Abstract
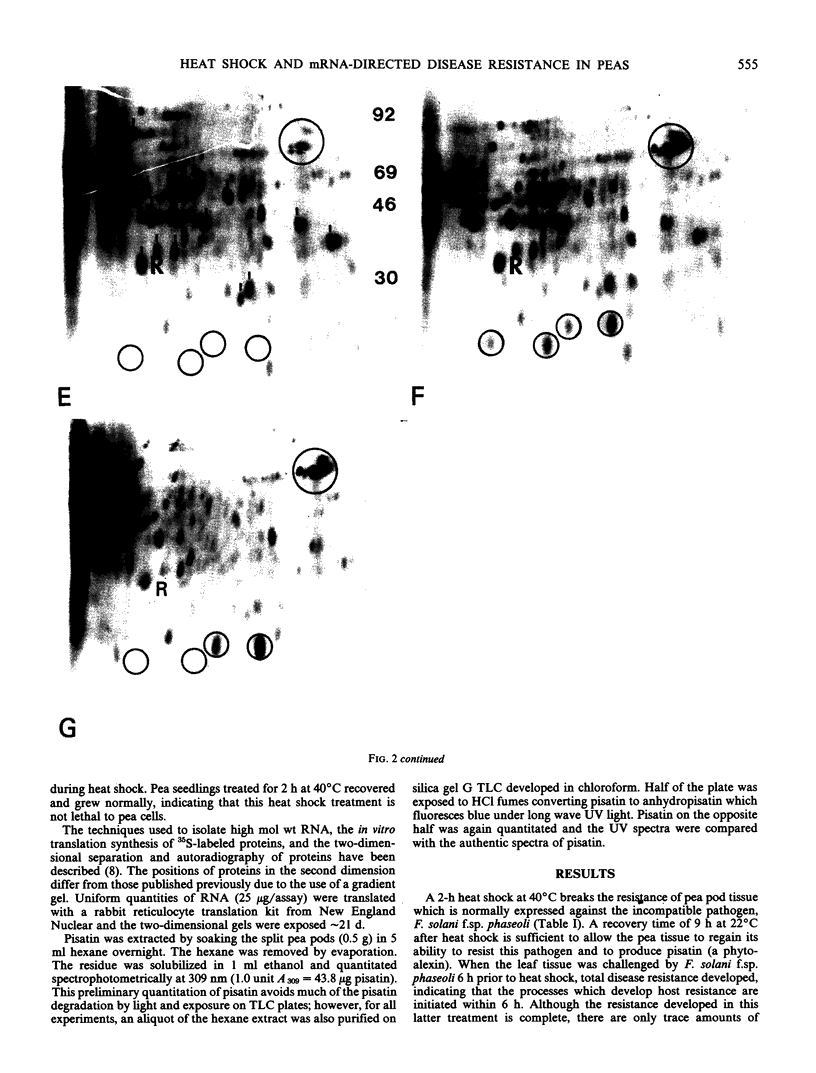
Pea tissue `heat shocked' for 2 hours at 40°C accumulates mRNAs that code for a series of new proteins called heat shock proteins. A different messenger RNA population, which codes for a high level of 20 or more `resistance proteins,' accumulates in pea tissue as it resists plant pathogenic fungi. Heat shock treatment applied prior to fungal inoculation prevents the high level accumulation of messenger RNA coding for the 20 resistance proteins and blocks disease resistance. If the resistance response is initiated before the heat shock treatment or after heat shock recovery, messenger RNA accumulates for the resistance proteins and disease resistance develops.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger L. A., Beckman J. M. Chitosan as a Component of Pea-Fusarium solani Interactions. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):205–211. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]