Abstract
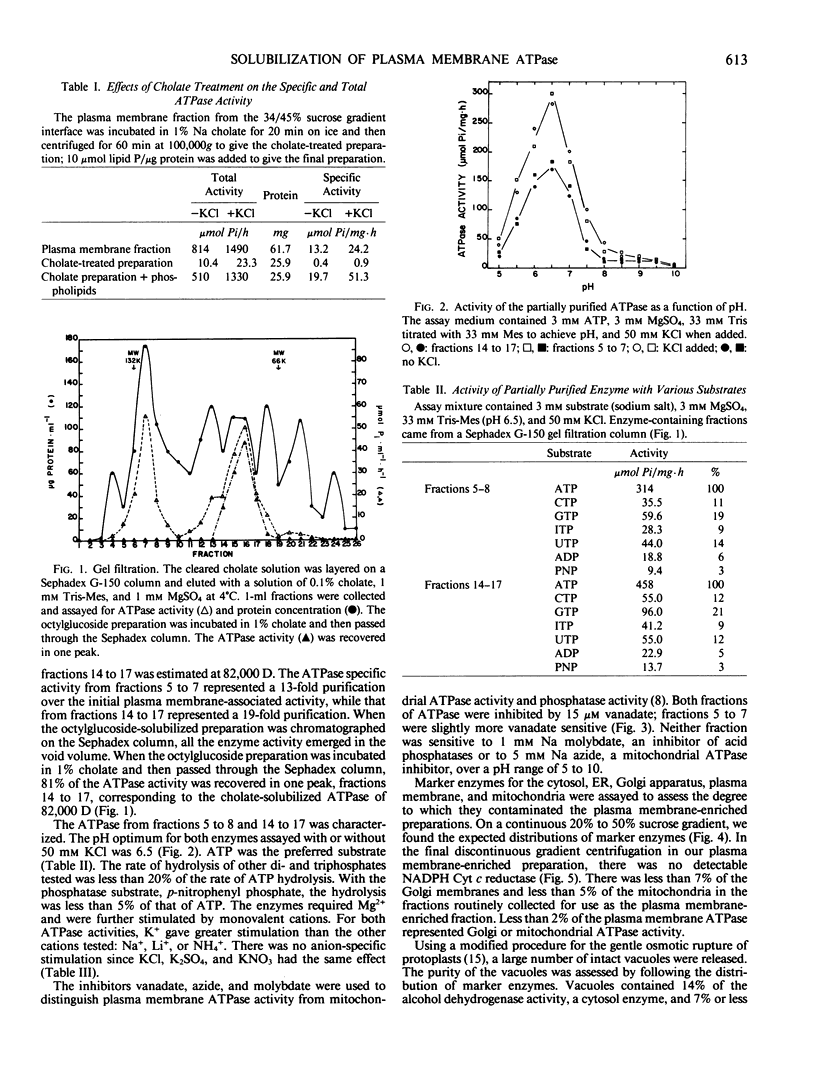
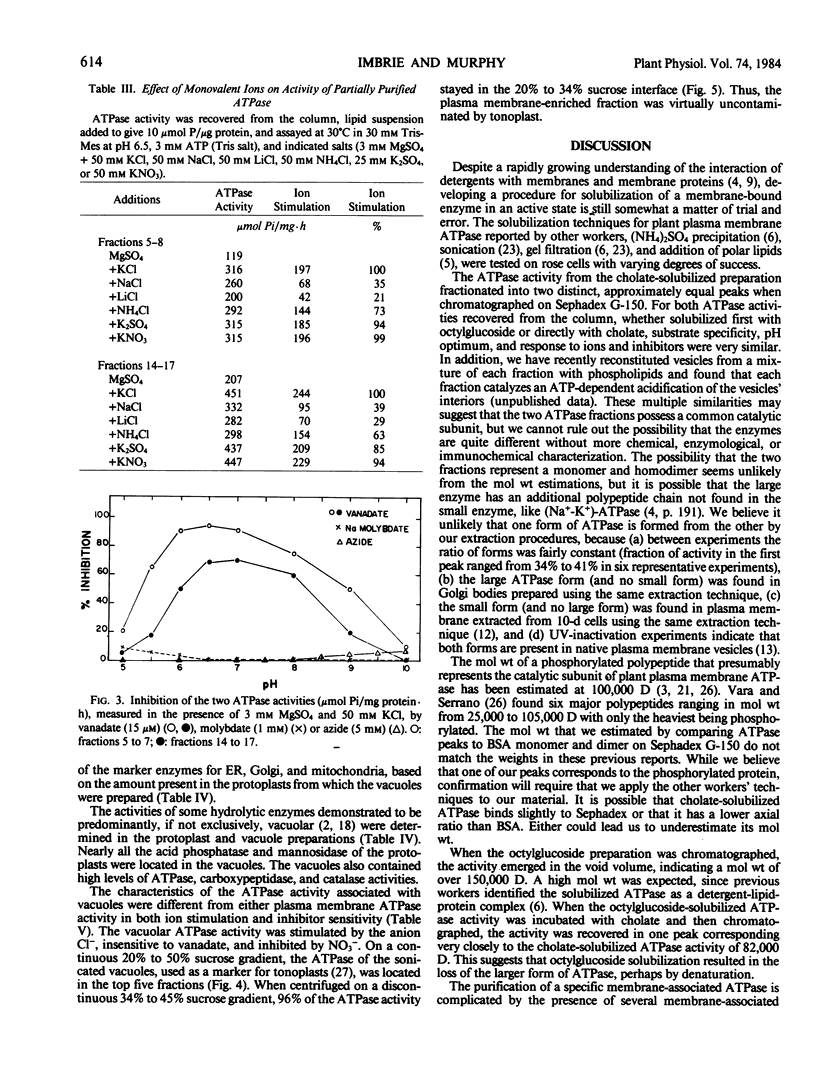
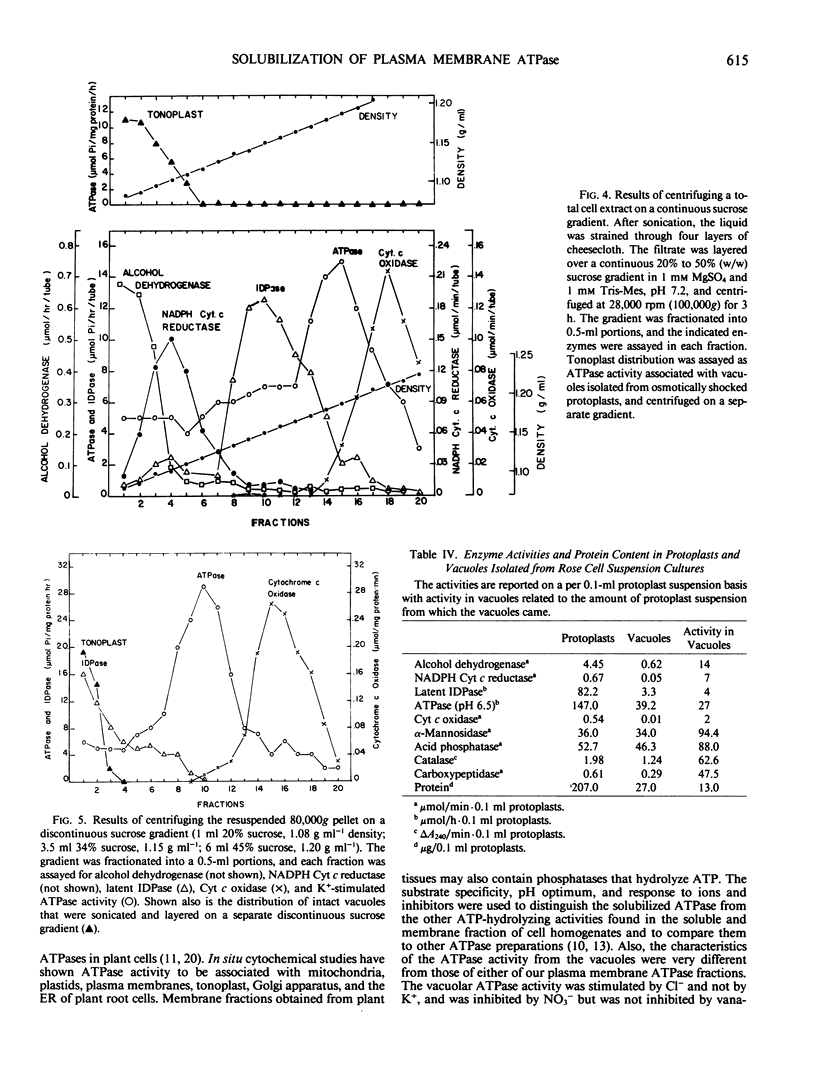
The K+-stimulated ATPase was partially purified from a plasma membrane fraction of suspension cultured cells of rose (Rosa damascena) by two different solubilization procedures. Solubilization with 30 mm octyl-β-d-glucopyranoside followed by precipitation with ammonium sulfate increased the specific activity of the enzyme about 6-fold. Solubilization with 1% cholate removed all but 1% of the phospholipids and resulted in an almost total loss of ATPase activity. The subsequent addition of polar lipids restored >90% of the ATPase activity with a doubling in specific activity. Fractionation of the cholate-solubilized ATPase activity on a Sephadex G-150 column resulted in 88% of the ATPase activity being recovered in two discrete, approximately equal peaks. Both ATPase activities were similar to plasma membrane ATPase activities in pH optimum, substrate specificity, ion stimulation, and inhibitor sensitivity. Assays of marker enzymes for Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria revealed only a low contamination (<7%) from other membranes in the plasma membrane-enriched preparations. Lacking an unequivocal marker for the tonoplast, intact vacuoles were isolated, and their membrane density and ATPase activity were characterized and shown not to correspond to those of the putative plasma membrane preparation. These results suggest that there are two forms of ATPase separable by size in the plasma membrane of rose.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson M. J., Tipton C. L. Purification and Characterization of a Cation-stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase from Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1978 Aug;62(2):165–172. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller T., Kende H. Hydrolytic enzymes in the central vacuole of plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jun;63(6):1123–1132. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Leonard R. T. Partial characterization of a phosphorylated intermediate associated with the plasma membrane ATPase of corn roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocucci M., Ballarin-Denti A. Effect of polar lipids on ATPase activity of membrane preparations from germinating radish seeds. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):377–381. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Leonard R. T. Solubilization and partial purification of the adenosine triphosphatase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):931–938. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher S. R., Leonard R. T. Effect of vanadate, molybdate, and azide on membrane-associated ATPase and soluble phosphatase activities of corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1335–1340. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Leonard R. T., Bracker C. E., Keenan T. W. Purification of an ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots: association with plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenbrot J. I. Ion transport in membranes: incorporation of biological ion-translocating proteins in model membrane systems. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:19–49. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Wittenbach V. A. Subcellular localization of proteases in wheat and corn mesophyll protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):969–972. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin B., Marin-Lanza M., Komor E. The protonmotive potential difference across the vacuo-lysosomal membrane of Hevea brasiliensis (rubber tree) and its modification by a membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 15;198(2):365–372. doi: 10.1042/bj1980365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura M., Beevers H. Hydrolases in vacuoles from castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):44–48. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'neill S. D., Bennett A. B., Spanswick R. M. Characterization of a NO(3)-Sensitive H-ATPase from Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):837–846. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalla R., Amory A., Rigaud J., Goffeau A. Phosphorylated intermediate of a transport ATPase and activity of protein kinase in membranes from corn roots. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. G., Cleland R. E. Evidence for a Cl-Stimulated MgATPase Proton Pump in Oat Root Membranes. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):798–803. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. G., Cleland R. E. Partial characterization of fusicoccin binding to receptor sites on oat root membranes. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):353–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze H. Characterization of nigericin-stimulated ATPase from sealed microsomal vesicles of tobacco callus. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):498–505. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Phosphorylated intermediate of the ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5334–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Cellular transport mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:933–965. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. F., Rinne R. W. Phospholipids in the developing soybean seed. Plant Physiol. 1974 Nov;54(5):744–747. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.5.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


