Abstract
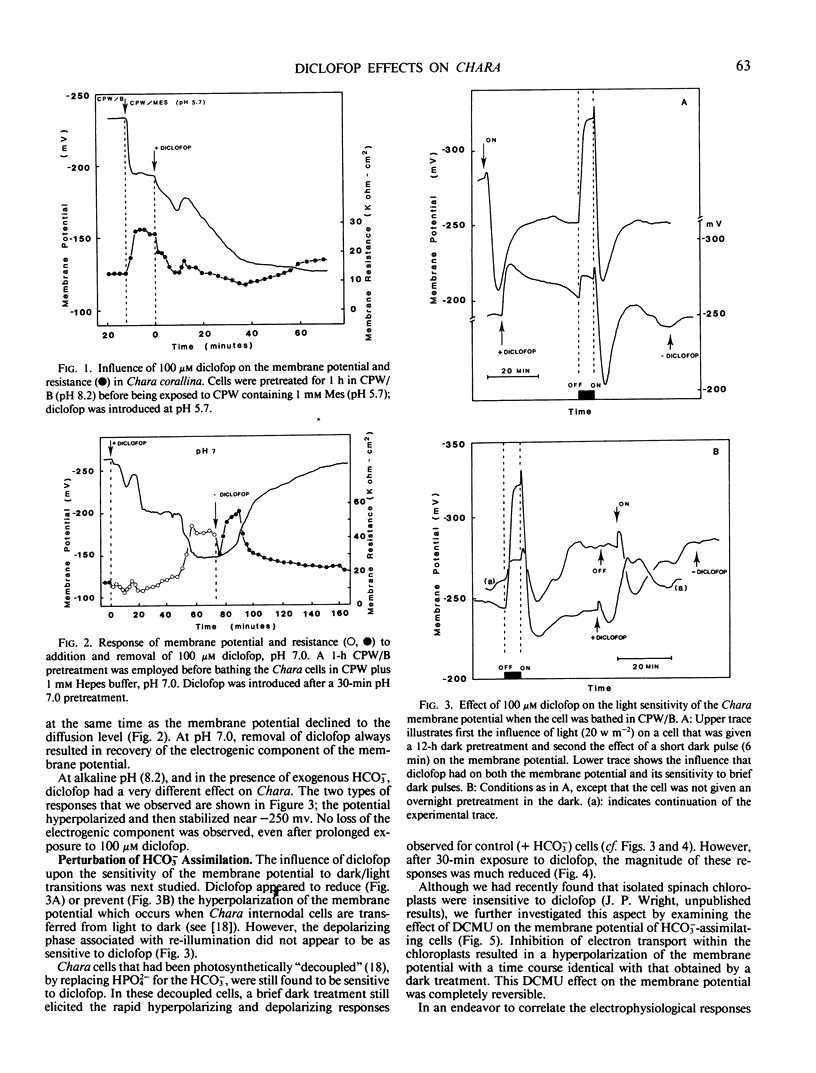
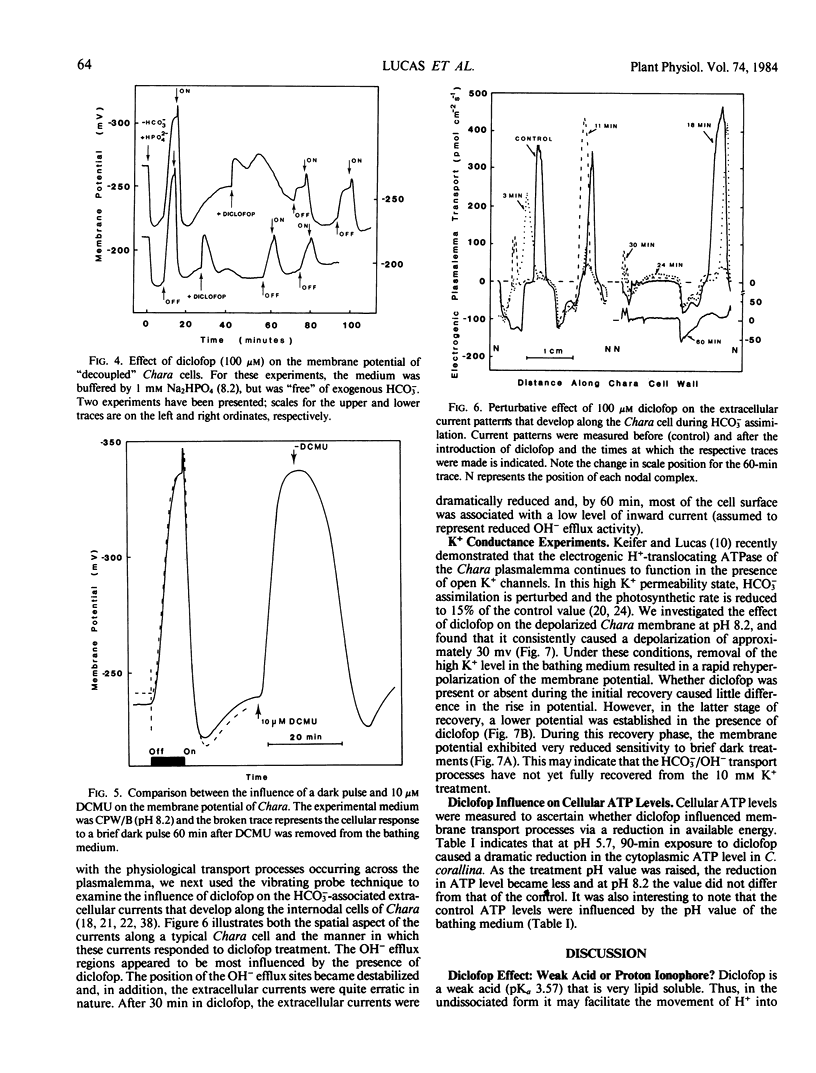
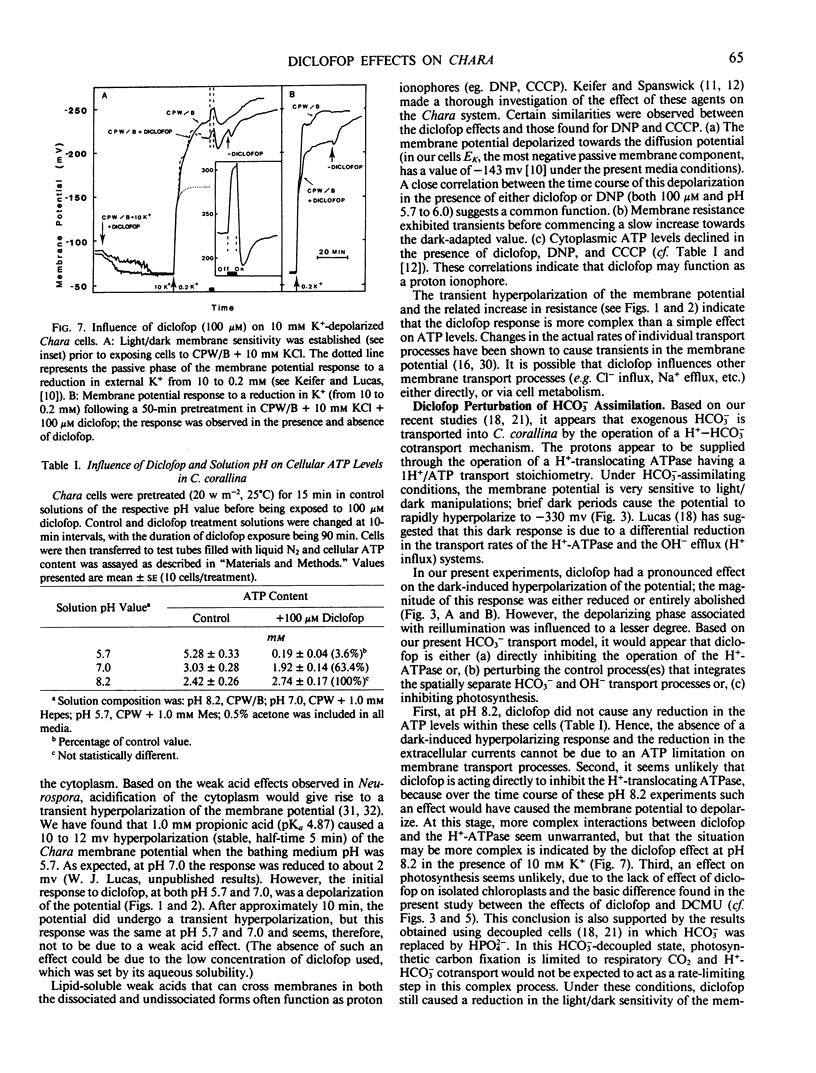
Electrophysiological measurements on internodal cells of Chara corallina Klein ex Willd., em. R.D.W. revealed that in the presence of (2-[4-(2′,4′-dichlorophenoxy)phenoxy]propionic acid) (diclofop) the membrane potential was very sensitive to the pH of the bathing medium. At pH 5.7, 100 micromolar diclofop caused a slow reduction in the electrogenic component of the membrane potential to the value of −123 ± 5 millivolts. Membrane resistance initially decreased, recovered transiently, then stabilized at approximately 65% of the control value. At pH 7.0, the potential appeared to plateau around −200 millivolts before rapidly declining to −140 ± 4 millivolts; removal of diclofop resulted in recovery of the electrogenic component. Diclofop reduced cytoplasmic ATP levels by 96.4% and 36.6% at pH 5.7 and 7.0, respectively. At pH 8.2, diclofop did not change the ATP concentration significantly, but induced a hyperpolarization of the membrane potential to near −250 millivolts, and also reduced or inhibited the dark-induced hyperpolarization; the light-induced depolarization was reduced to a lesser extent. DCMU applied in the light elicited the same response at the plasmalemma as placing cells in the dark. When K+ channels were opened and cells depolarized with 10 millimolar K+, diclofop induced a further depolarization of approximately 30 millivolts. Cells decoupled with HPO4−2 were still sensitive to diclofop. Currents associated with OH− efflux and HCO3− influx, as measured with a vibrating probe technique, became spatially destabilized and reduced in magnitude in the presence of diclofop. After 60 minutes, most of the cell surface was engaged in a low level of OH− efflux activity. The results indicate that diclofop may be a proton ionophore at pH 7.0 and 5.7. At pH 8.2, diclofop may inhibit the operation of the H+-ATPase and OH− efflux systems associated with HCO3− transport by perturbing the control processes that integrate the two, without a reduction in ATP concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benisek W. F., Ogez J. R. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of Pseudomonas testosteroni 3-oxo-delta 5-steroid isomerase and its interaction with 17 beta-estradiol. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5816–5825. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Fall L., Atkinson D. E. Adenylate energy charge in Escherichia coli during growth and starvation. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1072–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1072-1086.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J., Williams E. J., Johnston R. J. A simplified method for measuring membrane resistances in Nitella translucens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):518–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F., Nuccitelli R. An ultrasensitive vibrating probe for measuring steady extracellular currents. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):614–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keifer D. W., Lucas W. J. Potassium Channels in Chara corallina: CONTROL AND INTERACTION WITH THE ELECTROGENIC H PUMP. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):781–788. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keifer D. W., Spanswick R. M. Activity of the Electrogenic Pump in Chara corallina as Inferred from Measurements of the Membrane Potential, Conductance, and Potassium Permeability. Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):653–661. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keifer D. W., Spanswick R. M. Correlation of Adenosine Triphosphate Levels in Chara corallina with the Activity of the Electrogenic Pump. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):165–168. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J., Brand J. S. Assay of picomole amounts of ATP, ADP, and AMP using the luciferase enzyme system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):187–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtner F. T., Spanswick R. M. Electrogenic sucrose transport in developing soybean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):869–874. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas W. J., Dainty J. HCO(3) Influx Across the Plasmalemma of Chara corallina: Divalent Cation Requirement. Plant Physiol. 1977 Dec;60(6):862–867. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.6.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas W. J. HCO(3) Influx across the Plasmalemma of Chara corallina: Physiological and Biophysical Influence of 10 mm K. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):487–493. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D., Hansen U. P., Slayman C. L. Role of the plasma membrane proton pump in pH regulation in non-animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5903–5907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D., Slayman C. L. Control of intracellular pH. Predominant role of oxidative metabolism, not proton transport, in the eukaryotic microorganism Neurospora. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Sep;80(3):377–402. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.3.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seliger H. H., McElroy W. D. THE COLORS OF FIREFLY BIOLUMINESCENCE: ENZYME CONFIGURATION AND SPECIES SPECIFICITY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52(1):75–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


