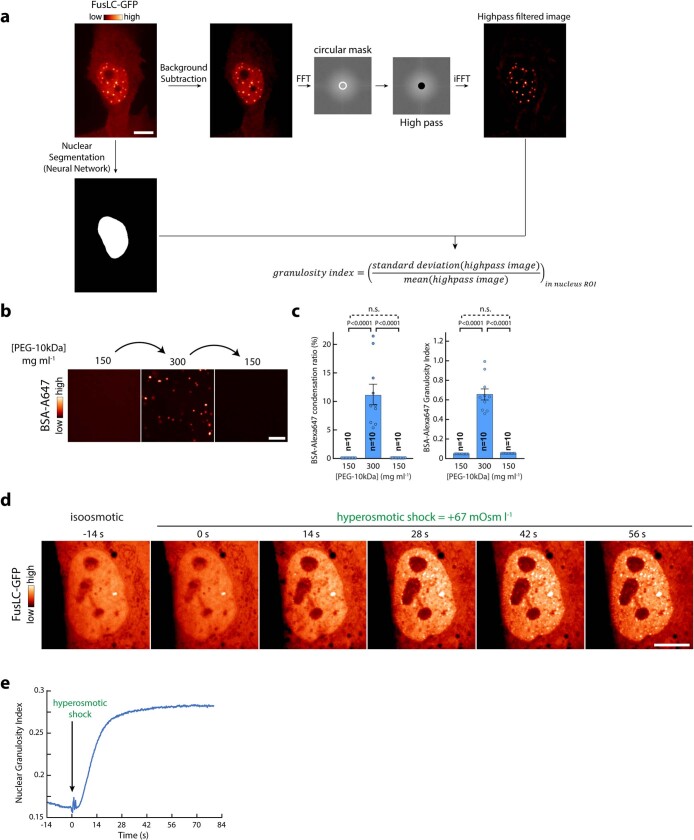
Extended Data Fig. 6. Imaging pipelines used for automated quantification of condensation in live cells.
(a) Imaging pipeline to quantify the fraction of signal that is condensed in live cell experiments. The granulosity index is computed as follows: Raw images were processed for homogenous background subtraction, then Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), then high-pass filter via a circular mask and inverse FFT. The ratio between the standard deviation and the mean of the signal in the high-pass-filtered image is then computed in specific ROIs (for instance, the nucleus). Note that the granulosity index is measured in real space, while the condensation ratio is measured in the Fourier space. (b-c) Comparison of the results obtained by the granulosity index and the condensation ratio. BSA-Alexa-647 (1 µM) was shifted from 150 mg ml−1 PEG-10kDa to 300 mg ml−1 PEG-10kDa before dilution back to 150 mg ml−1 PEG-10kDa. The state of condensation of BSA was imaged by SDCM (b) and quantified (c; mean ± SEM of condensation ratio). For the granulosity index, the whole image was used as ROI. Statistics: one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test (P value indicated, n: number of images per sample). Note that the two methods give similar results. The images in (b) and the left panel of (c) are the same as in Extended Data Fig. 9f-g, reproduced here for convenience. (d-e) Illustration of the capacity of the above-described imaging pipeline to resolve dynamic changes in protein condensation in live cells. (d) U2OS cells transiently expressing FusLC-GFP were imaged live at high-speed by SDCM (single plane, stream at 140 ms per frame), and a hyperosmotic shock was induced after 100 frames. (e) The granulosity index of the nucleus was then computed over time. Note that condensation induced by hyperosmotic shock is fast (in the timeframe of seconds) and homogenous. See also Supplementary Video 2. Scale bar: 5 µm (b) and 10 µm (a,c).