Abstract
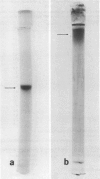
A protein, extracted from Katahdin potato (Solanum tuberosum L. cv `Katahdin') tubers and purified by ion exchange chromatography and gel filtration, agglutinates avirulent strains of the bacterial wilt pathogen, Pseudomonas solanacearum, but only weakly agglutinates virulent strains. The agglutinin has very low hemagglutinating activity (in contrast to potato lectin) and is a glycoprotein containing about 61% carbohydrate. The carbohydrate moiety contains 91% (weight%) arabinose, 5% galactose, 3% glucose, and 1% glucosamine. The protein portion is rich in hydroxyproline (42%), lysine (16%), serine (9%), and proline (9%). The entire agglutinin has a molecular weight of 91,000 ± 5,000 and is very basic (pI > 11). Shape estimations based on the concentration dependence of the sedimentation coefficient, the high viscosity ([η] = 92.7), the frictional coefficient (f/fo = 2.15), and axial ratio (a/b = 25) indicate that the agglutinin is a prolate ellipsoid.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. K., Desai N. N., Neuberger A., Creeth J. M. Properties of potato lectin and the nature of its glycoprotein linkages. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):665–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1710665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A. K., Neuberger A. The purification and properties of the lectin from potato tubers, a hydroxyproline-containing glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj1350307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brysk M. M., Chrispeels M. J. Isolation and partial characterization of a hydroxyproline-rich cell wall glycoprotein and its cytoplasmic precursor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions: I. A Structural Investigation of Cell Wall Hydroxyproline-rich Glycoproteins Which Accumulate in Fungus-infected Plants. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):314–319. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLOP P. M. Studies on a parent gelatin from ichthyocol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Feb;54(2):501–512. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. L., Sequeira L., Huang T. S. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides as inducers of disease resistance in tobacco. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):424–432. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.424-432.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horejsí V., Kocourek J. Studies on lectins. XXXVII. Isolation and characterization of the lectin from Jimson-weed seeds (Datura stramonium L.). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 25;532(1):92–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINKOVICH V. A. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE HEMAGGLUTININ PRESENT IN POTATOES. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:732–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick P. J., Chandrasekhar S., Millis A. J. Direct visualization of collagens and procollagens in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 1;97(2):359–366. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Lamport D. T. Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride deglycosylates glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara T., Doty P. THE SONIC FRAGMENTATION OF COLLAGEN MACROMOLECULES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 May;44(5):411–417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.5.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. A., Varner J. E. Purification and Characterization of a Salt-extractable Hydroxyproline-rich Glycoprotein from Aerated Carrot Discs. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):787–792. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. H., Liener I. E. The use of glutaraldehyde-treated erythrocytes for assaying the agglutinating activity of lectins. Anal Biochem. 1975 Oct;68(2):651–653. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90663-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]