Abstract
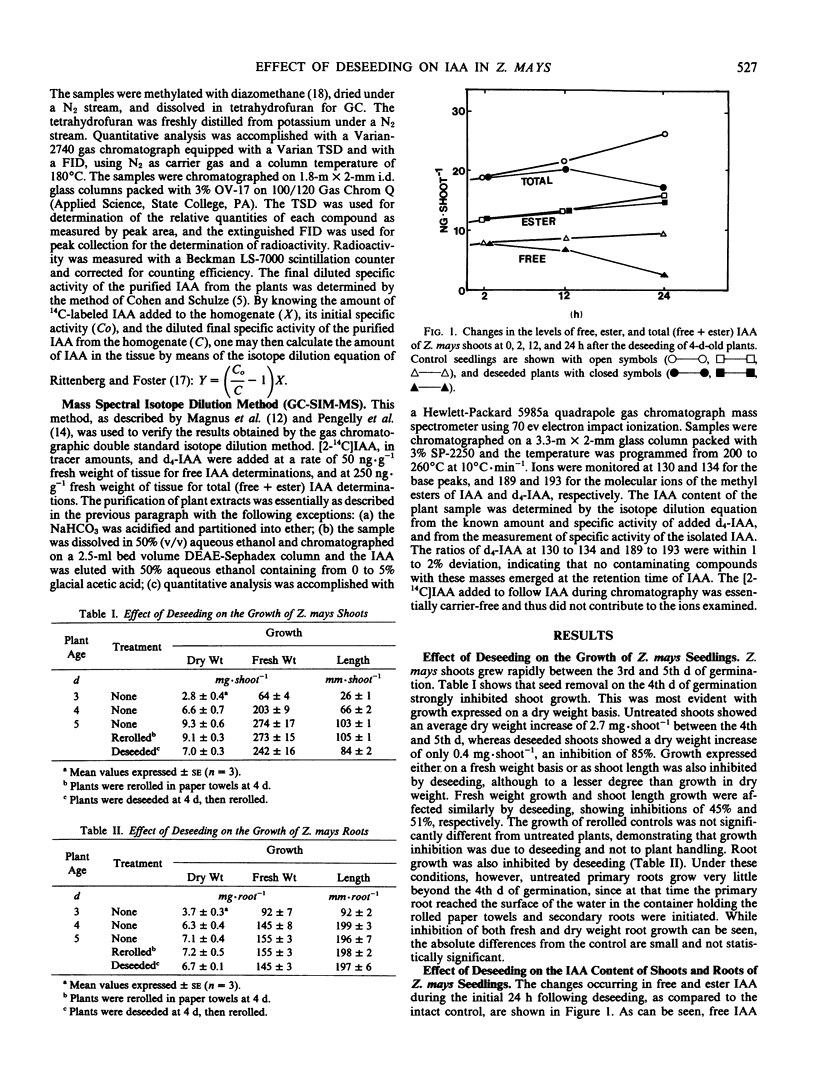
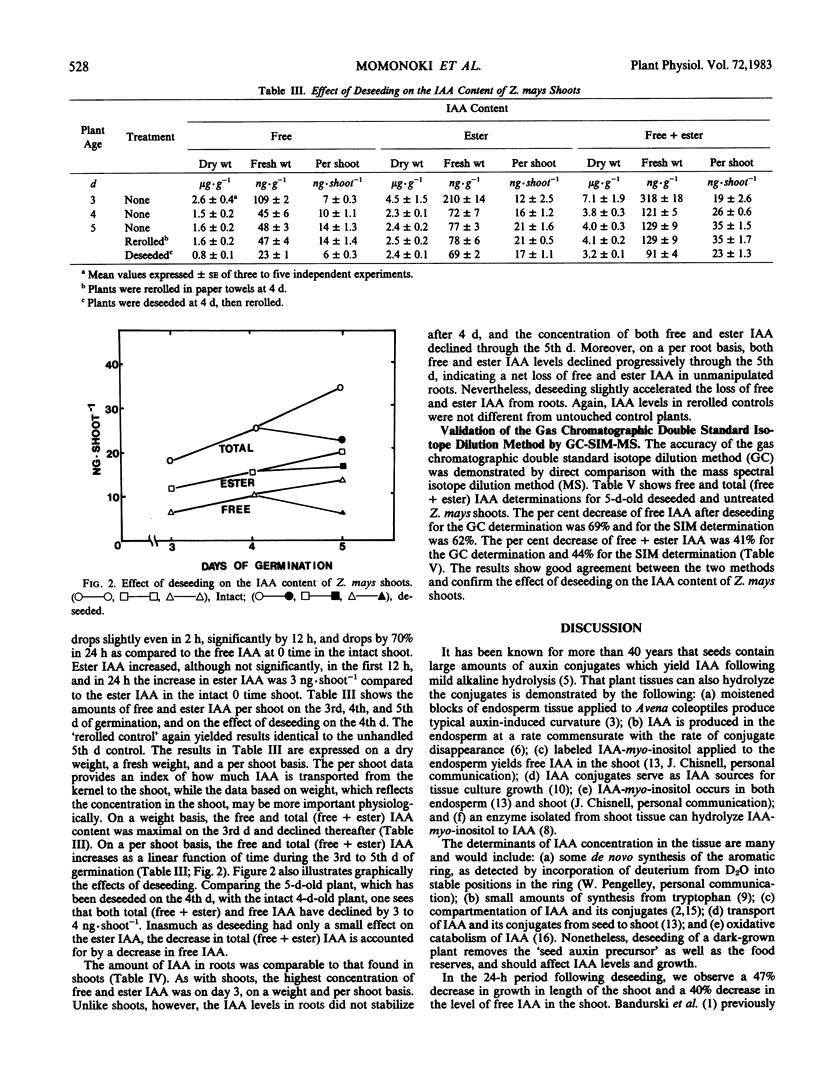
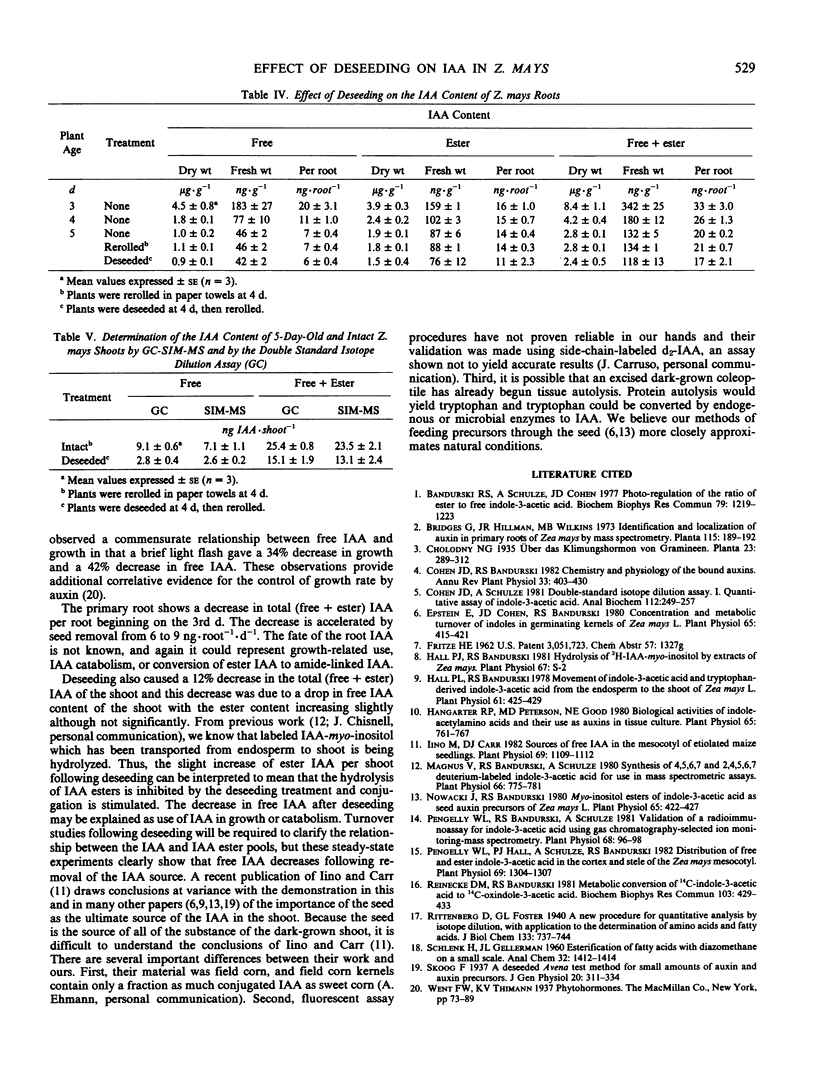
We wished to determine the effect of endosperm removal on the amounts of free and esterified indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) in young Zea mays seedlings. The increases of IAA derived from endosperm and from biosynthesis, but without correction for catabolic losses, were 0.9 picomole of free IAA per shoot per hour, and 1.1 picomoles per shoot per hour of ester IAA. After deseeding, free IAA in the shoot declines by 40% following kernel removal and total (free + ester) IAA declines at a rate of about 1 picomole per shoot per hour. A slight, but insignificant increase of ester IAA occurs following endosperm removal. In the primary roots, the decreases of free IAA and total (free + ester) IAA are accelerated by seed removal. Thus, the endosperm appears to be a major source of IAA for the shoot and root.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandurski R. S., Schulze A., Cohen J. D. Photo-regulation of the ratio of ester to free indole-3-acetic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1219–1223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. D., Schulze A. Double-standard isotope dilution assay. I. Quantitative assay of indole-3-acetic acid. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Cohen J. D., Bandurski R. S. Concentration and Metabolic Turnover of Indoles in Germinating Kernels of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):415–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. L., Bandurski R. S. Movement of Indole-3-acetic Acid and Tryptophan-derived Indole-3-acetic Acid from the Endosperm to the Shoot of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):425–429. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hangarter R. P., Peterson M. D., Good N. E. Biological activities of indoleacetylamino acids and their use as auxins in tissue culture. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):761–767. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Carr D. J. Sources of Free IAA in the Mesocotyl of Etiolated Maize Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1109–1112. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M. Isolation of Functionally Intact Rhodoplasts from Griffithsia monilis (Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta). Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):5–8. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnus V., Bandurski R. S., Schulze A. Synthesis of 4,5,6,7 and 2,4,5,6,7 Deuterium-labeled Indole-3-Acetic Acid for Use in Mass Spectrometric Assays. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):775–781. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowacki J., Bandurski R. S. Myo-Inositol Esters of Indole-3-acetic Acid as Seed Auxin Precursors of Zea mays L. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):422–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pengelly W. L., Bandurski R. S., Schulze A. Validation of a radioimmunoassay for indole-3-acetic Acid using gas chromatography-selected ion monitoring-mass spectrometry. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):96–98. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pengelly W. L., Hall P. J., Schulze A., Bandurski R. S. Distribution of Free and Ester Indole-3-Acetic Acid in the Cortex and Stele of the Zea mays Mesocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jun;69(6):1304–1307. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.6.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke D. M., Bandurski R. S. Metabolic conversion of 14C-indole-3-acetic acid to 14C-oxindole-3-acetic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90470-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


