Abstract
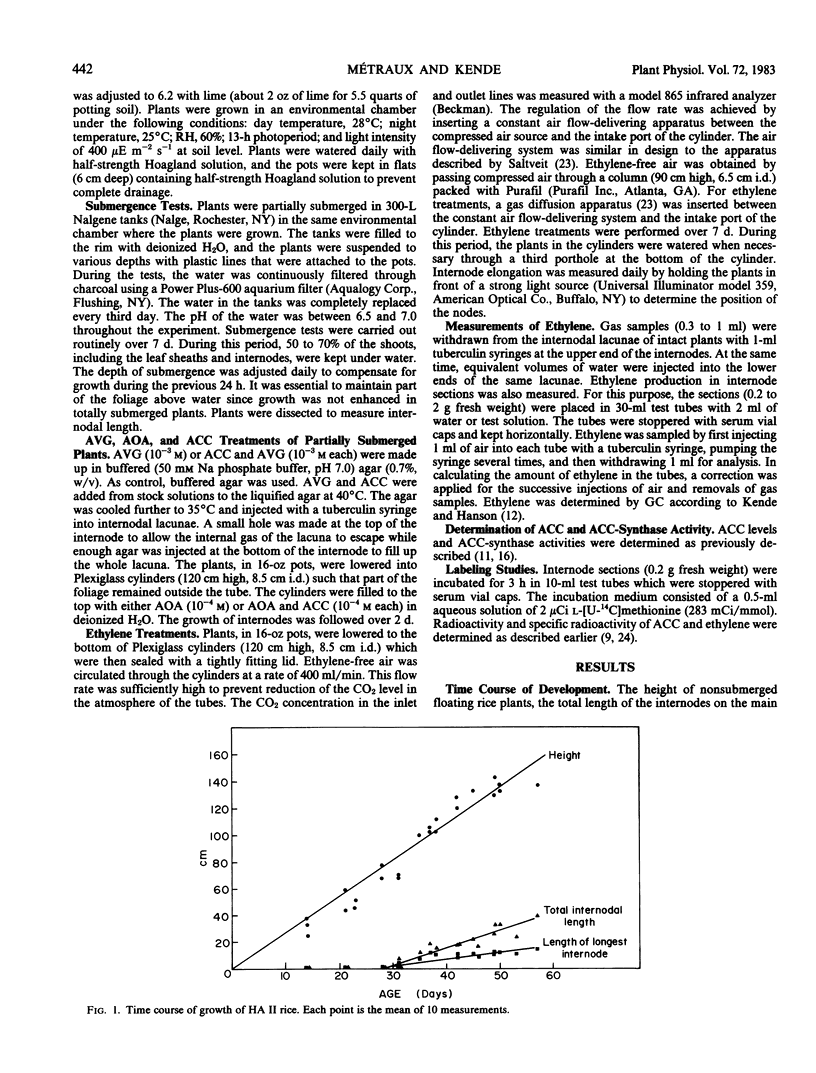
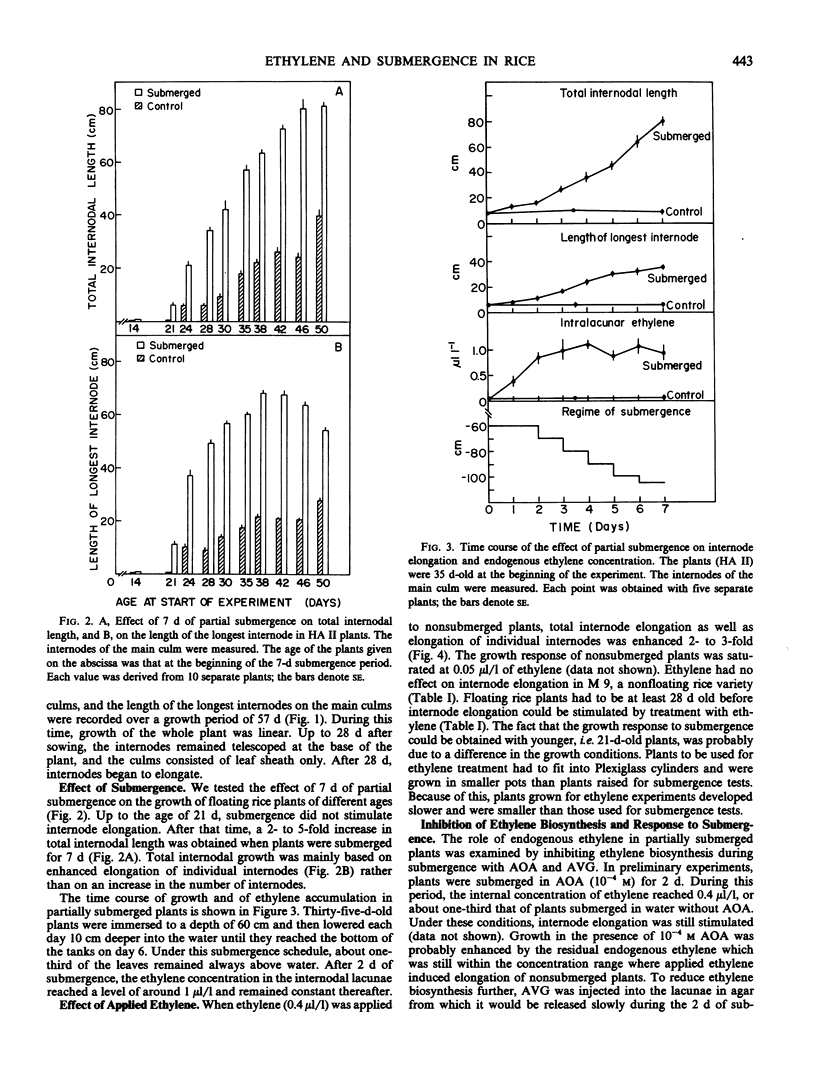
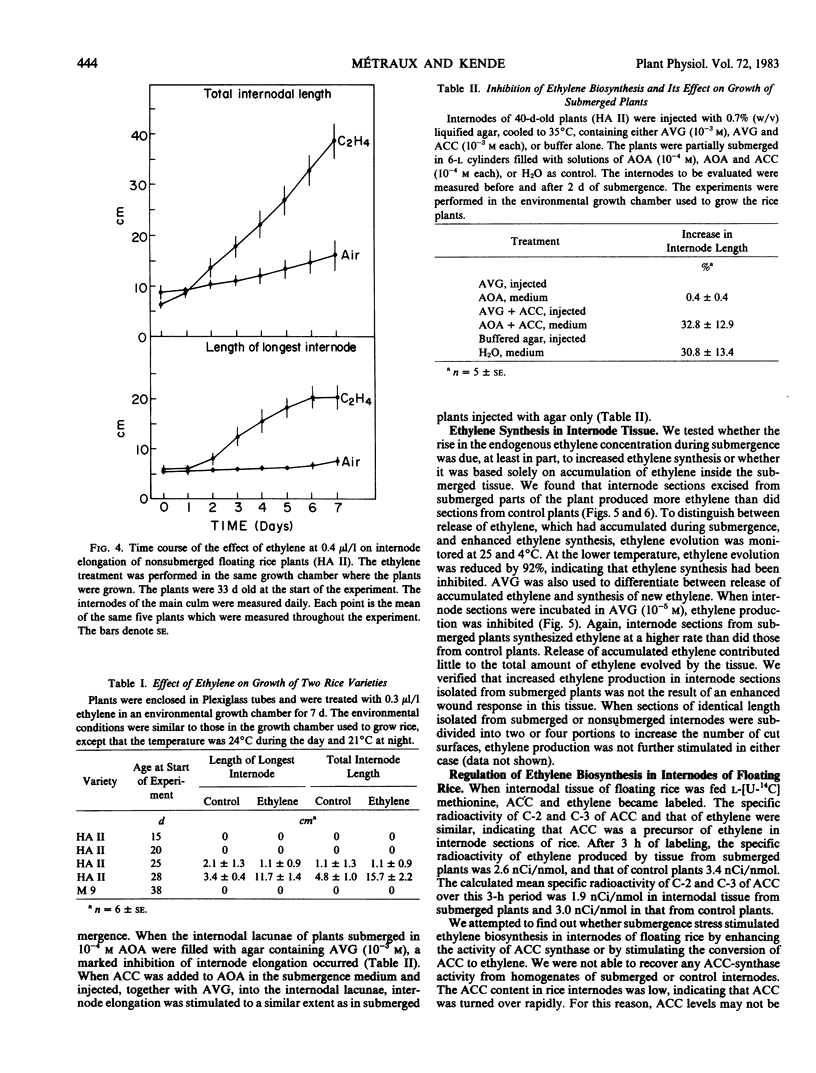
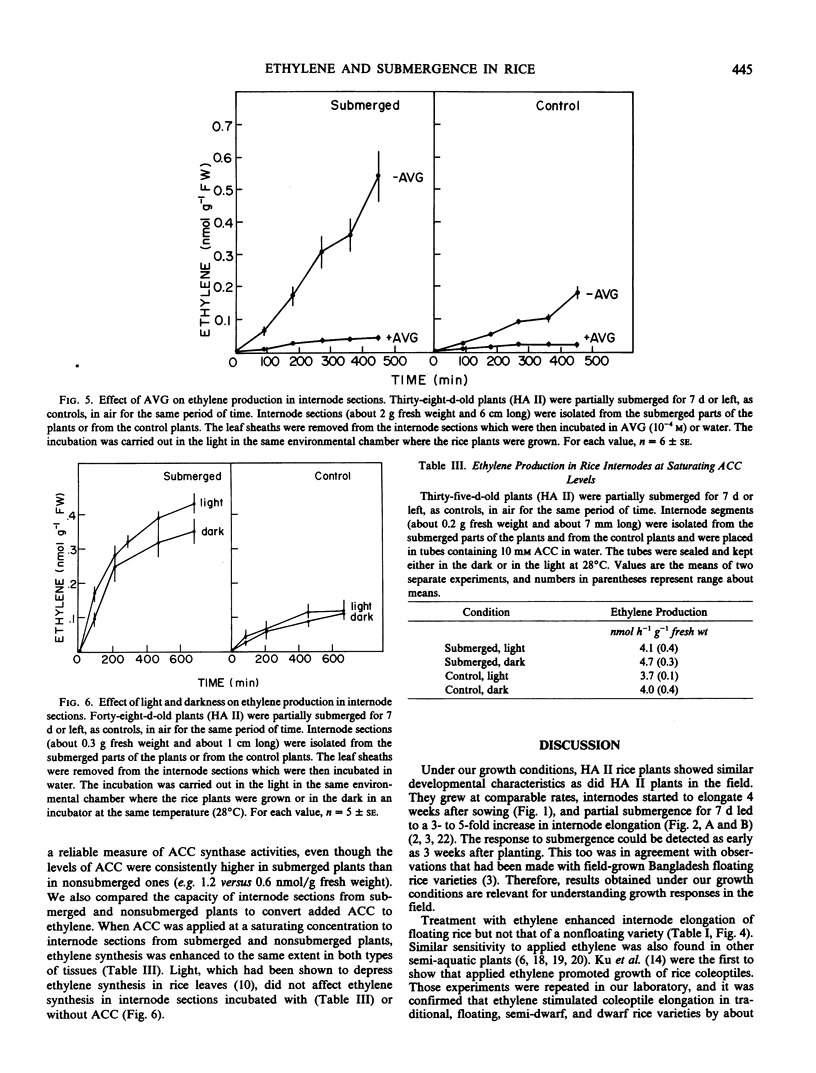
We investigated the effect of partial submergence on internode elongation in a Bangladesh variety of floating or deep water rice (Oryza sativa L., cv. Habiganj Aman II). In plants which were at least 21 days old, 7 days of submergence led to a 3- to 5-fold increase in internodal length. During submergence, the ethylene concentration in the internodes increased from about 0.02 to 1 microliters per liter. Treatment of nonsubmerged plants with ethylene also stimulated internode elongation. When ethylene synthesis in partially submerged plants was blocked with aminooxyacetic acid and aminoethoxyvinylglycine, internode elongation was inhibited. This growth inhibition was reversed when ethylene biosynthesis was restored with 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC). Radio-labeling studies showed that ethylene in floating rice was synthesized from methionine via ACC. Internodal tissue from submerged plants had a much higher capacity to form ethylene than did internodal tissue from nonsubmerged plants. This increase in ethylene synthesis appeared to be due to enhanced ACC formation rather than to increased conversion of ACC to ethylene. Our results indicate that ethylene produced during submergence is required for the stimulation of growth in submerged floating rice plants.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Yang S. F. Ethylene biosynthesis: Identification of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid as an intermediate in the conversion of methionine to ethylene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):170–174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kende H., Hanson A. D. Relationship between Ethylene Evolution and Senescence in Morning-Glory Flower Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):523–527. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konze J. R., Jones J. F., Boller T., Kende H. Effect of 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid on the Production of Ethylene in Senescing Flowers of Ipomoea tricolor Cav. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):566–571. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizada M. C., Yang S. F. A simple and sensitive assay for 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):140–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Adams D. O. Chilling-Induced Ethylene Production in Cucumbers (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):424–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. B., Yang S. F. Biosynthesis of wound ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):281–285. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


