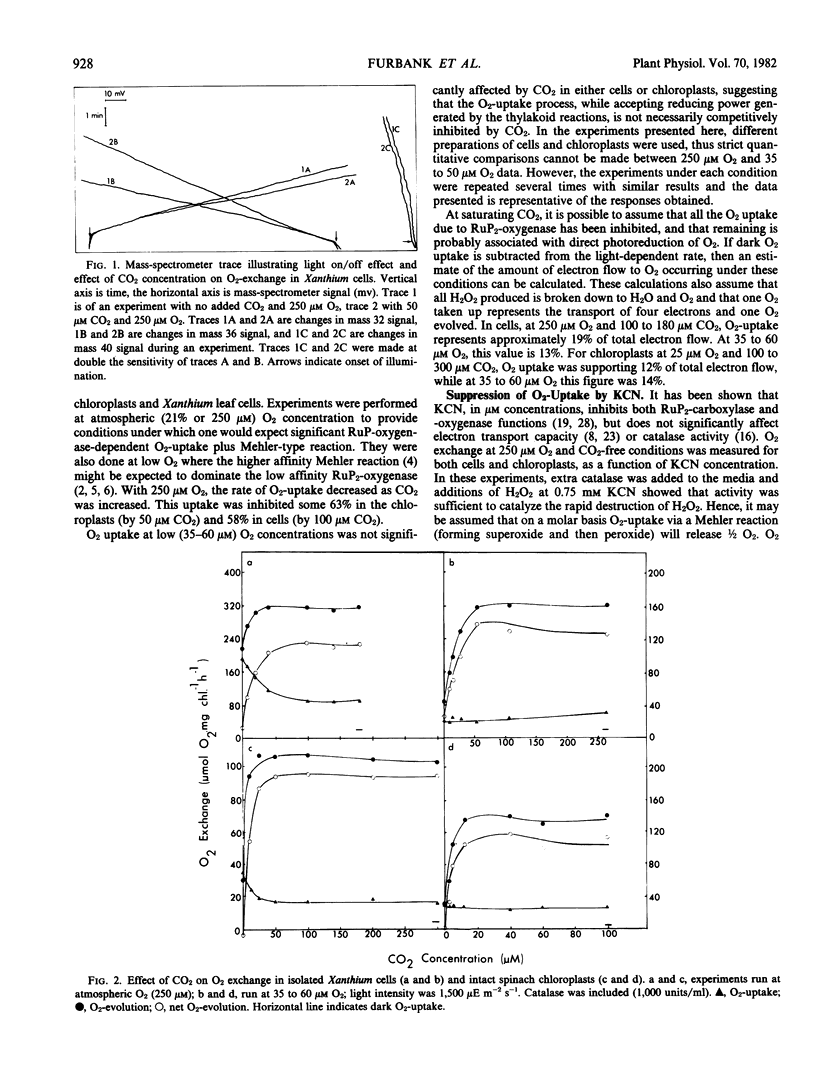
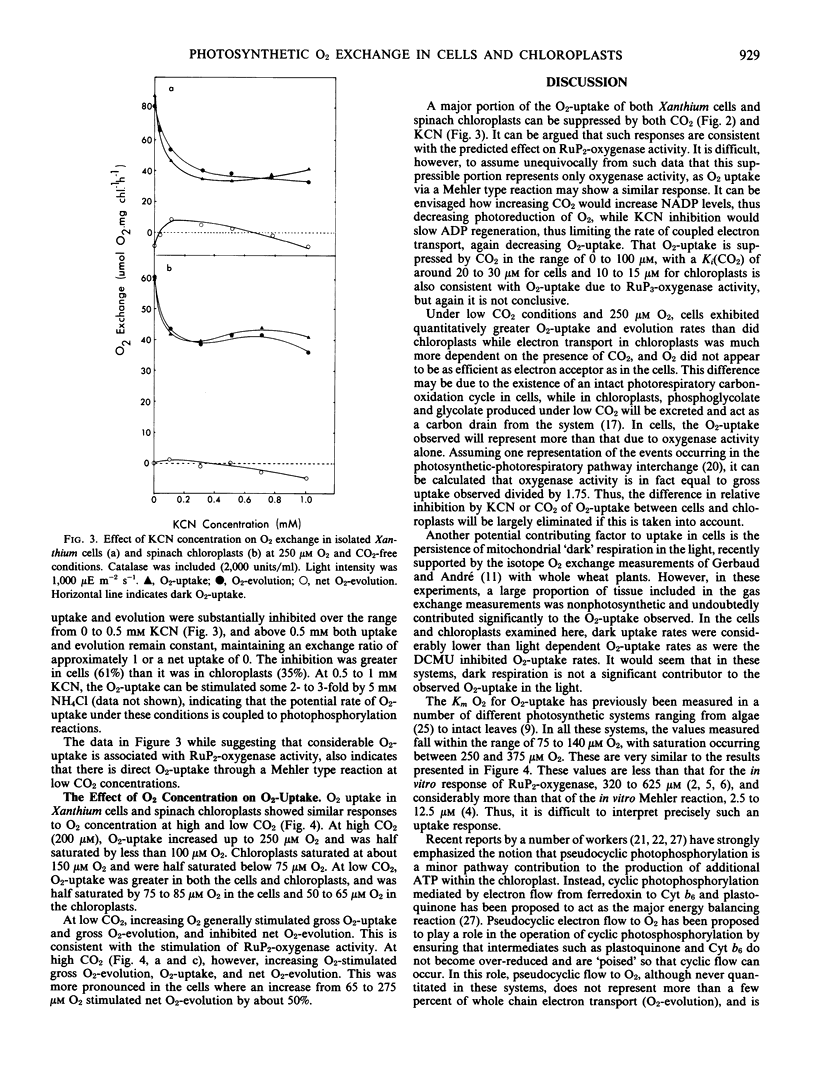
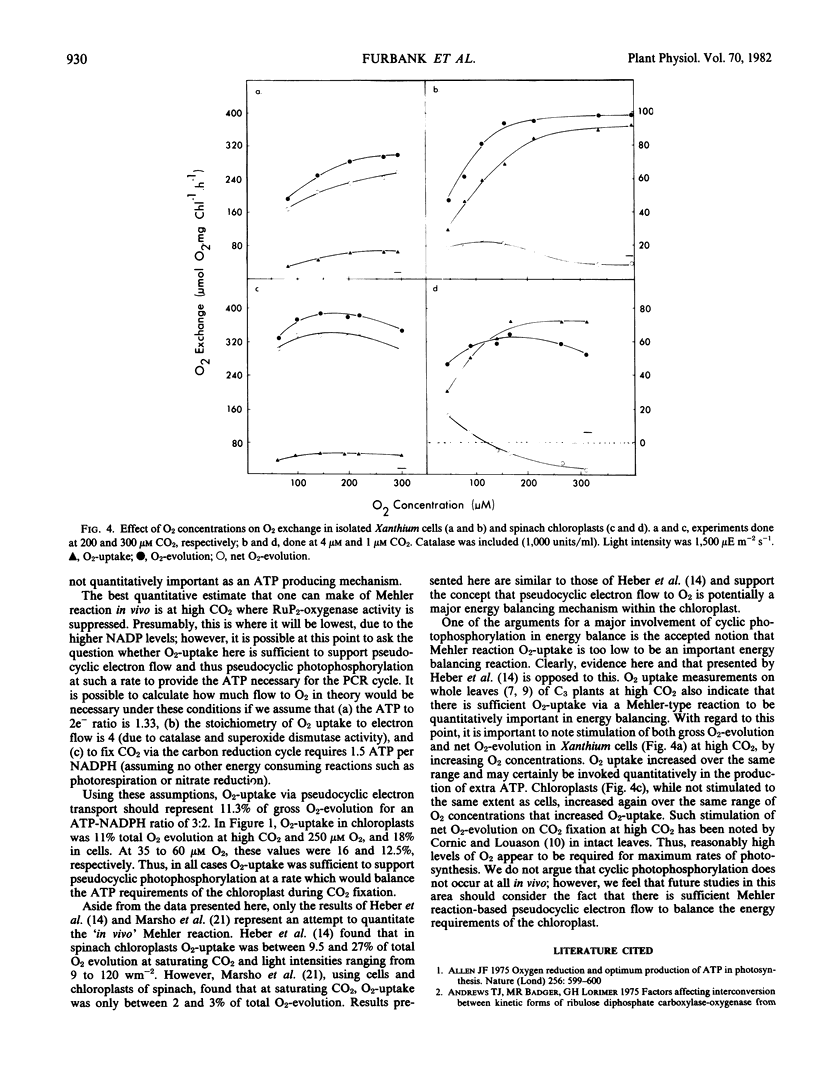
Photosynthetic O2-production and photorespiratory O2-uptake were measured, using stable isotope techniques, in isolated intact leaf cells of the C3 plant Xanthium strumarium L., and isolated intact chloroplasts of Spinacia oleracea L (var. Yates 102). Considerable light dependent O2-uptake was observed in both systems, a proportion of which could be suppressed by CO2 (63% suppression in chloroplasts by 50 micromolar CO2, 58% in cells by 100 micromolar CO2 and 250 micromolar O2). At low O2, O2-uptake was CO2 insensitive. At high CO2 up to 19% of total electron flow was to O2 in cells and up to 14% in chloroplasts. O2-uptake showed inhibition by KCN (61% in cells, 35% in chloroplasts by 0.2 millimolar KCN). O2-uptake half saturated at 75 to 85 micromolar O2 in cells and 50 to 65 micromolar O2 in chloroplasts, at low CO2. The results are discussed in terms of the RuP2-oxygenase reaction and direct photoreduction of O2 via a Mehler reaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP N. I., SPIKES J. D. Inhibition by cyanide of the photochemical activity of isolated chloroplasts. Nature. 1955 Aug 13;176(4476):307–308. doi: 10.1038/176307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canvin D. T., Berry J. A., Badger M. R., Fock H., Osmond C. B. Oxygen exchange in leaves in the light. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):302–307. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbaud A., André M. Effect of CO(2), O(2), and Light on Photosynthesis and Photorespiration in Wheat. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1032–1036. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCH G., OWENS O. V., KOK B. Photosynthesis and respiration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Apr;101:171–180. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber U., Santarius K. A. Direct and indirect transfer of ATP and ADP across the chloroplast envelope. Z Naturforsch B. 1970 Jul;25(7):718–728. doi: 10.1515/znb-1970-0714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber U. Stoichiometry of reduction and phosphorylation during illumination of intact chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 27;305(1):140–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Walker D. A. The reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate by reconstituted chloroplasts and by chloroplast extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 19;368(3):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Andrews T. J., Tolbert N. E. Ribulose diphosphate oxygenase. II. Further proof of reaction products and mechanism of action. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):18–23. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsho T. V., Behrens P. W. Photosynthetic oxygen reduction in isolated intact chloroplasts and cells in spinach. Plant Physiol. 1979 Oct;64(4):656–659. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.4.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. D., Slovacek R. E., Hind G. Cyclic electron transport in isolated intact chloroplasts. Further studies with antimycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 9;504(2):298–309. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouitrakul R., Izawa S. Electron transport and photophosphorylation in chloroplasts as a function of the electron acceptor. II. Acceptor-specific inhibition by KCN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 27;305(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmer R. J., Kok B. Photoreduction of O(2) Primes and Replaces CO(2) Assimilation. Plant Physiol. 1976 Sep;58(3):336–340. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmer R., Kok B., Ollinger O. Kinetics and Apparent K(m) of Oxygen Cycle under Conditions of Limiting Carbon Dioxide Fixation. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jun;61(6):915–917. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.6.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey T. D., Raschke K. Effects of phaseic Acid and dihydrophaseic Acid on stomata and the photosynthetic apparatus. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):291–297. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slovacek R. E., Crowther D., Hind G. Relative activities of linear and cyclic electron flows during chloroplast CO2-fixation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 3;592(3):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishnick M., Lane M. D. Inhibition of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase by cyanide. Inactive ternary complex of enzyme, ribulose diphosphate, and cyanide. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelitch I. Pathways of carbon fixation in green plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:123–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


